Activity of Spiking Neurons Stimulated by External Signals of
... deliver signals and act like an “input device”. Soma is the “central processing unit” that generates a signal if the total input exceeds a certain threshold (about -30 mV) and the axon transmits the signals to other neurons. Synapses are the contact points for transferring information between neuron ...
... deliver signals and act like an “input device”. Soma is the “central processing unit” that generates a signal if the total input exceeds a certain threshold (about -30 mV) and the axon transmits the signals to other neurons. Synapses are the contact points for transferring information between neuron ...
Memory and Law
... meaningful association. Long term memory is encoded “semantically” (for meaning and association). ...
... meaningful association. Long term memory is encoded “semantically” (for meaning and association). ...
1050927abstract
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
Capacity Analysis of Attractor Neural Networks with Binary Neurons and Discrete Synapses
... Inspired by the delay activity observed in numerous delayed match-to-sample (DMS) experiments, the attractor states of neural network dynamics are considered to be the underlying mechanism of memory storage in neural networks. For the simplest network with binary neurons and standard asynchronous dy ...
... Inspired by the delay activity observed in numerous delayed match-to-sample (DMS) experiments, the attractor states of neural network dynamics are considered to be the underlying mechanism of memory storage in neural networks. For the simplest network with binary neurons and standard asynchronous dy ...
INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL NEUROBIOLOGY Tamás
... the thalamic nuclei will be classified as they belong to either of two basic operational units; to a group of subnuclei (1) working relatively independently and relaying sub-thalamic (mainly sensory) inputs to primary sensory cortical areas; or to the other set of subnuclei (2), the higher order nuc ...
... the thalamic nuclei will be classified as they belong to either of two basic operational units; to a group of subnuclei (1) working relatively independently and relaying sub-thalamic (mainly sensory) inputs to primary sensory cortical areas; or to the other set of subnuclei (2), the higher order nuc ...
Memory Capacity of a Hebbian Learning Model with Inhibition
... parameters governing the stochastic learning process are fixed, the storage capacity of the model to learn a stream of uncorrelated stimuli is as low as O(log N), where N is the number of neurons in the network. If the coding level (proportion of active neurons) of the stimuli can vary with N as f ∼ ...
... parameters governing the stochastic learning process are fixed, the storage capacity of the model to learn a stream of uncorrelated stimuli is as low as O(log N), where N is the number of neurons in the network. If the coding level (proportion of active neurons) of the stimuli can vary with N as f ∼ ...
Cognitive Neuroscience of Language: 18: Memory and language
... vocabulary learning, although it need not be seen as specifically linguistic Polarities such as abstractionist vs episodic, amodal vs modality-specific, need to be cashed out neuroanatomically, rather than one pole of the relationship being pursued ...
... vocabulary learning, although it need not be seen as specifically linguistic Polarities such as abstractionist vs episodic, amodal vs modality-specific, need to be cashed out neuroanatomically, rather than one pole of the relationship being pursued ...
Neurons, Synapses and Long-term Potentiation
... changes in the cellular level • So what are the cellular changes? ...
... changes in the cellular level • So what are the cellular changes? ...
Memory notes Explaining memory Learning required memorisation
... Second change – to the structure of the slug’ neuron where the number of branches increases as they become bushier through the growth of smaller ‘offshoots’ called dendritic spines and thereby strengthen the connection. Third change – involves the synapse; when a memory is formed, new synaptic conne ...
... Second change – to the structure of the slug’ neuron where the number of branches increases as they become bushier through the growth of smaller ‘offshoots’ called dendritic spines and thereby strengthen the connection. Third change – involves the synapse; when a memory is formed, new synaptic conne ...
Consciousness, Thought, and Memory
... cell damage and death. People afflicted with this disease present all the symptoms one would expect from a disorder of its nature; forgetfulness, personality changes, poor judgment, etc. These symptoms demonstrate the complexity of the nervous system, particularly the cerebrum as it pertains to cons ...
