Net Ionic Prep Session NMSI INSTRUCTOR
... part (ii). In part (i), coefficients should be in terms of lowest whole numbers. Assume that solutions are aqueous unless otherwise indicated. Represent substances in solutions as ions if the substances are extensively ionized. Omit formulas for any ions or molecules that are unchanged by the reacti ...
... part (ii). In part (i), coefficients should be in terms of lowest whole numbers. Assume that solutions are aqueous unless otherwise indicated. Represent substances in solutions as ions if the substances are extensively ionized. Omit formulas for any ions or molecules that are unchanged by the reacti ...
mass mass calc
... Solution #1 shows the pattern most often used by students in this course because it tends to be the one that is the most flexible when new problems are presented later on. Choose one of the three methods that suits you best or make up your own. Regardless of how you choose to solve these problems, b ...
... Solution #1 shows the pattern most often used by students in this course because it tends to be the one that is the most flexible when new problems are presented later on. Choose one of the three methods that suits you best or make up your own. Regardless of how you choose to solve these problems, b ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... iii. An increase in temperature will cause the relative amount of reactants to increase and products to decrease. This can be explained by noting that the value of ∆Hrxn is negative, which means that adding heat will shift the reaction to the left. Another argument is that as the temperature increas ...
... iii. An increase in temperature will cause the relative amount of reactants to increase and products to decrease. This can be explained by noting that the value of ∆Hrxn is negative, which means that adding heat will shift the reaction to the left. Another argument is that as the temperature increas ...
chapter 13 - Humble ISD
... insoluble in water. That mean they do not dissolve in water, right? Actually, a very, very, very tiny amount will dissolve in water. We use the Ksp (Constant for Solid Products) to determine the amount that will dissolve. ...
... insoluble in water. That mean they do not dissolve in water, right? Actually, a very, very, very tiny amount will dissolve in water. We use the Ksp (Constant for Solid Products) to determine the amount that will dissolve. ...
Solving Equilibrium Problems
... Now, fill the table with all known concentrations These are the concentrations that are given in the problem Example - Suppose for the equilibrium reaction below, the initial concentrations of A and B were given as 0.750 M in A and 1.500 M in B The table will look as follows: aA I C E ...
... Now, fill the table with all known concentrations These are the concentrations that are given in the problem Example - Suppose for the equilibrium reaction below, the initial concentrations of A and B were given as 0.750 M in A and 1.500 M in B The table will look as follows: aA I C E ...
Chapter 4 Student Notes
... The other product, H2O, is a common weak electrolyte. A typical example of a neutralization reaction is the reaction between an acid and a metal hydroxide: o Mg(OH)2 (milk of magnesia) is a suspension. o As HCl is added, the magnesium hydroxide dissolves, and a clear solution containing Mg 2+ and Cl ...
... The other product, H2O, is a common weak electrolyte. A typical example of a neutralization reaction is the reaction between an acid and a metal hydroxide: o Mg(OH)2 (milk of magnesia) is a suspension. o As HCl is added, the magnesium hydroxide dissolves, and a clear solution containing Mg 2+ and Cl ...
1. (a) Write the electronic structure of a manganese atom and a Mn
... The addition of excess aqueous silver nitrate to aqueous solutions of either of these two salts produces a precipitate of silver chloride, AgCl. ...
... The addition of excess aqueous silver nitrate to aqueous solutions of either of these two salts produces a precipitate of silver chloride, AgCl. ...
Redox
... The half-equation shows either the oxidation or the reduction step of a redox change. In a half-equation: ...
... The half-equation shows either the oxidation or the reduction step of a redox change. In a half-equation: ...
Heat transfer mechanisms of laminar flames of hydrogen+ oxygen
... to an initially relatively cold plate is studied analytically and numerically. For the case of very small distances to the solid surface, the situation can be regarded effectively as one-dimensional. Fig. 1 presents the one-dimensional (1D) computational setup. By fixing the gas composition, tempera ...
... to an initially relatively cold plate is studied analytically and numerically. For the case of very small distances to the solid surface, the situation can be regarded effectively as one-dimensional. Fig. 1 presents the one-dimensional (1D) computational setup. By fixing the gas composition, tempera ...
1 - A-Level Chemistry
... can only score M2 if d10 in M1 correct allow ‘full d orbital’ if d10 in M1 do not allow d block ...
