Biology First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... The total number of fossils, and their locations in rock formations and sedimentary layers which provides information about those organisms ...
... The total number of fossils, and their locations in rock formations and sedimentary layers which provides information about those organisms ...
Science Associated with Producing GMOs
... protein is provided to an organism. By doing so, an organism is given new abilities that were not historically present in the organism. A natural example of this is seen during viral infections, such as HIV, in which the HIV virus will insert its genes into the DNA of white blood cells, causing the ...
... protein is provided to an organism. By doing so, an organism is given new abilities that were not historically present in the organism. A natural example of this is seen during viral infections, such as HIV, in which the HIV virus will insert its genes into the DNA of white blood cells, causing the ...
GMOs – The Hidden Science
... and building blocks for the cell. It can also be rejected. The other response is to close over the foreign DNA and deactivate it. All of these responses are defence mechanisms to overcome attacks by pathogens (disease). The host organism defends itself by getting rid of the foreign material. This is ...
... and building blocks for the cell. It can also be rejected. The other response is to close over the foreign DNA and deactivate it. All of these responses are defence mechanisms to overcome attacks by pathogens (disease). The host organism defends itself by getting rid of the foreign material. This is ...
The Good, the bad and the ugly of Genetic Engineering
... our insulin gene even though the insulin protein doesn’t do anything for a bacterial cell. Then we can take out the insulin protein and use it to treat diabetics. ...
... our insulin gene even though the insulin protein doesn’t do anything for a bacterial cell. Then we can take out the insulin protein and use it to treat diabetics. ...
Applying Our Knowledge of Genetics
... • We use restriction enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences (A’s, C’s, G’s, & T’s) and remove the gene from the human cell’s DNA. It is then put into a bacterial cell plasmid (DNA) that is cut open using the same restriction enzyme. • Some of the plasmids will adopt the gene and when the bacteri ...
... • We use restriction enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences (A’s, C’s, G’s, & T’s) and remove the gene from the human cell’s DNA. It is then put into a bacterial cell plasmid (DNA) that is cut open using the same restriction enzyme. • Some of the plasmids will adopt the gene and when the bacteri ...
Punnett Squares: Drag and Drop Monohybrid Crosses
... cross from the genotypes of the parents and mode of inheritance (autosomal or X-linked, dominant or recessive). BI3. b. Students know the genetic basis for Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment. Objectives: SWBAT… Explain the genetic factors that influence the way we look. Re ...
... cross from the genotypes of the parents and mode of inheritance (autosomal or X-linked, dominant or recessive). BI3. b. Students know the genetic basis for Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment. Objectives: SWBAT… Explain the genetic factors that influence the way we look. Re ...
Genetic engineering
... Genetics: Is the branch of biology that deals with heredity and variation. It allowing us to understand how life can exist at all levels of complexity and its continuity from generation to generation, ranging from the molecular to the population level. Genetic variation is the root of the natural di ...
... Genetics: Is the branch of biology that deals with heredity and variation. It allowing us to understand how life can exist at all levels of complexity and its continuity from generation to generation, ranging from the molecular to the population level. Genetic variation is the root of the natural di ...
PPT File
... two strands of DNA molecules at slightly different places. Short, single-stranded leftover pieces of DNA remain are the cut ends. These DNA fragments are said to have “sticky ends” because of their unpaired bases. Gene Splicing-adding or gluing pieces of DNA from an organism to another of the sticky ...
... two strands of DNA molecules at slightly different places. Short, single-stranded leftover pieces of DNA remain are the cut ends. These DNA fragments are said to have “sticky ends” because of their unpaired bases. Gene Splicing-adding or gluing pieces of DNA from an organism to another of the sticky ...
“What is that, where is it found and why can it live there
... these are diseases and are considered disadvantageous to humans but some mutations may give organisms an advantage or be neutral at that time and/or place. ...
... these are diseases and are considered disadvantageous to humans but some mutations may give organisms an advantage or be neutral at that time and/or place. ...
No Slide Title
... disease in order to understand the basis of disease and be able to diagnose and treat it more effectively. Even with sequence in hand, there are major problems in gene identification and cloning – need knowledge of map position therefore linkage analysis continues to be of major importance – ultimat ...
... disease in order to understand the basis of disease and be able to diagnose and treat it more effectively. Even with sequence in hand, there are major problems in gene identification and cloning – need knowledge of map position therefore linkage analysis continues to be of major importance – ultimat ...
Biology 105
... History of Genetics Mid 1800’s Gregor Mendel worked with pea plants and proposed the basic principles of genetics. This was unaccepted by many for several decades. However, in the early 1900’s, after science advancements, Mendel’s ideas gained momentum ...
... History of Genetics Mid 1800’s Gregor Mendel worked with pea plants and proposed the basic principles of genetics. This was unaccepted by many for several decades. However, in the early 1900’s, after science advancements, Mendel’s ideas gained momentum ...
