chemical reaction
... Chemical reactions are described by chemical equations. A chemical equation represents, with symbols and formulas, the identities and relative molecular or molar amounts of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. For example, the following chemical equation shows that the reactant ammoni ...
... Chemical reactions are described by chemical equations. A chemical equation represents, with symbols and formulas, the identities and relative molecular or molar amounts of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. For example, the following chemical equation shows that the reactant ammoni ...
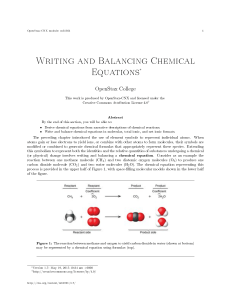
Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
... 1. The substances undergoing reaction are called reactants, and their formulas are placed on the left side of the equation. 2. The substances generated by the reaction are called products, and their formulas are placed on the right sight of the equation. 3. Plus signs (+) separate individual reactan ...
... 1. The substances undergoing reaction are called reactants, and their formulas are placed on the left side of the equation. 2. The substances generated by the reaction are called products, and their formulas are placed on the right sight of the equation. 3. Plus signs (+) separate individual reactan ...
How to Balance Chemical Equations
... Since the hydrogen atoms come in pairs we need ____ pairs to make 4. ...
... Since the hydrogen atoms come in pairs we need ____ pairs to make 4. ...
Document
... 1. Predict the products of the double-replacement reaction and indicate the solubility of both of the products by placing the symbol "(aq)" after the soluble product and the symbol "(s)" after the insoluble product. Use the “Solubility Rules” handout (at end of notes) to determine the solubility. I ...
... 1. Predict the products of the double-replacement reaction and indicate the solubility of both of the products by placing the symbol "(aq)" after the soluble product and the symbol "(s)" after the insoluble product. Use the “Solubility Rules” handout (at end of notes) to determine the solubility. I ...
GatorHyde CG Technical Data Sheet
... APPLICATION EQUIPMENT: GatorHyde CG must be applied utilizing a high pressure, plural component pump (1:1 by Volume) such as the Graco Reactor E-10, E-XP1, E-XP2 or Graco HXP2. When ready to spray this material, the proportioning unit must be capable of supplying the correct pressure and heat which ...
... APPLICATION EQUIPMENT: GatorHyde CG must be applied utilizing a high pressure, plural component pump (1:1 by Volume) such as the Graco Reactor E-10, E-XP1, E-XP2 or Graco HXP2. When ready to spray this material, the proportioning unit must be capable of supplying the correct pressure and heat which ...
Chapter 4: Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... weighs out a known mass (and, therefore, number of moles) of the solute. The solute is added to a volumetric flask, and solvent is added to the line on the neck of the flask. ...
... weighs out a known mass (and, therefore, number of moles) of the solute. The solute is added to a volumetric flask, and solvent is added to the line on the neck of the flask. ...
atomic number
... - tiny, hard, unbreakable, spheres. (we will see that atoms can be broken up) All atoms of an element are identical - atoms of different elements are different - every carbon atom is identical to every other carbon atom because they have the same chemical and physical properties - but carbon atoms a ...
... - tiny, hard, unbreakable, spheres. (we will see that atoms can be broken up) All atoms of an element are identical - atoms of different elements are different - every carbon atom is identical to every other carbon atom because they have the same chemical and physical properties - but carbon atoms a ...
Name: Per: Date: Unit 1. Materials: Formulating Matter B. Periodic
... 38. Fill in the data table for each ionic compound described below. Number one is filled in as an example. Use the two tables of common ions below. a. Potassium chloride is “lite salt”, used by many people with hypertension. b. CaSO4 is a component of plaster. c. A substance composed of Ca2+ and PO ...
... 38. Fill in the data table for each ionic compound described below. Number one is filled in as an example. Use the two tables of common ions below. a. Potassium chloride is “lite salt”, used by many people with hypertension. b. CaSO4 is a component of plaster. c. A substance composed of Ca2+ and PO ...
