Maths for Chemistry Facts and Formulae
... state variables, F , chosen from amongst temperature, pressure and species compositions in each phase, which must be specified to fix the thermodynamic state of a system in equilibrium. Clapeyron equation relates change in pressure to change in temperature at a phase boundary. The slope of the phase ...
... state variables, F , chosen from amongst temperature, pressure and species compositions in each phase, which must be specified to fix the thermodynamic state of a system in equilibrium. Clapeyron equation relates change in pressure to change in temperature at a phase boundary. The slope of the phase ...
Jon Abbatt - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Physics
... not: Growth factor = [Size at high RH]/[Size at low RH] Solution droplets tend to promote cloud droplet formation more easily than do pure solids. Heterogeneous chemistry tends to go faster on solutions than on solids, although ice is an exception. ...
... not: Growth factor = [Size at high RH]/[Size at low RH] Solution droplets tend to promote cloud droplet formation more easily than do pure solids. Heterogeneous chemistry tends to go faster on solutions than on solids, although ice is an exception. ...
Types of Reactions
... reaction, of known stoichiometry, with another substance whose concentration is known (standard solution). Example: Suppose we know the molarity of an NaOH solution and we want to find the molarity of an HCl solution. • What do we know? • molarity of NaOH, volume of HCl • What do we want? • molarity ...
... reaction, of known stoichiometry, with another substance whose concentration is known (standard solution). Example: Suppose we know the molarity of an NaOH solution and we want to find the molarity of an HCl solution. • What do we know? • molarity of NaOH, volume of HCl • What do we want? • molarity ...
pH scale. Buffer solutions. Colligative properties of solutions
... solute, R − universal gas constant. If two solutions are of equal concentration and, hence, of the same osmotic pressure, they are said to be isotonic. If two solutions are of unequal osmotic pressures, the more concentrated solution is said to be hypertonic and the more dilute solution is described ...
... solute, R − universal gas constant. If two solutions are of equal concentration and, hence, of the same osmotic pressure, they are said to be isotonic. If two solutions are of unequal osmotic pressures, the more concentrated solution is said to be hypertonic and the more dilute solution is described ...
Strumenti tutor LIM
... A chemical transformation takes place when....................(atoms in the reactants are rearranged to form new substabces)(old bonds are broken and new bonds are formed)( at least one new substance is formed) We can realize that a chemical reaction is taking place when...........( there is a chang ...
... A chemical transformation takes place when....................(atoms in the reactants are rearranged to form new substabces)(old bonds are broken and new bonds are formed)( at least one new substance is formed) We can realize that a chemical reaction is taking place when...........( there is a chang ...
Adsorption and desorption
... Inserting and resolving for Θr yields the equations for isotherms/isobars: ...
... Inserting and resolving for Θr yields the equations for isotherms/isobars: ...
ch6 - ChemistryVCE
... c They do not conduct electricity in the solid state but will conduct when molten or dissolved in water. A21. The information in Table 6.1 (page 94) is an excellent summary. a The electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive and negative ions are strong and will be overcome only at high t ...
... c They do not conduct electricity in the solid state but will conduct when molten or dissolved in water. A21. The information in Table 6.1 (page 94) is an excellent summary. a The electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive and negative ions are strong and will be overcome only at high t ...
Chapter 7 lecture notes: Solutions
... Pure water does not conduct an electric current. When an _______________compound is dissolved in water, the solution conducts electricity. ...
... Pure water does not conduct an electric current. When an _______________compound is dissolved in water, the solution conducts electricity. ...
Unit 6 Study Guide - Dorman High School
... Given the reaction A(g) + B(g) C(g) + D(g). You have the gases A, B, C, and D at equilibrium. Upon adding gas A, the value of K A) increases because when A is added, more products are made, increasing the product-to-reactant ratio B) decreases because A is a reactant, so the product-toreactant ratio ...
... Given the reaction A(g) + B(g) C(g) + D(g). You have the gases A, B, C, and D at equilibrium. Upon adding gas A, the value of K A) increases because when A is added, more products are made, increasing the product-to-reactant ratio B) decreases because A is a reactant, so the product-toreactant ratio ...
Water: The Universal Solvent
... to sulfate ion. The manganese product depends upon the pH of the reaction mixture. The mole ratio of oxidizing to reducing agent is two to five at pH 1 (acidic), and is two to one at pH 13 (basic). For each of these cases, write a balanced equation for the reaction, and indicate the oxidation state ...
