4. Nervous System: Synapses
... • Theory: info is stored in form of increased flow of info at synapses in particular pathways • Certain neurotransmitters and structural changes in synapses may affect short vs. intermediate vs. long term memories • Ex: more synapses and receptors are built when we create long term memories ...
... • Theory: info is stored in form of increased flow of info at synapses in particular pathways • Certain neurotransmitters and structural changes in synapses may affect short vs. intermediate vs. long term memories • Ex: more synapses and receptors are built when we create long term memories ...
... To investigate brain substrates of spatial memory, the cellular expression of c-Fos protein in rats was studied after training the animals to perform a spatial reference memory task and a working reference memory task in a Morris water maze. The number of c-Fos positive neuronal nuclei was quantifie ...
case studies In-depth examinations of an individual or a single event
... reconsolidation A process that occurs when a previously consolidated memory is reactivated. When the old memory undergoes reconsolidation, it enters a labile state in which it can be ...
... reconsolidation A process that occurs when a previously consolidated memory is reactivated. When the old memory undergoes reconsolidation, it enters a labile state in which it can be ...
Cognitive Information Processing
... of new information. Memory is related to the ability to recall information that has been previously learned Storage - the process by which new information is placed in memory Retrieval - the process by which people “find’ the information they have previously stored so they can use it again Encoding ...
... of new information. Memory is related to the ability to recall information that has been previously learned Storage - the process by which new information is placed in memory Retrieval - the process by which people “find’ the information they have previously stored so they can use it again Encoding ...
1 - U-System
... - infant amnesia we don’t remember much from our first five years, but we still can establish procedural memories (tying shoes, walking, eating with a fork), even if we don’t form factual memories that will last long - infants have memory problems because hippocampus is slow to mature; old people ...
... - infant amnesia we don’t remember much from our first five years, but we still can establish procedural memories (tying shoes, walking, eating with a fork), even if we don’t form factual memories that will last long - infants have memory problems because hippocampus is slow to mature; old people ...
December 3
... I sometimes feel in reviewing the evidence on the localization of the memory trace, that the necessary conclusion is that learning just is not possible.” pg 276 of text ...
... I sometimes feel in reviewing the evidence on the localization of the memory trace, that the necessary conclusion is that learning just is not possible.” pg 276 of text ...
Consolidation theory
... Consolidation Theory (cont...) • EVIDENCE for the Consolidation Theory: – People who have experienced brain trauma reported they could not remember anything that occurred during a period of about 30 minutes prior to the brain injury – Animal research shows that rats that were given ElectroConvulsiv ...
... Consolidation Theory (cont...) • EVIDENCE for the Consolidation Theory: – People who have experienced brain trauma reported they could not remember anything that occurred during a period of about 30 minutes prior to the brain injury – Animal research shows that rats that were given ElectroConvulsiv ...
HSTMemoryLecture - Psychology
... “What interests me a great deal is the mistiness of the past” Harold Pinter, Conversation prior to the opening of Old Times, 1971 ...
... “What interests me a great deal is the mistiness of the past” Harold Pinter, Conversation prior to the opening of Old Times, 1971 ...
Chap 5: The Cognitive Approach II
... In the whole report condition, participants attempted to recall the entire array but could only remember several letters. In the partial-report condition, they were cued after the display to report the letters in one row only. They could remember all the letters. This shows iconic memory has a high ...
... In the whole report condition, participants attempted to recall the entire array but could only remember several letters. In the partial-report condition, they were cued after the display to report the letters in one row only. They could remember all the letters. This shows iconic memory has a high ...
When neurons form memories
... Although the study by Hoffman and McNaughton provided important new insights, it also raises new questions. The most important unresolved issue is probably whether the observed neocortical reactivations are truly a correlate of consolidation of declarative memory or whether ...
... Although the study by Hoffman and McNaughton provided important new insights, it also raises new questions. The most important unresolved issue is probably whether the observed neocortical reactivations are truly a correlate of consolidation of declarative memory or whether ...
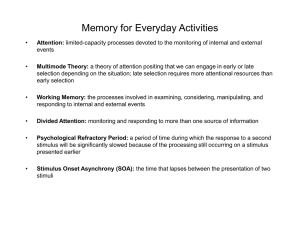
Memory for Everyday Activities
... Episodic Buffer: component of working memory that is responsible for integrating information processed by the articulatory loop and the visuospatial sketchpad, as well as relevant information from long-term memory ...
