Ch 23 Evolution of Populations Guided Rdg
... 8. List the five conditions that must exist for a population to exist in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. ...
... 8. List the five conditions that must exist for a population to exist in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. ...
Evolution Bingo Review KEY
... 3. Evolution occurs as a result of __ NATURAL SELECTION _ (2 words). 4. The 5 conditions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are: a. Large _POPULATION__. b. Random _MATING__. c. No __MUTATIONS__ that cause changes in genes. d. No movement of genetic information from one population to another - _IMMIGRATIO ...
... 3. Evolution occurs as a result of __ NATURAL SELECTION _ (2 words). 4. The 5 conditions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are: a. Large _POPULATION__. b. Random _MATING__. c. No __MUTATIONS__ that cause changes in genes. d. No movement of genetic information from one population to another - _IMMIGRATIO ...
Ch 23 Notes
... interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Hardy-Weinberg studied evolution in populations. Hardy-Weinberg theorem: The frequencies of alleles and genotypes in populations remain constant in generations – UNLESS acted upon by agents* other than Mendelian segregation and recombination of alleles. What ...
... interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Hardy-Weinberg studied evolution in populations. Hardy-Weinberg theorem: The frequencies of alleles and genotypes in populations remain constant in generations – UNLESS acted upon by agents* other than Mendelian segregation and recombination of alleles. What ...
Factors Causing Evolution
... A few seeds of a plant are carried by a bird or by winds to a distant volcanic island, where they germinate and rapidly establish a large population, whose gene pool is different from the population of plants where they originated. ...
... A few seeds of a plant are carried by a bird or by winds to a distant volcanic island, where they germinate and rapidly establish a large population, whose gene pool is different from the population of plants where they originated. ...
READING GUIDE: 17.1 – Genes and Variation (p. 482
... 7) PREDICT: Suppose a dominant allele causes a plant disease that usually kills the plant before it can reproduce. Over time, what would probably happen to the frequency of that dominant allele in the population? ...
... 7) PREDICT: Suppose a dominant allele causes a plant disease that usually kills the plant before it can reproduce. Over time, what would probably happen to the frequency of that dominant allele in the population? ...
06_prughNS
... New population has different allele frequencies (and less diversity) because of “sampling error” Example: Amish in Pennsylvania - descended from 200 Germans - commonly have Ellis-van Creveld syndrome - inbreeding makes impact of bottlenecks and founder effect worse ...
... New population has different allele frequencies (and less diversity) because of “sampling error” Example: Amish in Pennsylvania - descended from 200 Germans - commonly have Ellis-van Creveld syndrome - inbreeding makes impact of bottlenecks and founder effect worse ...
Population Genetics
... traits in a population over several generations Evolution is only apparent when a population is tracked over time ...
... traits in a population over several generations Evolution is only apparent when a population is tracked over time ...
Microevolution is a change in a population*s gene pool
... A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance GENETIC DRIFT ALL populations are subject to genetic drift ...
... A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance GENETIC DRIFT ALL populations are subject to genetic drift ...
Evolution of Populations
... • Population genetics: the study of genetic variability within populations • Gene pool: combined aggregate of genes in a population at any one time • Species: a group of populations that have the potential to interbreed and produce fertile offspring in nature ...
... • Population genetics: the study of genetic variability within populations • Gene pool: combined aggregate of genes in a population at any one time • Species: a group of populations that have the potential to interbreed and produce fertile offspring in nature ...
Changing Allele Frequencies
... Many members of a population die and only a few are left to re-populate Much more restricted gene pool than original population Ex: Pingalapese people of the East Caroline Islands in Micronesia – Typhoon wiped out all but 9 males and 10 females – Autosomal recessive achromatopsia very prevalent Colo ...
... Many members of a population die and only a few are left to re-populate Much more restricted gene pool than original population Ex: Pingalapese people of the East Caroline Islands in Micronesia – Typhoon wiped out all but 9 males and 10 females – Autosomal recessive achromatopsia very prevalent Colo ...
16-1 Genes and Variation
... allele (T) occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles (t) occur. ...
... allele (T) occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles (t) occur. ...
Ch 23 Evolution of Populations
... source of new genes and NEW alleles. • Deletions, duplications or rearrangements of many loci are usually harmful. • Point mutations may or may not change an amino acid/protein. • Duplications within ONE gene provide a large variation for selection to work. ...
... source of new genes and NEW alleles. • Deletions, duplications or rearrangements of many loci are usually harmful. • Point mutations may or may not change an amino acid/protein. • Duplications within ONE gene provide a large variation for selection to work. ...
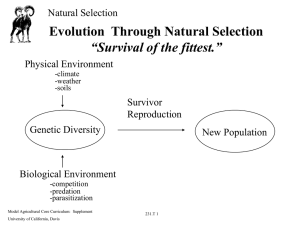
Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.”
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
Mechanism of Evolution
... The South Atlantic island of Tristan da Cunha was colonized by 15 Britons in 1814, one of them carrying an allele for retinitis pigmentosum. Among their 240 descendents living on the island today, 4 are blind by the disease and 9 others are ...
... The South Atlantic island of Tristan da Cunha was colonized by 15 Britons in 1814, one of them carrying an allele for retinitis pigmentosum. Among their 240 descendents living on the island today, 4 are blind by the disease and 9 others are ...
Evolution
... Effects of Mutation • Negative effects – Persist in very low frequencies – Could be a lethal mutation or cause sterility ...
... Effects of Mutation • Negative effects – Persist in very low frequencies – Could be a lethal mutation or cause sterility ...
Population Genetics
... species at same place and time • Species = individuals that can reproduce and produce fertile offspring ...
... species at same place and time • Species = individuals that can reproduce and produce fertile offspring ...
Enriched Biology Dremann Metzendorf Bag 3
... 5. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s… 6. In a population, the sum of the relative frequencies of all alleles for a particular trait is… 7. A change in a sequence of DNA is called a… 8. The two main sources of genetic variation are… 9. In genetic drift, ...
... 5. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s… 6. In a population, the sum of the relative frequencies of all alleles for a particular trait is… 7. A change in a sequence of DNA is called a… 8. The two main sources of genetic variation are… 9. In genetic drift, ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.