... to sulfate ion. The manganese product depends upon the pH of the reaction mixture. The mole ratio of oxidizing to reducing agent is two to five at pH 1 (acidic), and is two to one at pH 13 (basic). For each of these cases, write a balanced equation for the reaction, and indicate the oxidation state ...
9.5. Combined Methods: Electrochemical
... determination of dopamine (DA) in the presence of ascorbic acid (AA) (47, 48), which is important for patients with Parkinson’s disease and the determination of uric acid (UA) in the presence of AA (53). Unfortunately, the determination of DA in the presence of AA at oxidized diamond can only be car ...
... determination of dopamine (DA) in the presence of ascorbic acid (AA) (47, 48), which is important for patients with Parkinson’s disease and the determination of uric acid (UA) in the presence of AA (53). Unfortunately, the determination of DA in the presence of AA at oxidized diamond can only be car ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... c. XeF2 is nonpolar. Both Xe–F bond dipoles are the same size, but due to the linear geometry they offset each other. XeF4 is nonpolar. All Xe–F bond dipoles are the same size, but due to the square planar geometry they offset each other. XeO3 is polar. The Xe–O bond dipoles are the same size, and t ...
... c. XeF2 is nonpolar. Both Xe–F bond dipoles are the same size, but due to the linear geometry they offset each other. XeF4 is nonpolar. All Xe–F bond dipoles are the same size, but due to the square planar geometry they offset each other. XeO3 is polar. The Xe–O bond dipoles are the same size, and t ...
PS_CHEM7_ch4 - WordPress.com
... expected to be soluble in water, and the solubility rules confirm this. • b) Glycine (H2NCH2COOH) is a covalent compound, but it contains polar N–H and O–H bonds. This would make the molecule interact well with polar water molecules, and make it likely that it would be soluble. c) Pentane (C5H12) ha ...
... expected to be soluble in water, and the solubility rules confirm this. • b) Glycine (H2NCH2COOH) is a covalent compound, but it contains polar N–H and O–H bonds. This would make the molecule interact well with polar water molecules, and make it likely that it would be soluble. c) Pentane (C5H12) ha ...
Oxidation numbers
... Sodium chloride exhibits properties quite distinct and different from sodium and chlorine. The changes in physical as well as chemical properties are due to the formation of cations and anions via the oxidation-reduction process, and the resultant, powerful attractive force that develops between the ...
... Sodium chloride exhibits properties quite distinct and different from sodium and chlorine. The changes in physical as well as chemical properties are due to the formation of cations and anions via the oxidation-reduction process, and the resultant, powerful attractive force that develops between the ...
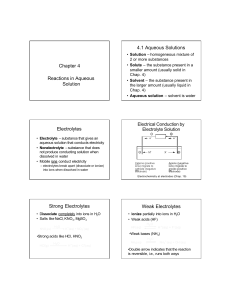
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution 4.1 Aqueous Solutions
... • Reversible reaction - can occur in both directions • Reactants form products as soon as reaction begins • Once products are formed, they in turn react to re-form reactants • Chemical Equilibrium - when reactants form products as fast as products form reactants, no further net change in concentrati ...
... • Reversible reaction - can occur in both directions • Reactants form products as soon as reaction begins • Once products are formed, they in turn react to re-form reactants • Chemical Equilibrium - when reactants form products as fast as products form reactants, no further net change in concentrati ...
5548-4.pdf
... The assumption that the diffusion coefficient is independent of composition will introduce significant error in the concentration profiles of coatings produced in a low activity pack. In this case, only the NiAl phase is formed, in which the interdiffusion coefficient varies by approximately three o ...
... The assumption that the diffusion coefficient is independent of composition will introduce significant error in the concentration profiles of coatings produced in a low activity pack. In this case, only the NiAl phase is formed, in which the interdiffusion coefficient varies by approximately three o ...
MEMS Processing
... - Amorphous/columnar grained structures: Compressive stress - Equiaxed grained structures: Tensile stress - Thick films have less stress than thinner films -ANNEALING CAN REDUCE STRESSES BY A FACTOR OF 10-100 ...
... - Amorphous/columnar grained structures: Compressive stress - Equiaxed grained structures: Tensile stress - Thick films have less stress than thinner films -ANNEALING CAN REDUCE STRESSES BY A FACTOR OF 10-100 ...
GCE Chemistry Question Paper Unit 05 - Energetics, Redox
... outside the box around each page or on blank pages. l All working must be shown. l Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work you do not want to be marked. ...
... outside the box around each page or on blank pages. l All working must be shown. l Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work you do not want to be marked. ...
