Forming Impressions (3-1)
... The process of ______________________________________________ The study of how we _____________________ impressions about others The processes by which we come to know about and think about others –their characteristics, qualities, inner states. II. Key sources of information 1. Appearance: in impre ...
... The process of ______________________________________________ The study of how we _____________________ impressions about others The processes by which we come to know about and think about others –their characteristics, qualities, inner states. II. Key sources of information 1. Appearance: in impre ...
Module 12 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... – refers to the inability to retrieve, recall, or recognize information that was stored or is still stored in longterm memory • Repression – according to Freud, repression is a mental process that automatically hides emotionally threatening or anxiety-producing information in the unconscious, from w ...
... – refers to the inability to retrieve, recall, or recognize information that was stored or is still stored in longterm memory • Repression – according to Freud, repression is a mental process that automatically hides emotionally threatening or anxiety-producing information in the unconscious, from w ...
Module_12vs9_Final
... • according to Sigmund Freud, repression is a mental process that automatically hides emotionally threatening or anxiety-producing information in the unconscious (from which repressed memories can’t be recalled voluntarily, but something may cause them to enter consciousness at a later time) ...
... • according to Sigmund Freud, repression is a mental process that automatically hides emotionally threatening or anxiety-producing information in the unconscious (from which repressed memories can’t be recalled voluntarily, but something may cause them to enter consciousness at a later time) ...
Memory
... Figure 2.25 The cerebral cortex, dorsal and lateral views Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers ...
... Figure 2.25 The cerebral cortex, dorsal and lateral views Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers ...
Consolidation theory
... consolidation is required to ensure it is permanently stored. • Consolidation refers to the physical changes are made to the neurons in the brain when something new is being learned and immediately following learning. • These changes form the ‘memory’ of what has been learned. • If there is a disrup ...
... consolidation is required to ensure it is permanently stored. • Consolidation refers to the physical changes are made to the neurons in the brain when something new is being learned and immediately following learning. • These changes form the ‘memory’ of what has been learned. • If there is a disrup ...
Neuroscience 19b – Memory
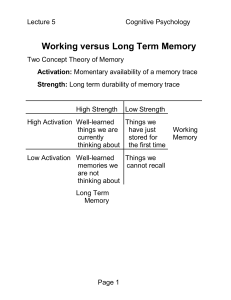
... time (2 seconds) after which is either forgotten or encoded into a different type of memory. It’s written over by subsequent perceptual information. Short term Memory: or working memory. It is limited by its amount rather than its time. Things are remembered more easily when they are split into chun ...
... time (2 seconds) after which is either forgotten or encoded into a different type of memory. It’s written over by subsequent perceptual information. Short term Memory: or working memory. It is limited by its amount rather than its time. Things are remembered more easily when they are split into chun ...
05powerpoint
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
Knowledge Representation
... • I saw the racing pigeons flying to Paris. • I saw the Eiffel Tower flying to Paris. • The boy kicked the ball under the tree. • The boy kicked the wall under the tree. • Put the apple in the basket on the shelf ...
... • I saw the racing pigeons flying to Paris. • I saw the Eiffel Tower flying to Paris. • The boy kicked the ball under the tree. • The boy kicked the wall under the tree. • Put the apple in the basket on the shelf ...
Memory kaleidoscope: enhancing memory to improve learning
... proteins, and electrical impulses. If the information does not receive sufficient attention or if it is not deemed necessary for the long-term,it will be encoded for short-term use only and ultimately discarded unless reclassified. The encoding process takes into consideration the emotional nature, ...
... proteins, and electrical impulses. If the information does not receive sufficient attention or if it is not deemed necessary for the long-term,it will be encoded for short-term use only and ultimately discarded unless reclassified. The encoding process takes into consideration the emotional nature, ...
Chapter_3_ID2e_slides
... from the mass of stimuli around us • Involves audio and/or visual senses • Information at the interface should be structured to ...
... from the mass of stimuli around us • Involves audio and/or visual senses • Information at the interface should be structured to ...
on Memory
... me what you remember about it. What exact details can you provide? – What were you wearing? – How did you get to school? ...
... me what you remember about it. What exact details can you provide? – What were you wearing? – How did you get to school? ...
Pubertal Influences on Sleep
... leads to another • History example: – U.S.’s entry into WWII vs. Japan’s ...
... leads to another • History example: – U.S.’s entry into WWII vs. Japan’s ...
Memory - Hensley
... 6. We store information in memory as libraries store their books, that is, in discrete precise locations. 7. When people learn something while intoxicated, they recall it best when they are again intoxicated. 8. The hour before sleep is good time to commit information to memory. 9. Repeatedly imagin ...
