CHANGES IN DNA CAN PRODUCE VARIATIONS
... • Exposure to ultraviolet radiation, x-rays, & toxins can damage DNA. Any change in DNA is called a MUTATION. • Cells have different ways to repair mistakes (through enzymes). • If a mutation occurs in a gene (the 5% of DNA that’s the coding region) the wrong amino acid may be placed in the amino-ac ...
... • Exposure to ultraviolet radiation, x-rays, & toxins can damage DNA. Any change in DNA is called a MUTATION. • Cells have different ways to repair mistakes (through enzymes). • If a mutation occurs in a gene (the 5% of DNA that’s the coding region) the wrong amino acid may be placed in the amino-ac ...
Glossary - Bioethics Advisory Committee
... A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. It is made up of DNA which carries instructions to make molecules of RNA and proteins. Every person has two copies of each gene, one inherited from each parent. Most genes are commonly found in all people, but about one percent of each pe ...
... A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. It is made up of DNA which carries instructions to make molecules of RNA and proteins. Every person has two copies of each gene, one inherited from each parent. Most genes are commonly found in all people, but about one percent of each pe ...
organisms - Lyndhurst Schools
... Smallest unit capable of all life functions Unicellular Organisms Entire organism is made up of one single cell Example:Bacteria and protists ...
... Smallest unit capable of all life functions Unicellular Organisms Entire organism is made up of one single cell Example:Bacteria and protists ...
2015 Test 3 study guide Bio 105
... 6.11 Cancer part one • What is a mutagen • What is a carcinogen 6.12 Cancer part two • Loss of control of cell cycle can cause cancer • What is a proto-oncogene and what is a oncogene • Differences between benign tumor and malignant tumor • Treatments for cancer 6.13 Genetic engineering ...
... 6.11 Cancer part one • What is a mutagen • What is a carcinogen 6.12 Cancer part two • Loss of control of cell cycle can cause cancer • What is a proto-oncogene and what is a oncogene • Differences between benign tumor and malignant tumor • Treatments for cancer 6.13 Genetic engineering ...
CHAPTER 14 VOCAB
... centesis a puncture (amniocentesis: a technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus by the presence of certain chemicals or defective fetal cells in the amniotic fluid, obtained by aspiration from a needle inserted into the uterus) co- together (codominance: phenotype in which both domi ...
... centesis a puncture (amniocentesis: a technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus by the presence of certain chemicals or defective fetal cells in the amniotic fluid, obtained by aspiration from a needle inserted into the uterus) co- together (codominance: phenotype in which both domi ...
Genetic Red Flags
... gene may have a natural predisposition to endurance events, in one copy of their ACTN3 gene may be equally suited for both endurance and sprint/power events, in neither copy of their ACTN3 gene may have a natural predisposition to sprint/power events. Knowing this information may be helpful, not in ...
... gene may have a natural predisposition to endurance events, in one copy of their ACTN3 gene may be equally suited for both endurance and sprint/power events, in neither copy of their ACTN3 gene may have a natural predisposition to sprint/power events. Knowing this information may be helpful, not in ...
Gene Expression - Pleasantville High School
... ◦ Sarcomas: _______ and muscular tissue. ◦ Lymphomas: solid tumors in blood-forming tissue and may cause ___________. ◦ Leukemia: uncontrolled production of _________ blood cells. ...
... ◦ Sarcomas: _______ and muscular tissue. ◦ Lymphomas: solid tumors in blood-forming tissue and may cause ___________. ◦ Leukemia: uncontrolled production of _________ blood cells. ...
Genetics Review File - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... 6. How many chromosomes do humans have? a. 12 pairs b. 20 pairs c. 23 pairs d. 46 pairs ...
... 6. How many chromosomes do humans have? a. 12 pairs b. 20 pairs c. 23 pairs d. 46 pairs ...
2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clot _____________________________________ (e) the ability to read _____________________________________ ...
... (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clot _____________________________________ (e) the ability to read _____________________________________ ...
1 - Genetic Alliance
... The human genome (total composition of genetic material within a cell) is packaged into larger units known as chromosomes—physically separate molecules that range in length from about 50 million to 250 million base pairs. Human cells contain two sets of chromosomes, one set inherited from each paren ...
... The human genome (total composition of genetic material within a cell) is packaged into larger units known as chromosomes—physically separate molecules that range in length from about 50 million to 250 million base pairs. Human cells contain two sets of chromosomes, one set inherited from each paren ...
Genetics Unit Test
... 26. Three bases code for one a. cell. c. protein. b. DNA. d. amino acid. 27. In what type of mutation is one base left out? a. substitution c. insertion b. deletion d. cell 28. DNA is made of subunits called what? a. proteins c. traits b. deoxyribonucleic acids d. nucleotides 29. Nucleotides are mad ...
... 26. Three bases code for one a. cell. c. protein. b. DNA. d. amino acid. 27. In what type of mutation is one base left out? a. substitution c. insertion b. deletion d. cell 28. DNA is made of subunits called what? a. proteins c. traits b. deoxyribonucleic acids d. nucleotides 29. Nucleotides are mad ...
