Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Analyze: Our task is to write a net ionic equation for a precipitation reaction, given the names of the reactants present in solution. Plan: We first need to write the chemical formulas of the reactants and products and to determine which product is insoluble. Then we write and balance the molecular ...
... Analyze: Our task is to write a net ionic equation for a precipitation reaction, given the names of the reactants present in solution. Plan: We first need to write the chemical formulas of the reactants and products and to determine which product is insoluble. Then we write and balance the molecular ...
Chemical Dynamics at Surfaces
... Gas Cleaning: methane from natural gas is cleaned, mainly to remove sulfur impurities that would poison the catalysts ...
... Gas Cleaning: methane from natural gas is cleaned, mainly to remove sulfur impurities that would poison the catalysts ...
Notes
... KP = 81.9. Initially a reaction mixture at this temperature contains PI2 = 0.100 atm, PCl2 = 0.100 atm and PICl = 0.100 atm. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressures of I2, Cl2, and ICl. ...
... KP = 81.9. Initially a reaction mixture at this temperature contains PI2 = 0.100 atm, PCl2 = 0.100 atm and PICl = 0.100 atm. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressures of I2, Cl2, and ICl. ...
Class 3 updated Sep 30 2011
... evaporant, which melts locally. The evaporant metal forms its own crucible and the contact with the hearth is too cool for chemical reaction. Results in fewer source contamination problems than in the case of resistive heating. Disadvantage: The process may cause x-ray damage or ion damage on the su ...
... evaporant, which melts locally. The evaporant metal forms its own crucible and the contact with the hearth is too cool for chemical reaction. Results in fewer source contamination problems than in the case of resistive heating. Disadvantage: The process may cause x-ray damage or ion damage on the su ...
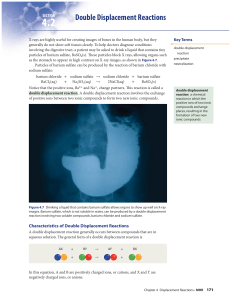
Double Displacement Reactions
... When two solutions are mixed, the formation of a solid precipitate or a gas is evidence that a reaction has occurred. However, there is one type of double displacement reaction that occurs with no outward evidence of a reaction. This type of reaction forms water as a product, but, because the reacta ...
... When two solutions are mixed, the formation of a solid precipitate or a gas is evidence that a reaction has occurred. However, there is one type of double displacement reaction that occurs with no outward evidence of a reaction. This type of reaction forms water as a product, but, because the reacta ...
Balancing Reaction Equations Oxidation State Reduction
... Oxidation: Loss of electrons from an element. Oxidation number increases Reduction: Gain of electrons by an element. Oxidation number decreases ...
... Oxidation: Loss of electrons from an element. Oxidation number increases Reduction: Gain of electrons by an element. Oxidation number decreases ...
Fritz-Haber-Institut der Max-Planck
... Sulfated zirconia (SZ) and Mn-promoted SZ were studied in situ during activation in different atmospheres and during n-butane isomerization. DRIFT spectra show that activation at 773 K leads to about 90% dehydration (60–125 µmol H2O/g remain). Comparison of SO single and double bond vibrations in th ...
... Sulfated zirconia (SZ) and Mn-promoted SZ were studied in situ during activation in different atmospheres and during n-butane isomerization. DRIFT spectra show that activation at 773 K leads to about 90% dehydration (60–125 µmol H2O/g remain). Comparison of SO single and double bond vibrations in th ...
Chapter 4 2013
... 3. Break the compounds into their ions and write the ionic equation for the reaction. 3. Refer to the table of solubility rules and decide whether any of the ion combinations is insoluble. 4. If a candidate is insoluble, that reaction will occur. 5. Remove the spectator ions and write the net ionic ...
... 3. Break the compounds into their ions and write the ionic equation for the reaction. 3. Refer to the table of solubility rules and decide whether any of the ion combinations is insoluble. 4. If a candidate is insoluble, that reaction will occur. 5. Remove the spectator ions and write the net ionic ...
Chemistry 12 Keq WORKSHEET #1
... 1. A sample containing 0.800 moles of POCl3 is enclosed in a 0.500 litre vessel at a certain temperature. When the equilibrium for the dissociation reaction POCl3 (g) <===> POCl (g) + Cl2 (g) is attained, it is found that the vessel contains 0.259 moles of Cl2. Calculate the equilibrium constant. ...
... 1. A sample containing 0.800 moles of POCl3 is enclosed in a 0.500 litre vessel at a certain temperature. When the equilibrium for the dissociation reaction POCl3 (g) <===> POCl (g) + Cl2 (g) is attained, it is found that the vessel contains 0.259 moles of Cl2. Calculate the equilibrium constant. ...
