Memory for Everyday Activities
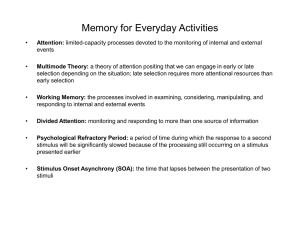
... Multimode Theory: a theory of attention positing that we can engage in early or late selection depending on the situation; late selection requires more attentional resources than early selection ...
... Multimode Theory: a theory of attention positing that we can engage in early or late selection depending on the situation; late selection requires more attentional resources than early selection ...
Module 3 - socialscienceteacher
... • refers to change in the structure and function of neurons after they have been repeatedly stimulated • neuroscientists believe that the LTP process, which changes the structure and function of neurons, is the most likely basis for learning and memory in animals and humans ...
... • refers to change in the structure and function of neurons after they have been repeatedly stimulated • neuroscientists believe that the LTP process, which changes the structure and function of neurons, is the most likely basis for learning and memory in animals and humans ...
Spatial Working Memory
... associated with prefrontal cortex, especially lateral prefrontal cortex. Dorso-lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), as opposed to ventral PFC, has been associated more with spatial memory, in particular in the right hemisphere. However, some current investigators associated DLPFC more with executive c ...
... associated with prefrontal cortex, especially lateral prefrontal cortex. Dorso-lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), as opposed to ventral PFC, has been associated more with spatial memory, in particular in the right hemisphere. However, some current investigators associated DLPFC more with executive c ...
Consciousness, Thought, and Memory
... Memory is the storage and retrieval of information. The two stages of memory are short term (STM) and long term (LTM). STM is the first step, and is limited to seven or eight chunks of information. Some 5% of sensory input is transferred to the STM. The LTM is of limitless capacity, but its ability ...
... Memory is the storage and retrieval of information. The two stages of memory are short term (STM) and long term (LTM). STM is the first step, and is limited to seven or eight chunks of information. Some 5% of sensory input is transferred to the STM. The LTM is of limitless capacity, but its ability ...
CHAPTER SIX Memory The experience of pain cannot be separated
... experience. This process takes time, perhaps as long as a few minutes. As we all know, the act of rote memorization takes a while, and as we also know, a recently acquired memory is one of the most fragile things in nature, easily lost by distraction or the diversion of attention to other matters. G ...
... experience. This process takes time, perhaps as long as a few minutes. As we all know, the act of rote memorization takes a while, and as we also know, a recently acquired memory is one of the most fragile things in nature, easily lost by distraction or the diversion of attention to other matters. G ...
“Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to
... “Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to learning based on current literature.” The difference between learning and memory is rather subtle; learning is the process by which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that i ...
... “Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to learning based on current literature.” The difference between learning and memory is rather subtle; learning is the process by which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that i ...
Cognitive Information Processing
... Learning vs. Memory - learning is viewed as the acquisition of new information. Memory is related to the ability to recall information that has been previously learned Storage - the process by which new information is placed in memory Retrieval - the process by which people “find’ the information th ...
... Learning vs. Memory - learning is viewed as the acquisition of new information. Memory is related to the ability to recall information that has been previously learned Storage - the process by which new information is placed in memory Retrieval - the process by which people “find’ the information th ...
Lecture 16
... processes make it easier for the neuron to respond again This increased responsiveness is longterm potentiation It is now accepted that the structure of synapses change after learning ...
... processes make it easier for the neuron to respond again This increased responsiveness is longterm potentiation It is now accepted that the structure of synapses change after learning ...
Storage and Retrieval
... 5. The fact that you need to drive your sister home from school 6.The fact that the smell of eggs makes you sick and you don’t know why ...
... 5. The fact that you need to drive your sister home from school 6.The fact that the smell of eggs makes you sick and you don’t know why ...
Brain Jeopardy Game
... This is where the brain takes multiple items and considers them a single entity (as a way of bypassing the limitations of working memory). ...
... This is where the brain takes multiple items and considers them a single entity (as a way of bypassing the limitations of working memory). ...