Chemistry Name Mr. Reger Review Guide – Ch. 9
... 10. Using the reaction below, how many grams of NaCl can be produced from 10.9 g NaOH? 3 Cl2(g) + 6 NaOH(aq) 5 NaCl(aq) + NaClO3(aq) + 3 H2O(l) 11. Use the equation in the question above to answer the following: a) What is the theoretical yield of NaClO3 if 4.0mol Cl2 is reacted with excess NaOH? ...
... 10. Using the reaction below, how many grams of NaCl can be produced from 10.9 g NaOH? 3 Cl2(g) + 6 NaOH(aq) 5 NaCl(aq) + NaClO3(aq) + 3 H2O(l) 11. Use the equation in the question above to answer the following: a) What is the theoretical yield of NaClO3 if 4.0mol Cl2 is reacted with excess NaOH? ...
PPT: Chemical Reactions Review
... “Yields”; indicates result of reaction Used to indicate a reversible reaction (equilibrium) ...
... “Yields”; indicates result of reaction Used to indicate a reversible reaction (equilibrium) ...
Practice problems
... Using the standard reduction potentials listed in Appendix E, determine which of the following reactions are spontaneous under standard conditions: ...
... Using the standard reduction potentials listed in Appendix E, determine which of the following reactions are spontaneous under standard conditions: ...
Photocatalysis on TiOn Surfaces: Principles, Mechanisms, and
... exchange require orbital overlap between the interacting centers. When both processes are thermodynamically allowed, electron transfer predominates since the electron exchange process requires simultaneous overlap of two orbital pairs, whereas only one such overlap is necessary for electron t r a n ...
... exchange require orbital overlap between the interacting centers. When both processes are thermodynamically allowed, electron transfer predominates since the electron exchange process requires simultaneous overlap of two orbital pairs, whereas only one such overlap is necessary for electron t r a n ...
Document
... equation. Remember that one of the reactants, Mg(OH)2, is a solid. Identify any strong electrolytes and rewrite the equation showing strong electrolytes as ions. Identify and cancel the spectator ions. Solution Mg(OH)2(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2H2O(l) + MgCl2(aq) Think About It Make sure your equation is bal ...
... equation. Remember that one of the reactants, Mg(OH)2, is a solid. Identify any strong electrolytes and rewrite the equation showing strong electrolytes as ions. Identify and cancel the spectator ions. Solution Mg(OH)2(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2H2O(l) + MgCl2(aq) Think About It Make sure your equation is bal ...
Experimental determination of hydromagnesite precipitation rates
... Hydromagnesite precipitation rates were measured in closed-system reactors at far to near to equilibrium conditions in NaHCO3/Na2CO3 bearing aqueous solutions at pH from 8.5 to 11 and temperatures from 22.5 to 75 °C. Resulting rates (r) were fit following the method described by Harouiya et al. [1] ...
... Hydromagnesite precipitation rates were measured in closed-system reactors at far to near to equilibrium conditions in NaHCO3/Na2CO3 bearing aqueous solutions at pH from 8.5 to 11 and temperatures from 22.5 to 75 °C. Resulting rates (r) were fit following the method described by Harouiya et al. [1] ...
Double layer forces

Double layer forces occur between charged objects across liquids, typically water. This force acts over distances that are comparable to the Debye length, which is on the order of one to a few tenths of nanometers. The strength of these forces increases with the magnitude of the surface charge density (or the electrical surface potential). For two similarly charged objects, this force is repulsive and decays exponentially at larger distances, see figure. For unequally charged objects and eventually at shorted distances, these forces may also be attractive. The theory due to Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DLVO) combines such double layer forces together with Van der Waals forces in order to estimate the actual interaction potential between colloidal particles.An electrical double layer develops near charged surfaces (or another charged objects) in aqueous solutions. Within this double layer, the first layer corresponds to the charged surface. These charges may originate from tightly adsorbed ions, dissociated surface groups, or substituted ions within the crystal lattice. The second layer corresponds to the diffuse layer, which contains the neutralizing charge consisting of accumulated counterions and depleted coions. The resulting potential profile between these two objects leads to differences in the ionic concentrations within the gap between these objects with respect to the bulk solution. These differences generate an osmotic pressure, which generates a force between these objects.These forces are easily experienced when hands are washed with soap. Adsorbing soap molecules make the skin negatively charged, and the slippery feeling is caused by the strongly repulsive double layer forces. These forces are further relevant in many colloidal or biological systems, and may be responsible for their stability, formation of colloidal crystals, or their rheological properties.