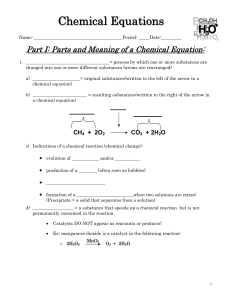
chem equation Pkt Student2
... changed into one or more different substances (atoms are rearranged) a) _____________________= original substances(written to the left of the arrow in a chemical equation) b) ________________________ = resulting substances(written to the right of the arrow in a chemical equation) ...
... changed into one or more different substances (atoms are rearranged) a) _____________________= original substances(written to the left of the arrow in a chemical equation) b) ________________________ = resulting substances(written to the right of the arrow in a chemical equation) ...
Class XII Chemistry IMPORTANT QUESTIONS and COMMON
... When cyclohexane is added to ethyl alcohol, the molecules of cyclohexane try to occupy the spaces in between ethyl alcohol molecules. Consequently some hydrogen bonds in alcohol molecules break and attractive forces between the molecules are weakened . The escaping tendency of the molecules of ethan ...
... When cyclohexane is added to ethyl alcohol, the molecules of cyclohexane try to occupy the spaces in between ethyl alcohol molecules. Consequently some hydrogen bonds in alcohol molecules break and attractive forces between the molecules are weakened . The escaping tendency of the molecules of ethan ...
Chapter 20 Electrochemistry
... Sample Exercise 20.10 Using Standard Reduction Potentials to Calculate G and K (a) Use the standard reduction potentials in Table 20.1 to calculate the standard free-energy change, G,and the equilibrium constant, K, at 298 K for the reaction (b) Suppose the reaction in part (a) is written What ...
... Sample Exercise 20.10 Using Standard Reduction Potentials to Calculate G and K (a) Use the standard reduction potentials in Table 20.1 to calculate the standard free-energy change, G,and the equilibrium constant, K, at 298 K for the reaction (b) Suppose the reaction in part (a) is written What ...
Surface chemistry of carbon dioxide - Max-Planck
... the 2n u orbital. The six occupied orbitals may be classified as two cy-C-O bonds (3cyg,2%) and two lone pairs (4%, 3%). The lnu represents the n C - O bonds and lng the n lone pairs. In order to judge the stability of the linear geometry, Fig. 1 shows, in a qualitative way, the energy positions of ...
... the 2n u orbital. The six occupied orbitals may be classified as two cy-C-O bonds (3cyg,2%) and two lone pairs (4%, 3%). The lnu represents the n C - O bonds and lng the n lone pairs. In order to judge the stability of the linear geometry, Fig. 1 shows, in a qualitative way, the energy positions of ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... – Only affects reactions in which gases are involved – In order for it to have an affect total moles of gas on the left must be different than total moles of gas on the right ...
... – Only affects reactions in which gases are involved – In order for it to have an affect total moles of gas on the left must be different than total moles of gas on the right ...
Chemical Reaction
... (+) used when there is two or more products or reactants heat is used to start the reaction (s) the compound is a solid (l) the compound is a liquid (g) the compound is a gas (aq) aqueous, the compound is dissolved in water ...
... (+) used when there is two or more products or reactants heat is used to start the reaction (s) the compound is a solid (l) the compound is a liquid (g) the compound is a gas (aq) aqueous, the compound is dissolved in water ...
Equilibrium - District 196
... ***The only stressor that can affect these concentration ratios is temperature ***Keq is temperature dependant ...
... ***The only stressor that can affect these concentration ratios is temperature ***Keq is temperature dependant ...
AP Chemistry: Chapter 13 Gaseous Equilibrium Section 1: Multiple
... of the gases at equilibrium without the catalyst? Justify your answer. (Assume that the volume of the solid catalyst is negligible.) In another experiment involving the same reaction, a rigid 2.00 L container initially contains 10.0 g of C(s), plus CO(g) and CO2(g), each at a partial pressure of 2.0 ...
... of the gases at equilibrium without the catalyst? Justify your answer. (Assume that the volume of the solid catalyst is negligible.) In another experiment involving the same reaction, a rigid 2.00 L container initially contains 10.0 g of C(s), plus CO(g) and CO2(g), each at a partial pressure of 2.0 ...
Step 2
... number to each element wherever it appears in the equation. If the reaction is a redox reaction, identify the element that undergoes an increase in oxidation number and the elements the undergoes a decrease. Find the numerical values of the increase and decrease. Determine the smallest whole-number ...