... can only score M2 if d10 in M1 correct allow ‘full d orbital’ if d10 in M1 do not allow d block ...
Aqueous Reactions
... equations, which show the compounds as individual ions. Until now, you have been writing chemical equations in this form: Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) + 2KI(aq) Æ PbI 2 (s) + 2KNO 3 (aq) Equations written this way are known as molecular equations. They have a variation known as a complete ionic equation, in whi ...
... equations, which show the compounds as individual ions. Until now, you have been writing chemical equations in this form: Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) + 2KI(aq) Æ PbI 2 (s) + 2KNO 3 (aq) Equations written this way are known as molecular equations. They have a variation known as a complete ionic equation, in whi ...
States of Matter
... means that the neighboring molecules must be at least as far away as the sum of the two radii, and this in turn affects the possible locations of more distant concentric shells of molecules. An important consequence of the disordered arrangement of molecules in a liquid is the presence of void spaces ...
... means that the neighboring molecules must be at least as far away as the sum of the two radii, and this in turn affects the possible locations of more distant concentric shells of molecules. An important consequence of the disordered arrangement of molecules in a liquid is the presence of void spaces ...
CHEM 30 REDOX
... of unreacted mixture in the photocell system, which produces an electric current that causes the needle in the meter to move from its resting place. The operator then rotates a knob to bring the needle back to the resting place and reads the level of alcohol from the knob -- the more the operator mu ...
... of unreacted mixture in the photocell system, which produces an electric current that causes the needle in the meter to move from its resting place. The operator then rotates a knob to bring the needle back to the resting place and reads the level of alcohol from the knob -- the more the operator mu ...
Physical Vapor Deposition
... – {a,b} are van der Waals parameters. – For large volumes and small particle numbers, van der Waals equation of state is approximated by the ideal gas law: P = NRT/V. P isotherms T4 T3 T2 T1 ...
... – {a,b} are van der Waals parameters. – For large volumes and small particle numbers, van der Waals equation of state is approximated by the ideal gas law: P = NRT/V. P isotherms T4 T3 T2 T1 ...
STOICHIOMETRY REVIEW WORKSHEET
... Part 1: Mole ←→ Mass Conversions Convert the following number of moles of chemical into its corresponding mass in grams. 1. 0.436 moles of ammonium chloride 2. 2.360 moles of lead (II) oxide 3. 0.031 moles of aluminum iodide 4. 1.077 moles of magnesium phosphate 5. 0.50 moles of calcium nitrate Conv ...
... Part 1: Mole ←→ Mass Conversions Convert the following number of moles of chemical into its corresponding mass in grams. 1. 0.436 moles of ammonium chloride 2. 2.360 moles of lead (II) oxide 3. 0.031 moles of aluminum iodide 4. 1.077 moles of magnesium phosphate 5. 0.50 moles of calcium nitrate Conv ...
Unit 5 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
PIB - Unit 6 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
C - Thierry Karsenti
... Practical experiments will be given to evaluate your understanding of theory-practice relations Simulated experiments/exercise will give to test your understanding of certain concepts Learning activities ...
... Practical experiments will be given to evaluate your understanding of theory-practice relations Simulated experiments/exercise will give to test your understanding of certain concepts Learning activities ...
Vacuum Evaporation
... Since the vapor pressure at the new temperature is much higher, they will not reevaporate and adhere to the substrate. The deposition thickness is a function of the evaporation rate, the geometry of the source and the substrate and the time of evaporation. ...
... Since the vapor pressure at the new temperature is much higher, they will not reevaporate and adhere to the substrate. The deposition thickness is a function of the evaporation rate, the geometry of the source and the substrate and the time of evaporation. ...
Dynamics of molecule-surface interactions from first
... dissipation channels such as radiation. However, reactions at surfaces differ from gas-phase reactions insofar as the whole substrate can serve as an efficient energy sink. There are two main channels for energy dissipation, namely phonon and electron-hole pair excitations. In fact, the theorectical ...
... dissipation channels such as radiation. However, reactions at surfaces differ from gas-phase reactions insofar as the whole substrate can serve as an efficient energy sink. There are two main channels for energy dissipation, namely phonon and electron-hole pair excitations. In fact, the theorectical ...