... cell damage and death. People afflicted with this disease present all the symptoms one would expect from a disorder of its nature; forgetfulness, personality changes, poor judgment, etc. These symptoms demonstrate the complexity of the nervous system, particularly the cerebrum as it pertains to cons ...
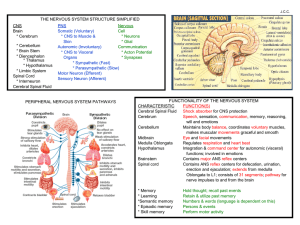
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... Oblongata to L1; consists of 31 segments; pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain * Memory * Learning *Semantic memory * Episodic memory * Skill memory ...
... Oblongata to L1; consists of 31 segments; pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain * Memory * Learning *Semantic memory * Episodic memory * Skill memory ...
Biological Basis of Memory
... Amnesia – Severe Memory Loss – 3 Major Types: 1. Retrograde amnesia—inability to remember past information; common after head injury Reason for this is it may disrupt: o Memory – gradual, physical process of converting a long-term memory to a stable and enduring memory code. o If disturbed before th ...
... Amnesia – Severe Memory Loss – 3 Major Types: 1. Retrograde amnesia—inability to remember past information; common after head injury Reason for this is it may disrupt: o Memory – gradual, physical process of converting a long-term memory to a stable and enduring memory code. o If disturbed before th ...
Justin Smith - USD Biology
... – EPM, light-dark box, open field, elevated zero maze – No effect in: Tail suspension or forced swim ...
... – EPM, light-dark box, open field, elevated zero maze – No effect in: Tail suspension or forced swim ...
The Neural Basis Of Memory
... neurons can be seen by the naked eye, so can be observed, stimulated or removed . ...
... neurons can be seen by the naked eye, so can be observed, stimulated or removed . ...
“Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to
... “Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to learning based on current literature.” The difference between learning and memory is rather subtle; learning is the process by which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that i ...
... “Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to learning based on current literature.” The difference between learning and memory is rather subtle; learning is the process by which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that i ...
CHAPTER SIX Memory The experience of pain cannot be separated
... We usually think of memory as an experiential phenomenon. It is a product of consciousness. We experience something that commands our awareness, and we register it as memory. A memory, however, is nothing more than a rearrangement of neurotransmitters on the surface of the neuron. This rearrangement ...
... We usually think of memory as an experiential phenomenon. It is a product of consciousness. We experience something that commands our awareness, and we register it as memory. A memory, however, is nothing more than a rearrangement of neurotransmitters on the surface of the neuron. This rearrangement ...
Spatial Working Memory
... spatial memory, in particular in the right hemisphere. However, some current investigators associated DLPFC more with executive control. DLPFC forms part of a VWM network that includes a number of areas closely related to attention and eye movement, including FEF, Cingulate, PEF, and some subcortica ...
... spatial memory, in particular in the right hemisphere. However, some current investigators associated DLPFC more with executive control. DLPFC forms part of a VWM network that includes a number of areas closely related to attention and eye movement, including FEF, Cingulate, PEF, and some subcortica ...
Brain Jeopardy Game
... “Immediate memory” and “working memory”are the two components of this type of memory. ...
... “Immediate memory” and “working memory”are the two components of this type of memory. ...
Nervous System Exam Review
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
Immediate Memory….
... rework ideas for eventual storage somewhere else. Generally captures our focus and demands our attention. Can handle only a few items at once. Adolescents can process items intently up to 10-20 minutes before becoming fatigued. Adults, up to 45. ...
... rework ideas for eventual storage somewhere else. Generally captures our focus and demands our attention. Can handle only a few items at once. Adolescents can process items intently up to 10-20 minutes before becoming fatigued. Adults, up to 45. ...
Chap2
... McConnell (1962) – cut up planaria (flatworms) and fed them to other worms who showed the same learning. ...
... McConnell (1962) – cut up planaria (flatworms) and fed them to other worms who showed the same learning. ...