... number to each element wherever it appears in the equation. If the reaction is a redox reaction, identify the element that undergoes an increase in oxidation number and the elements the undergoes a decrease. Find the numerical values of the increase and decrease. Determine the smallest whole-number ...
Chemistry Test Ch 11 Stoichiometry
... 6. Use the following equation to answer these questions: 2 Na (s) + 2 H20 (l) ---> 2 NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) A. How many liters of water is needed to produce 87.69 L H2? B. If 90.0 grams of sodium is dropped into 80.0 g of water, how many liters of hydrogen would be produced? (hint this is a limiting rea ...
... 6. Use the following equation to answer these questions: 2 Na (s) + 2 H20 (l) ---> 2 NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) A. How many liters of water is needed to produce 87.69 L H2? B. If 90.0 grams of sodium is dropped into 80.0 g of water, how many liters of hydrogen would be produced? (hint this is a limiting rea ...
General Concepts of Chemical Equilibrium
... and D. The equilibrium constant of the reaction is 4.0x108. It is clear that we have a high equilibrium constant which suggests that very little reactants may have been left and thus we build our solution on the assumption that A will mainly be of a very little concentration x as a result of the che ...
... and D. The equilibrium constant of the reaction is 4.0x108. It is clear that we have a high equilibrium constant which suggests that very little reactants may have been left and thus we build our solution on the assumption that A will mainly be of a very little concentration x as a result of the che ...
Physical Chemistry II
... As you make your way through this learning activity you will come across problems to test your conceptual understanding of the subject matter Rapid quizzes are provided to check your understanding Practical experiments will be given to evaluate your understanding of theory-practice relations Simulat ...
... As you make your way through this learning activity you will come across problems to test your conceptual understanding of the subject matter Rapid quizzes are provided to check your understanding Practical experiments will be given to evaluate your understanding of theory-practice relations Simulat ...
AP Chemistry: Total Notes Review
... Might as well do one of these so you don’t screw it up on the test. These have a reactant that limits the amount of product produced because one of the reactants runs out. For example: “A 55.8g sample of pure iron is submerged in a solution containing 339.0g of silver nitrate. Fe(NO3)3 and solid sil ...
... Might as well do one of these so you don’t screw it up on the test. These have a reactant that limits the amount of product produced because one of the reactants runs out. For example: “A 55.8g sample of pure iron is submerged in a solution containing 339.0g of silver nitrate. Fe(NO3)3 and solid sil ...
Chemical Equations
... changed into one or more different substances (atoms are rearranged) a) _____________________= original substances(written to the left of the arrow in a chemical equation) b) ________________________ = resulting substances(written to the right of the arrow in a chemical equation) ...
... changed into one or more different substances (atoms are rearranged) a) _____________________= original substances(written to the left of the arrow in a chemical equation) b) ________________________ = resulting substances(written to the right of the arrow in a chemical equation) ...
Physical Chemistry 2.pdf
... be examined to enable one predict whether a particular mixture will mix to form a solution or not. What role do the intermolecular forces play in the formation of a solution? What is the effect of temperature and pressure on the solubility of a substance? How can we use thermodynamics to explain and ...
... be examined to enable one predict whether a particular mixture will mix to form a solution or not. What role do the intermolecular forces play in the formation of a solution? What is the effect of temperature and pressure on the solubility of a substance? How can we use thermodynamics to explain and ...
Double layer forces

Double layer forces occur between charged objects across liquids, typically water. This force acts over distances that are comparable to the Debye length, which is on the order of one to a few tenths of nanometers. The strength of these forces increases with the magnitude of the surface charge density (or the electrical surface potential). For two similarly charged objects, this force is repulsive and decays exponentially at larger distances, see figure. For unequally charged objects and eventually at shorted distances, these forces may also be attractive. The theory due to Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DLVO) combines such double layer forces together with Van der Waals forces in order to estimate the actual interaction potential between colloidal particles.An electrical double layer develops near charged surfaces (or another charged objects) in aqueous solutions. Within this double layer, the first layer corresponds to the charged surface. These charges may originate from tightly adsorbed ions, dissociated surface groups, or substituted ions within the crystal lattice. The second layer corresponds to the diffuse layer, which contains the neutralizing charge consisting of accumulated counterions and depleted coions. The resulting potential profile between these two objects leads to differences in the ionic concentrations within the gap between these objects with respect to the bulk solution. These differences generate an osmotic pressure, which generates a force between these objects.These forces are easily experienced when hands are washed with soap. Adsorbing soap molecules make the skin negatively charged, and the slippery feeling is caused by the strongly repulsive double layer forces. These forces are further relevant in many colloidal or biological systems, and may be responsible for their stability, formation of colloidal crystals, or their rheological properties.