... 6. We store information in memory as libraries store their books, that is, in discrete precise locations. 7. When people learn something while intoxicated, they recall it best when they are again intoxicated. 8. The hour before sleep is good time to commit information to memory. 9. Repeatedly imagin ...
Storage: Long
... Retrieval Cues After learning to move a mobile by kicking, infants had their learning reactivated most strongly when retested in the same rather than a different context (Butler & Rovee-Collier, 1989). ...
... Retrieval Cues After learning to move a mobile by kicking, infants had their learning reactivated most strongly when retested in the same rather than a different context (Butler & Rovee-Collier, 1989). ...
Lecture Note
... - Signal transmission in a synapse is based on the lock-key mechanism between the ligands and the receptors. - Short-term memory is stored by strengthening the chemical transmission mechanisms through secreting neurotransmitters at the synapses. ...
... - Signal transmission in a synapse is based on the lock-key mechanism between the ligands and the receptors. - Short-term memory is stored by strengthening the chemical transmission mechanisms through secreting neurotransmitters at the synapses. ...
Lecture05
... Subjects studied and recalled 12 lists of 10 common unrelated words. Then they had to recall all lists a second time cued by the first word of each list. Narrative subjects were to make a story incorporating the words in the list. Control subjects were told just to study each of the list and were gi ...
... Subjects studied and recalled 12 lists of 10 common unrelated words. Then they had to recall all lists a second time cued by the first word of each list. Narrative subjects were to make a story incorporating the words in the list. Control subjects were told just to study each of the list and were gi ...
INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL NEUROBIOLOGY Tamás
... function only in mutual relationship with other cortical areas. The elements of the thalamocorticalcorticothalamic circuit and the generation of different oscillations within the circuit will also be explained. The second part of the presentation will focus on the “less known part”, the higher order ...
... function only in mutual relationship with other cortical areas. The elements of the thalamocorticalcorticothalamic circuit and the generation of different oscillations within the circuit will also be explained. The second part of the presentation will focus on the “less known part”, the higher order ...
Cognitive information processing
... Connectionistic theory • Information is stored in multiple locations throughout the brain in the form of networks of connections • More connections to a single idea or concept, the more likely it is to be stored and retrieved ...
... Connectionistic theory • Information is stored in multiple locations throughout the brain in the form of networks of connections • More connections to a single idea or concept, the more likely it is to be stored and retrieved ...
Midterm Review Project
... Memory- learning that has persisted over time; it has been acquired, stored, and can be retrieved In order to remember something it must be: ● Encoded- perceived by the brain ● Stored- retained in the brain for a long period of time ● Retrieved- come back out of storage and into conscious thought Pa ...
... Memory- learning that has persisted over time; it has been acquired, stored, and can be retrieved In order to remember something it must be: ● Encoded- perceived by the brain ● Stored- retained in the brain for a long period of time ● Retrieved- come back out of storage and into conscious thought Pa ...
Information Processing and Memory
... used to assist schema refinement if it varies in only one way from the designated example. H. Simon (1974) has estimated that each new bit of information takes ten seconds to process in order to be stored in long-term memory. The implications for lecture-based instruction are significant. On a neuro ...
... used to assist schema refinement if it varies in only one way from the designated example. H. Simon (1974) has estimated that each new bit of information takes ten seconds to process in order to be stored in long-term memory. The implications for lecture-based instruction are significant. On a neuro ...
Memory Systems
... Long term & Short Term Procedural & Working Experience Dependent Brain Development Anterograde and Retrograde Amnesia ...
... Long term & Short Term Procedural & Working Experience Dependent Brain Development Anterograde and Retrograde Amnesia ...
Readings
... Cues to identification are context and familiarity. Context is especially important in auditory information. “Your fuel is low” is better than “low fuel.” ...
... Cues to identification are context and familiarity. Context is especially important in auditory information. “Your fuel is low” is better than “low fuel.” ...
Cognitive Neuroscience of Language: 18: Memory and language
... and rehearsal, where rehearsal is equivalent (but not identical with) subvocal rehearsal Left posterior parietal cortex is implicated in storage ...
... and rehearsal, where rehearsal is equivalent (but not identical with) subvocal rehearsal Left posterior parietal cortex is implicated in storage ...
Biological Basis of Memory
... may not involve the hippocampus but knowing they are there ( memory) does not work showing the hippocampus is involved in these. 3. Infantile Amnesia – Inability to recall events from the first few of life. Possible Reasons for this: o Too many differences between the world of an and ours for us to ...
... may not involve the hippocampus but knowing they are there ( memory) does not work showing the hippocampus is involved in these. 3. Infantile Amnesia – Inability to recall events from the first few of life. Possible Reasons for this: o Too many differences between the world of an and ours for us to ...