The Anatomy of a Memory: Insights Into How Information is Stored in
... Each sensation is analyzed by specific receptors on the surface of the body and then transmitted to the area of the brain known as the cortex, where most sensations are elaborated and become consciousness. Each sensation is represented in specific sensory cortical areas. A common feature of these co ...
... Each sensation is analyzed by specific receptors on the surface of the body and then transmitted to the area of the brain known as the cortex, where most sensations are elaborated and become consciousness. Each sensation is represented in specific sensory cortical areas. A common feature of these co ...
Why is our capacity of working memory so large
... It is possible to achieve different numbers of concurrently stabilizable activity packets by varying physiological parameters such as the strength of the NMDA effect and the width of the interaction structure. However, realistic physiological parameters lead typically to a small number of concurrent ...
... It is possible to achieve different numbers of concurrently stabilizable activity packets by varying physiological parameters such as the strength of the NMDA effect and the width of the interaction structure. However, realistic physiological parameters lead typically to a small number of concurrent ...
McCulloch-Pitts Neuron
... The activation of a McCulloch Pitts neuron is binary. Neurons are connected by directed weighted paths. A connection path is excitatory if the weight on the path is positive else its inhibitory. All excitatory connections to a neuron have the same weights. Each neuron has a fixed threshold: f(n) = ...
... The activation of a McCulloch Pitts neuron is binary. Neurons are connected by directed weighted paths. A connection path is excitatory if the weight on the path is positive else its inhibitory. All excitatory connections to a neuron have the same weights. Each neuron has a fixed threshold: f(n) = ...
Cranial nerve of smell, plus olfactory pathway
... associated with childhood – general mood (such as contentment) Many memories, b/c that’s when we first experience most smells ...
... associated with childhood – general mood (such as contentment) Many memories, b/c that’s when we first experience most smells ...
2320Lecture22
... Capacity • For example: what if recalling interferes with memory? What if they forgot the information before they could report it? • How could you modify the experiment to measure the instantaneous capacity, before any forgetting can occur? ...
... Capacity • For example: what if recalling interferes with memory? What if they forgot the information before they could report it? • How could you modify the experiment to measure the instantaneous capacity, before any forgetting can occur? ...
PIPE CLEANER NEURON LESSON PLAN Part A
... Students will form a circle and “send” the message around the room. Each student will be a different part of the neuron and do a different dance to represent the function of that part. 1s – cell body – thinking motion (thinking face—finger tapping lips?) 2s – dendrites – reach out hands, wiggle fing ...
... Students will form a circle and “send” the message around the room. Each student will be a different part of the neuron and do a different dance to represent the function of that part. 1s – cell body – thinking motion (thinking face—finger tapping lips?) 2s – dendrites – reach out hands, wiggle fing ...
Transmission at the Synapse and the
... o There are 3 mechanisms of presynaptic inhibition: Activation of chloride channels in the PRE-synaptic neuron – that hyperpolarizes the excitatory nerve ending and thus reduced the magnitude of excitatory action potential; and that in turn reduces the amount of calcium that enters the excitatory ...
... o There are 3 mechanisms of presynaptic inhibition: Activation of chloride channels in the PRE-synaptic neuron – that hyperpolarizes the excitatory nerve ending and thus reduced the magnitude of excitatory action potential; and that in turn reduces the amount of calcium that enters the excitatory ...
Solutions - MsHughesPsychology
... 7. One inconsistency with the movie character’s condition and that of real-life sufferers of this type of amnesia is that: A. Usually women do not experience amnesia B. Real-life sufferers will learn to form new memories within a year C. Real-life sufferers cannot retain new memories for a whole da ...
... 7. One inconsistency with the movie character’s condition and that of real-life sufferers of this type of amnesia is that: A. Usually women do not experience amnesia B. Real-life sufferers will learn to form new memories within a year C. Real-life sufferers cannot retain new memories for a whole da ...
Excitatory_Inhibitory_Neural_Network_1
... Theoretical Neuroscience, by Peter Dayan and Larry Abbott, MIT Press, 2005 pp. 266-269 The system studied here is one the simplest types of neural networks to exhibit oscillatory activity. It can be regarded as a simplified model of a fully-connected network comprised of a large number of excitatory ...
... Theoretical Neuroscience, by Peter Dayan and Larry Abbott, MIT Press, 2005 pp. 266-269 The system studied here is one the simplest types of neural networks to exhibit oscillatory activity. It can be regarded as a simplified model of a fully-connected network comprised of a large number of excitatory ...
You - Ashton Southard
... › In a typical implicit memory task, you would be shown a list of words, then asked to fill in a word fragment (such as t—K). You would probably complete the sentence with a word you had just seen (task) rather than another word (took or teak) Without trying to do so, you would engage in recall ...
... › In a typical implicit memory task, you would be shown a list of words, then asked to fill in a word fragment (such as t—K). You would probably complete the sentence with a word you had just seen (task) rather than another word (took or teak) Without trying to do so, you would engage in recall ...
