Natural Selection
... • Homologous features- similar structure in different species • Analogous features - similar function different structure (convergent evolution) • Vestigial organs ...
... • Homologous features- similar structure in different species • Analogous features - similar function different structure (convergent evolution) • Vestigial organs ...
Evolution
... interbreeding but have different mating rituals or routines. i.e. eastern & western meadowlarks ...
... interbreeding but have different mating rituals or routines. i.e. eastern & western meadowlarks ...
Chapter 23 - Cloudfront.net
... allele frequency of a gene in a population. – _______ (in sex cells) are the source of new genes and new alleles. – Point mutations change little, chromosomal mutations cause greater changes. – Sexual _________ (crossing over, IA, and random fertilization) account for most variation. ...
... allele frequency of a gene in a population. – _______ (in sex cells) are the source of new genes and new alleles. – Point mutations change little, chromosomal mutations cause greater changes. – Sexual _________ (crossing over, IA, and random fertilization) account for most variation. ...
VOCAB- Evolution
... DISRUPTIVE SELECTION- The effect of natural selection when individuals at the extreme ends of the normal distribution curve have higher fitness than those near the center of the curve GENETIC DRIFT- Changes in allele frequency in a small population that are due to random chance and don’t follow the ...
... DISRUPTIVE SELECTION- The effect of natural selection when individuals at the extreme ends of the normal distribution curve have higher fitness than those near the center of the curve GENETIC DRIFT- Changes in allele frequency in a small population that are due to random chance and don’t follow the ...
DISRUPTING GENETIC EQUILIBRIUM
... Gene Pool = the total genetic material available in a population Adapting to new selection factors can only use existing genes found in the population Allele Frequency = the number of a certain allele in the population / the total number of all alleles The phenotype frequencies can change between ge ...
... Gene Pool = the total genetic material available in a population Adapting to new selection factors can only use existing genes found in the population Allele Frequency = the number of a certain allele in the population / the total number of all alleles The phenotype frequencies can change between ge ...
Name Date ____/ ____/____ Period ____ Test Review, Chapter 11
... natural selection is this an example of, and how does it differ from the other types? Example: _____________________________ Describe: ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 6. Describe how gene flow can increase genetic vari ...
... natural selection is this an example of, and how does it differ from the other types? Example: _____________________________ Describe: ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 6. Describe how gene flow can increase genetic vari ...
Lecture 2
... Change in chromosome number of less than an entire genome. Change in genotype other than by recombination. Change in genotype solely by chance effects. Evolution at the population level; change in allele frequencies over generations. Evolution of chromosome number which is a multiple of some ancestr ...
... Change in chromosome number of less than an entire genome. Change in genotype other than by recombination. Change in genotype solely by chance effects. Evolution at the population level; change in allele frequencies over generations. Evolution of chromosome number which is a multiple of some ancestr ...
Section 13.3 - CPO Science
... the population of a species are caused by random mutations in genes. • Random mutations in genes produce variations of traits in a population. ...
... the population of a species are caused by random mutations in genes. • Random mutations in genes produce variations of traits in a population. ...
Chapter 23 The Evolution of Populations
... Population genetics - genetics which emphasizes the extensive genetic variation within populations and recognizes the importance of quantitative characters Modern synthesis - a comprehensive theory of evolution that integrated ideas from paleontology, taxonomy, biogeography, and population genetics ...
... Population genetics - genetics which emphasizes the extensive genetic variation within populations and recognizes the importance of quantitative characters Modern synthesis - a comprehensive theory of evolution that integrated ideas from paleontology, taxonomy, biogeography, and population genetics ...
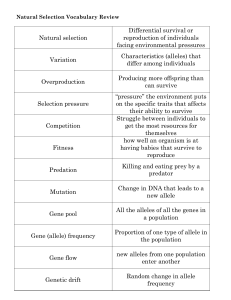
Natural selection Differential survival or reproduction of individuals
... a group of orgs. that interbreed under natural conditions to produce fertile offspring “special case” of natural selection; pressures that affect an individual’s success in mating Splitting of one species into two or more different species members of a species are isolated from one another due to a ...
... a group of orgs. that interbreed under natural conditions to produce fertile offspring “special case” of natural selection; pressures that affect an individual’s success in mating Splitting of one species into two or more different species members of a species are isolated from one another due to a ...
Natural Selection Depends on Genetic Variation
... Genetic variation that is favored by selection & is manifested as a trait that provides an advantage to an organism in a particular environment ...
... Genetic variation that is favored by selection & is manifested as a trait that provides an advantage to an organism in a particular environment ...
5 Agents of Evolutionary Change
... trait to become more common or rarer over time • Can produce evolutionary change • not caused by environmental or other kinds of stresses on individuals • Easier seen in small populations ...
... trait to become more common or rarer over time • Can produce evolutionary change • not caused by environmental or other kinds of stresses on individuals • Easier seen in small populations ...
Evolutionary Mechanisms
... Allows us to examine the frequencies of two alleles, and also to figure out what proportion should be ...
... Allows us to examine the frequencies of two alleles, and also to figure out what proportion should be ...
natural selection
... point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total number of the alleles from the gene pool. ...
... point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total number of the alleles from the gene pool. ...
Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations
... Geographic variation may be shown in a graded manner along a geographic axis known as a cline. What external factors might produce a cline? Why does the existence of a cline suggest naturalselection? ...
... Geographic variation may be shown in a graded manner along a geographic axis known as a cline. What external factors might produce a cline? Why does the existence of a cline suggest naturalselection? ...
Population Genetics and evolution with notes
... Darwin developed his theory of natural selection before knowledge of genetics Populations evolve, not individuals! An organism is born with its phenotype, and it never changes during its lifetime Evolution occurs as a population’s genes and their frequencies change over time Gene Pool: all of th ...
... Darwin developed his theory of natural selection before knowledge of genetics Populations evolve, not individuals! An organism is born with its phenotype, and it never changes during its lifetime Evolution occurs as a population’s genes and their frequencies change over time Gene Pool: all of th ...
Concept Sheet
... 1. Explain what a gene pool is. 2. Identify the main sources of inheritable variation in a population. 3. State what determines how a phenotype is expressed. 4. Explain how natural selection affects single-gene and polygenic traits 5. Describe genetic drift. 6. List the five conditions needed to mai ...
... 1. Explain what a gene pool is. 2. Identify the main sources of inheritable variation in a population. 3. State what determines how a phenotype is expressed. 4. Explain how natural selection affects single-gene and polygenic traits 5. Describe genetic drift. 6. List the five conditions needed to mai ...
Review for Final: Chap 16: Evolulution of Populations
... 8. Draw a curve diagram to show each of the 3 ways that natural selection affects phenotypes. ...
... 8. Draw a curve diagram to show each of the 3 ways that natural selection affects phenotypes. ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.