WELCOME TO CLASS XII ORIENTATION IN CHEMISTRY SOME
... zinc. On the other hand zinc being a strong reducing agent, can‘t be extracted by this method . Zinc has less tendency to form soluble complexes . Q Name the common elements present in anode mud in the electrolytic refining of copper. Why are they so present ? Ans The anode mud contains Ag, Au, ...
... zinc. On the other hand zinc being a strong reducing agent, can‘t be extracted by this method . Zinc has less tendency to form soluble complexes . Q Name the common elements present in anode mud in the electrolytic refining of copper. Why are they so present ? Ans The anode mud contains Ag, Au, ...
1 3. Molecular mass transport 3.1 Introduction to mass transfer 3.2
... Mass transfer always involves mixtures. Consequently, we must account for the variation of physical properties which normally exist in a given system. When a system contains three or more components, as many industrial fluid streams do, the problem becomes unwidely very quickly. The conventional eng ...
... Mass transfer always involves mixtures. Consequently, we must account for the variation of physical properties which normally exist in a given system. When a system contains three or more components, as many industrial fluid streams do, the problem becomes unwidely very quickly. The conventional eng ...
Density, Viscosity, Solubility, and Diffusivity of N2O in Aqueous
... using a commercial density meter (DMA 58, Anton Paar GmbH), and the viscosity using a Haake microviscometer (Haake MessTechnik GmbH). In both cases, the measurement temperature could be controlled within (0.05 K. Solubility. The solubility was measured in a thermostatic stirred vessel, provided with ...
... using a commercial density meter (DMA 58, Anton Paar GmbH), and the viscosity using a Haake microviscometer (Haake MessTechnik GmbH). In both cases, the measurement temperature could be controlled within (0.05 K. Solubility. The solubility was measured in a thermostatic stirred vessel, provided with ...
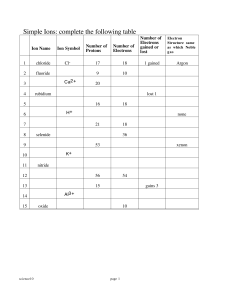
workbook Chem (WP)
... 1. consist of a metal and a nonmetal (cation and an anion) 2. charges must balance in the final formula to form a neutral compound 3. List the characteristics of an ionic compound. 4. Write the formula for the following: a. lithium chloride b. magnesium fluoride c. scandium sulfide d. calcium nitrid ...
... 1. consist of a metal and a nonmetal (cation and an anion) 2. charges must balance in the final formula to form a neutral compound 3. List the characteristics of an ionic compound. 4. Write the formula for the following: a. lithium chloride b. magnesium fluoride c. scandium sulfide d. calcium nitrid ...
ChBE 11: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
... The state is the condition in which we find a system at any given time and is defined by its intensive properties – A process brings the system from one state to another ...
... The state is the condition in which we find a system at any given time and is defined by its intensive properties – A process brings the system from one state to another ...
Double layer forces

Double layer forces occur between charged objects across liquids, typically water. This force acts over distances that are comparable to the Debye length, which is on the order of one to a few tenths of nanometers. The strength of these forces increases with the magnitude of the surface charge density (or the electrical surface potential). For two similarly charged objects, this force is repulsive and decays exponentially at larger distances, see figure. For unequally charged objects and eventually at shorted distances, these forces may also be attractive. The theory due to Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DLVO) combines such double layer forces together with Van der Waals forces in order to estimate the actual interaction potential between colloidal particles.An electrical double layer develops near charged surfaces (or another charged objects) in aqueous solutions. Within this double layer, the first layer corresponds to the charged surface. These charges may originate from tightly adsorbed ions, dissociated surface groups, or substituted ions within the crystal lattice. The second layer corresponds to the diffuse layer, which contains the neutralizing charge consisting of accumulated counterions and depleted coions. The resulting potential profile between these two objects leads to differences in the ionic concentrations within the gap between these objects with respect to the bulk solution. These differences generate an osmotic pressure, which generates a force between these objects.These forces are easily experienced when hands are washed with soap. Adsorbing soap molecules make the skin negatively charged, and the slippery feeling is caused by the strongly repulsive double layer forces. These forces are further relevant in many colloidal or biological systems, and may be responsible for their stability, formation of colloidal crystals, or their rheological properties.