... Episodic Buffer: component of working memory that is responsible for integrating information processed by the articulatory loop and the visuospatial sketchpad, as well as relevant information from long-term memory ...
Quiz 1 - Suraj @ LUMS
... parameters that may be adapted during learning. A neural network is said to learn if its free parameters are adapted in response to experience in order to improve performance at learning an input-output mapping. The free parameters can be: weights Activation function parameters Architectural p ...
... parameters that may be adapted during learning. A neural network is said to learn if its free parameters are adapted in response to experience in order to improve performance at learning an input-output mapping. The free parameters can be: weights Activation function parameters Architectural p ...
05powerpoint
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
Economic Attention Networks: Associative Memory and Resource
... More rapid learning of simpler procedures ...
... More rapid learning of simpler procedures ...
Intellectual Functions of the Brain
... • Presynaptic facilitation: Presynaptic neuron prolonges the action potentials (by closing K channels) ...
... • Presynaptic facilitation: Presynaptic neuron prolonges the action potentials (by closing K channels) ...
Small System of Neurons
... Biology of Memory Storage: A Dialog Between Genes and Synapses, December 8, 2000. Eric Kandel (1979) Small Systems of Neurons, ...
... Biology of Memory Storage: A Dialog Between Genes and Synapses, December 8, 2000. Eric Kandel (1979) Small Systems of Neurons, ...
Optical Stimulation of Engram-bearing Cells
... behavior. Our results argue that defined cell populations can form a cellular basis for fear memory engrams. The memory engram that we selectively labeled and manipulated is likely contextual in nature, as previous studies have demonstrated that hippocampal interventions affect conditioned freezing ...
... behavior. Our results argue that defined cell populations can form a cellular basis for fear memory engrams. The memory engram that we selectively labeled and manipulated is likely contextual in nature, as previous studies have demonstrated that hippocampal interventions affect conditioned freezing ...
Memory kaleidoscope: enhancing memory to improve learning
... proteins, and electrical impulses. If the information does not receive sufficient attention or if it is not deemed necessary for the long-term,it will be encoded for short-term use only and ultimately discarded unless reclassified. The encoding process takes into consideration the emotional nature, ...
... proteins, and electrical impulses. If the information does not receive sufficient attention or if it is not deemed necessary for the long-term,it will be encoded for short-term use only and ultimately discarded unless reclassified. The encoding process takes into consideration the emotional nature, ...
Storage: Long
... Retrieval Cues After learning to move a mobile by kicking, infants had their learning reactivated most strongly when retested in the same rather than a different context (Butler & Rovee-Collier, 1989). ...
... Retrieval Cues After learning to move a mobile by kicking, infants had their learning reactivated most strongly when retested in the same rather than a different context (Butler & Rovee-Collier, 1989). ...
Memory
... change (e.g., shape of terminal button, number of receptors) • This causes memories to be now be stored in the long term ...
... change (e.g., shape of terminal button, number of receptors) • This causes memories to be now be stored in the long term ...
memory drsidra
... Number of Neurons and Their Connectivities Often Change Significantly During Learning • Learning” is achieved in adult human beings and animals by modification of numbers of neurons in the memory circuits • Use it or lose it! ...
... Number of Neurons and Their Connectivities Often Change Significantly During Learning • Learning” is achieved in adult human beings and animals by modification of numbers of neurons in the memory circuits • Use it or lose it! ...
Lecture Note
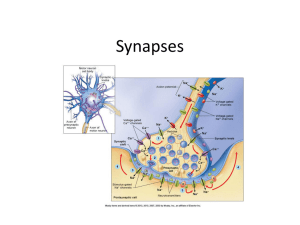
... - Signal transmission in a synapse is based on the lock-key mechanism between the ligands and the receptors. - Short-term memory is stored by strengthening the chemical transmission mechanisms through secreting neurotransmitters at the synapses. ...
... - Signal transmission in a synapse is based on the lock-key mechanism between the ligands and the receptors. - Short-term memory is stored by strengthening the chemical transmission mechanisms through secreting neurotransmitters at the synapses. ...
Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... Thus in a very indirect way, the associative effect of stimulation the facilitator neuron at the same time that the sensory neuron is stimulated causes prolonged increase in excitatory sensitivity of the sensory terminal, and this establishes the memory trace. ...
... Thus in a very indirect way, the associative effect of stimulation the facilitator neuron at the same time that the sensory neuron is stimulated causes prolonged increase in excitatory sensitivity of the sensory terminal, and this establishes the memory trace. ...