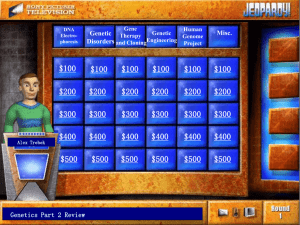
Human Genetics and Genetic Technology Test Review Jeopardy
... into to be delivered to the new host ...
... into to be delivered to the new host ...
Genetic Improvement of Crop Plants
... Like all new technologies there are concerns with the commercial application of biotechnology. These concerns can be divided into three areas [although in many cases the concern crosses more than one area]: ...
... Like all new technologies there are concerns with the commercial application of biotechnology. These concerns can be divided into three areas [although in many cases the concern crosses more than one area]: ...
Biology 3 Study Guide – Exam #3
... the concepts of evolution and natural selection various types of evidence for evolution various types of fossils and radiometric dating gene pools and allele frequencies Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and using the Hardy-Weinberg equation the role of mutations in evolution genetic drift and artificial s ...
... the concepts of evolution and natural selection various types of evidence for evolution various types of fossils and radiometric dating gene pools and allele frequencies Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and using the Hardy-Weinberg equation the role of mutations in evolution genetic drift and artificial s ...
Genetic Engineering: How and why scientists manipulate DNA in
... Using genetically modified E.coli to produce the expensive indigo dye that is used to color denim blue jeans. Use of recombinant DNA techniques in production of: __________, laundry detergents, paper production, and __________ ____________. ...
... Using genetically modified E.coli to produce the expensive indigo dye that is used to color denim blue jeans. Use of recombinant DNA techniques in production of: __________, laundry detergents, paper production, and __________ ____________. ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X chromosome. ...
... the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X chromosome. ...
Changes in DNA can produce variation
... • There is a large number of DNA bases in any organism that need to be copied • Errors can occur when DNA is copied or affected by environment – UV radiation – X-rays – Toxins ...
... • There is a large number of DNA bases in any organism that need to be copied • Errors can occur when DNA is copied or affected by environment – UV radiation – X-rays – Toxins ...
Biotechnology Unit Test Review
... 4. DNA ligase – Enzyme used to join the “sticky ends” of a recombinant DNA 5. Gel electrophoresis – Technique used to separate DNA or protein fragments based on size 6. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) – Technique used to make many copies of a piece of DNA so that it can be manipulated and visible on ...
... 4. DNA ligase – Enzyme used to join the “sticky ends” of a recombinant DNA 5. Gel electrophoresis – Technique used to separate DNA or protein fragments based on size 6. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) – Technique used to make many copies of a piece of DNA so that it can be manipulated and visible on ...
Genetic Technology
... – Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both processes. – Analyze scenarios and determine if the situation is an example of genetic engineering or selective breeding. ...
... – Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both processes. – Analyze scenarios and determine if the situation is an example of genetic engineering or selective breeding. ...
Genetic Engineering and Selective Breeding
... – Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both processes. – Analyze scenarios and determine if the situation is an example of genetic engineering or selective breeding. ...
... – Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both processes. – Analyze scenarios and determine if the situation is an example of genetic engineering or selective breeding. ...
Genetic Technology
... – Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both processes. – Analyze scenarios and determine if the situation is an example of genetic engineering or selective breeding. ...
... – Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both processes. – Analyze scenarios and determine if the situation is an example of genetic engineering or selective breeding. ...
Spring Exam Study Guide 2015 answers
... 9. Enzymes affect the reactions in living cells by changing the Speed of a reaction 10. What are the levels of organization in order? Organism, Population (species), community, ecosystem, biosphere 11. An organism that uses energy to produce its own food supply from inorganic compounds is called ...
... 9. Enzymes affect the reactions in living cells by changing the Speed of a reaction 10. What are the levels of organization in order? Organism, Population (species), community, ecosystem, biosphere 11. An organism that uses energy to produce its own food supply from inorganic compounds is called ...
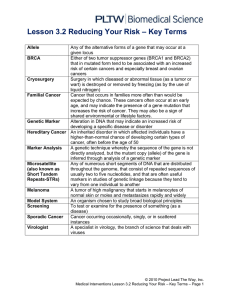
L3.2ReducingYourRisk - jj-sct
... age, and may indicate the presence of a gene mutation that increases the risk of cancer. They may also be a sign of shared environmental or lifestyle factors. Genetic Marker Alteration in DNA that may indicate an increased risk of developing a specific disease or disorder Hereditary Cancer An inheri ...
... age, and may indicate the presence of a gene mutation that increases the risk of cancer. They may also be a sign of shared environmental or lifestyle factors. Genetic Marker Alteration in DNA that may indicate an increased risk of developing a specific disease or disorder Hereditary Cancer An inheri ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.