PE #8 DNA Structure, Biotechnology, and its use in Conservation
... I can summarize the pairing rules for nitrogen bases within the structure of DNA. I can recognize that sections of DNA that code for proteins are genes. I can identify that the sections of DNA used for DNA profiling are not made up of genes, but nucleotides between the genes. ...
... I can summarize the pairing rules for nitrogen bases within the structure of DNA. I can recognize that sections of DNA that code for proteins are genes. I can identify that the sections of DNA used for DNA profiling are not made up of genes, but nucleotides between the genes. ...
mei4 - University of Vermont
... DSB repair and recombination are interrupted in mei4/mei4 mutants ...
... DSB repair and recombination are interrupted in mei4/mei4 mutants ...
Microarrays = Gene Chips
... 8. If the PCR product has stuck on it will glow 9. The computer can then say which of the bacterial species the PCR products have stuck to and this indicates which species are present in the sample ...
... 8. If the PCR product has stuck on it will glow 9. The computer can then say which of the bacterial species the PCR products have stuck to and this indicates which species are present in the sample ...
Genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Chromosome Gene Allele
... Genome All of the genetic information or hereditary material possessed by an organism; the entire genetic complement of an organism. Includes both nuclear & organelle genetic information. ...
... Genome All of the genetic information or hereditary material possessed by an organism; the entire genetic complement of an organism. Includes both nuclear & organelle genetic information. ...
Updated Semester Two Review Sheet Answer Key
... 1. Scientists have developed new species of plants and animals that can be mass produced for human consumption. Many of these new species were developed using the process of selective breeding, also known as artificial selection. Discuss the differences in the process of artificial selection and nat ...
... 1. Scientists have developed new species of plants and animals that can be mass produced for human consumption. Many of these new species were developed using the process of selective breeding, also known as artificial selection. Discuss the differences in the process of artificial selection and nat ...
Gene Hunting
... Cell signaling pathways in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis inferred from comparisons with other fungi • The identification of putative genes involved in the cellular signaling pathways was performed by the “search by key word” service provided by the bioinformatics group of the PbGenome project (Feli ...
... Cell signaling pathways in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis inferred from comparisons with other fungi • The identification of putative genes involved in the cellular signaling pathways was performed by the “search by key word” service provided by the bioinformatics group of the PbGenome project (Feli ...
Introductory to Biology
... G. Organisms that has genes from two or more separate species H. The accumulation of mutations I. When genes separate during meiosis, they have no influence on each other J. The total genetic makeup of an organism Match the terms of DNA transcription and translation with the definitions on the right ...
... G. Organisms that has genes from two or more separate species H. The accumulation of mutations I. When genes separate during meiosis, they have no influence on each other J. The total genetic makeup of an organism Match the terms of DNA transcription and translation with the definitions on the right ...
Techniques in Mouse
... • 4) Retroviral vectors – a more natural way or getting genes into cells ...
... • 4) Retroviral vectors – a more natural way or getting genes into cells ...
B. Sc. Part- II (GENETICS)
... Note: Question 1 will be compulsory and short answer type covering entire syllabi. Four questions will be set from each Section. Candidates have to answer five questions in all selecting two from each section. SECTION- A I. GENETIC MATERIAL: Evidence to prove that DNA is the genetic material, its st ...
... Note: Question 1 will be compulsory and short answer type covering entire syllabi. Four questions will be set from each Section. Candidates have to answer five questions in all selecting two from each section. SECTION- A I. GENETIC MATERIAL: Evidence to prove that DNA is the genetic material, its st ...
genetics
... Study of structure & function of genes • PAPULATION GENETICS: Study of genetic variations in human population and factors that determine allele frequency • DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS – study of genetic control of development • CLINICAL GENETICS – Diagnosis of genetic disease and care of patient with suc ...
... Study of structure & function of genes • PAPULATION GENETICS: Study of genetic variations in human population and factors that determine allele frequency • DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS – study of genetic control of development • CLINICAL GENETICS – Diagnosis of genetic disease and care of patient with suc ...
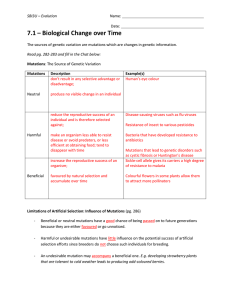
7.1 Solutions File
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
AQA Biology - Centre of the Cell
... • the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide • a functional RNA (including ribosomal RNA and tRNAs). A gene occupies a fixed position, called a locus, on a particular DNA molecule. A sequence of three DNA bases, called a triplet, codes for a specific amino acid. The genetic code is universal, non-over ...
... • the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide • a functional RNA (including ribosomal RNA and tRNAs). A gene occupies a fixed position, called a locus, on a particular DNA molecule. A sequence of three DNA bases, called a triplet, codes for a specific amino acid. The genetic code is universal, non-over ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering
... opposite sites without overhangs. SmaI is an example of an enzyme that generates blunt ends ...
... opposite sites without overhangs. SmaI is an example of an enzyme that generates blunt ends ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.