Ch05x
... • Memory: processes involved in retaining, retrieving, and using information about stimuli, images, events, ideas, and skills after the original information is no longer present ...
... • Memory: processes involved in retaining, retrieving, and using information about stimuli, images, events, ideas, and skills after the original information is no longer present ...
Storing and Keeping Memories
... 20,000 neurons when doing experiment involving long-term memory compared to the human brain which has about 100,000 billion neurons and 100 trillion synapses. How Alzheimer’s and other dementias destroy short- and long-term memory has been the subject of heated controversy in recent years. It may be ...
... 20,000 neurons when doing experiment involving long-term memory compared to the human brain which has about 100,000 billion neurons and 100 trillion synapses. How Alzheimer’s and other dementias destroy short- and long-term memory has been the subject of heated controversy in recent years. It may be ...
14/15 April 2008
... • Once trained, a guaranteed solution (recall of the correct memory). * Hertz, Krogh & Palmer Introduction to the theory of neural computation (1990). ...
... • Once trained, a guaranteed solution (recall of the correct memory). * Hertz, Krogh & Palmer Introduction to the theory of neural computation (1990). ...
Recalling the future
... recalling the past and imagining the future. Several reviews describe the construction system of the brain, which assembles imagined events from our past knowledge. We create altered versions of remembered situations by recombining primitive images with digested information from memory. Our experien ...
... recalling the past and imagining the future. Several reviews describe the construction system of the brain, which assembles imagined events from our past knowledge. We create altered versions of remembered situations by recombining primitive images with digested information from memory. Our experien ...
Clinically Relevant Functional Neuroanatomy
... • Not limited to one sensory modality or type of material • Normal IQ, attention span, “nondeclarative” forms of memory ...
... • Not limited to one sensory modality or type of material • Normal IQ, attention span, “nondeclarative” forms of memory ...
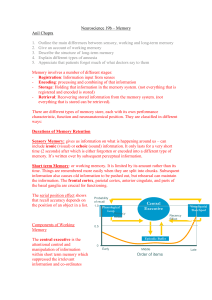
Neuroscience 19b – Memory
... include iconic (visual) or echoic (sound) information. It only lasts for a very short time (2 seconds) after which is either forgotten or encoded into a different type of memory. It’s written over by subsequent perceptual information. Short term Memory: or working memory. It is limited by its amount ...
... include iconic (visual) or echoic (sound) information. It only lasts for a very short time (2 seconds) after which is either forgotten or encoded into a different type of memory. It’s written over by subsequent perceptual information. Short term Memory: or working memory. It is limited by its amount ...
long-term memory
... Accessible to consciousness and can be readily communicated or declared to others. ...
... Accessible to consciousness and can be readily communicated or declared to others. ...
Slide 1
... weights. α is the learning rate (don’t overshoot) Repeat 3 and 4 until the d−y is smaller than a user-specified error threshold, or a predetermined number of iterations have ...
... weights. α is the learning rate (don’t overshoot) Repeat 3 and 4 until the d−y is smaller than a user-specified error threshold, or a predetermined number of iterations have ...
Is There a Connection Between the Brain and Learning?
... – increase of presynaptic terminals – increase of neurotransmitter – development of new neurons in the hippocampus ...
... – increase of presynaptic terminals – increase of neurotransmitter – development of new neurons in the hippocampus ...
on Memory
... • If you do remember this…why might be the reason for NOT forgetting? • If you do not remember anything about this day ...
... • If you do remember this…why might be the reason for NOT forgetting? • If you do not remember anything about this day ...
Back propagation-step-by-step procedure
... • Step 4: Present the pattern as inputs to {I}. Linear activation function is used as the output of the input layer. {O}I={I}I • Step 5: Compute the inputs to the hidden layers by multiplying corresponding weights of synapses as {I}H=[V]T{O}I • Step 6: The hidden layer units,evaluates the output us ...
... • Step 4: Present the pattern as inputs to {I}. Linear activation function is used as the output of the input layer. {O}I={I}I • Step 5: Compute the inputs to the hidden layers by multiplying corresponding weights of synapses as {I}H=[V]T{O}I • Step 6: The hidden layer units,evaluates the output us ...
Bump attractors and the homogeneity assumption
... Jij = -J0 + J2 cos (2π(i-j)/N) x if x > 0 0 if x < 0 ...
... Jij = -J0 + J2 cos (2π(i-j)/N) x if x > 0 0 if x < 0 ...
Silva & White - Walker Bioscience
... CREB block long term memory, but do not affect other memory stages. • Studies were performed using temperature sensitive CREB mutants, which were only inactivated in high temperature. • Wild type and mutant CREB flies grew up in the permissive (low) temperature, and were then given memory tasks at h ...
... CREB block long term memory, but do not affect other memory stages. • Studies were performed using temperature sensitive CREB mutants, which were only inactivated in high temperature. • Wild type and mutant CREB flies grew up in the permissive (low) temperature, and were then given memory tasks at h ...