Downloaded on 2017-02
... reactivity on and off at the level of single atomic layers. ALD shows great promise in achieving monolayer-by-monolayer materials growth 4 and is already used commercially to fabricate layers of high-permittivity dielectric just a few nanometres thick in nanoelectronic transistors and memory devices ...
... reactivity on and off at the level of single atomic layers. ALD shows great promise in achieving monolayer-by-monolayer materials growth 4 and is already used commercially to fabricate layers of high-permittivity dielectric just a few nanometres thick in nanoelectronic transistors and memory devices ...
Ch. 9
... – F-(fluoride), Cl-(chloride), O2-(oxide), S2-(sulfide), N3(nitride), P3-(phosphide), As3- (arsenide) ...
... – F-(fluoride), Cl-(chloride), O2-(oxide), S2-(sulfide), N3(nitride), P3-(phosphide), As3- (arsenide) ...
Document
... together as one ion. • When molecular compounds dissolve in water, the only ones that can form ions in solution are acids and bases. The rest will just dissolve as the complete molecule (if that molecule is soluble in water) ...
... together as one ion. • When molecular compounds dissolve in water, the only ones that can form ions in solution are acids and bases. The rest will just dissolve as the complete molecule (if that molecule is soluble in water) ...
Bulk and Surface Micromachining
... for the Miller Indices <110>:<100>:<111>, planar selectivity can be as high as 600:400:1. However, KOH is not used in micromachining because its potassium ion content bans it from clean room operations. Also, it is highly corrosive and attacks aluminum, which makes it undesirable for CMOS fabricatio ...
... for the Miller Indices <110>:<100>:<111>, planar selectivity can be as high as 600:400:1. However, KOH is not used in micromachining because its potassium ion content bans it from clean room operations. Also, it is highly corrosive and attacks aluminum, which makes it undesirable for CMOS fabricatio ...
E - Analytical Chemistry
... The difference in electric potential, E, between two points, is the work needed (or that can be done) when moving an electric charge from one point to the other. Potential difference is measured in volts (V = J/C). The greater the potential difference, the stronger will be the "push" on a charged pa ...
... The difference in electric potential, E, between two points, is the work needed (or that can be done) when moving an electric charge from one point to the other. Potential difference is measured in volts (V = J/C). The greater the potential difference, the stronger will be the "push" on a charged pa ...
Wizard Test Maker
... 36. If the apparatus illustrated in the diagram below is used in a conductivity test. Substances are placed into the glass to see if the bulb will light up. Which material would be the best conductor of an electric current? ...
... 36. If the apparatus illustrated in the diagram below is used in a conductivity test. Substances are placed into the glass to see if the bulb will light up. Which material would be the best conductor of an electric current? ...
Extended hydrodynamics from Enskog`s equation for a two
... functional of the density, temperature and heat flow. We find that, in fact, it is correct provided the system is not too far from equilibrium. This is consistent with the range predicted in Ref. [29] for this nontrivial pressure difference to appear. Note that one of the useful merits of Grad’s mom ...
... functional of the density, temperature and heat flow. We find that, in fact, it is correct provided the system is not too far from equilibrium. This is consistent with the range predicted in Ref. [29] for this nontrivial pressure difference to appear. Note that one of the useful merits of Grad’s mom ...
Chemical Equations & Reactions
... Balancing Chemical Equations An important point to remember 2 NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g) The 2 to the left of NO(g) and NO2(g) refers to the number of molecules present in the balanced equation. ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations An important point to remember 2 NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g) The 2 to the left of NO(g) and NO2(g) refers to the number of molecules present in the balanced equation. ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide (dissolved in the water). Include symbols for physical states in the formula equation. Then balance the formula equation to give a balanced chemical equation. ...
... sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide (dissolved in the water). Include symbols for physical states in the formula equation. Then balance the formula equation to give a balanced chemical equation. ...
Formation of amorphous silica surface layers by
... remains open, such that the weathering kinetics of the parent mineral are not affected. However, this may not hold true for weathering-carbonation reactions at low water:mineral ratios. Current studies in our laboratory [6] and elsewhere show that the porous structure of the silica layers can become ...
... remains open, such that the weathering kinetics of the parent mineral are not affected. However, this may not hold true for weathering-carbonation reactions at low water:mineral ratios. Current studies in our laboratory [6] and elsewhere show that the porous structure of the silica layers can become ...
Chapter 4 Packet
... Q1and Q2 = magnitude of the charges on the particles d is the distance between their centers k is constant determined by the units for Q and d ...
... Q1and Q2 = magnitude of the charges on the particles d is the distance between their centers k is constant determined by the units for Q and d ...
Chemistry 5350 Advanced Physical Chemistry Fall Semester 2013
... well. The well depth is a fraction of the total energy, and the molecule is unaffected by the attractive part of the potential. 2. Explain why attractive interactions between molecules in a gas make the pressure less than predicted by the ideal gas equation. The ideal gas equation assumes that the m ...
... well. The well depth is a fraction of the total energy, and the molecule is unaffected by the attractive part of the potential. 2. Explain why attractive interactions between molecules in a gas make the pressure less than predicted by the ideal gas equation. The ideal gas equation assumes that the m ...
Oxygen Reduction Reaction with the Rotating Ring Disk Electrode
... of the disk is swept. This is because the disk and the ring are in close proximity of each other (there is a separation of 375 μm between the disk and ring). Thus, the chemical environment at the disk influences the ring. As oxygen is reduced at the disk, reaction products, such as H2O2, diffuse fro ...
... of the disk is swept. This is because the disk and the ring are in close proximity of each other (there is a separation of 375 μm between the disk and ring). Thus, the chemical environment at the disk influences the ring. As oxygen is reduced at the disk, reaction products, such as H2O2, diffuse fro ...
chapter 6: chemical reactions: an introduction
... The changes which happen during a chemical reaction are shown by writing a chemical equation. The starting materials are called reactants and are shown on the left side of the chemical equation. The substances formed in a reaction are called products and are shown on the right side of the equation. ...
... The changes which happen during a chemical reaction are shown by writing a chemical equation. The starting materials are called reactants and are shown on the left side of the chemical equation. The substances formed in a reaction are called products and are shown on the right side of the equation. ...
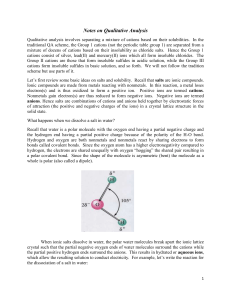
Notes on QA - Scarsdale Public Schools
... Qualitative analysis involves separating a mixture of cations based on their solubilities. In the traditional QA scheme, the Group 1 cations (not the periodic table group 1) are separated from a mixture of dozens of cations based on their insolubility as chloride salts. Hence the Group 1 cations con ...
... Qualitative analysis involves separating a mixture of cations based on their solubilities. In the traditional QA scheme, the Group 1 cations (not the periodic table group 1) are separated from a mixture of dozens of cations based on their insolubility as chloride salts. Hence the Group 1 cations con ...
Double layer forces

Double layer forces occur between charged objects across liquids, typically water. This force acts over distances that are comparable to the Debye length, which is on the order of one to a few tenths of nanometers. The strength of these forces increases with the magnitude of the surface charge density (or the electrical surface potential). For two similarly charged objects, this force is repulsive and decays exponentially at larger distances, see figure. For unequally charged objects and eventually at shorted distances, these forces may also be attractive. The theory due to Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DLVO) combines such double layer forces together with Van der Waals forces in order to estimate the actual interaction potential between colloidal particles.An electrical double layer develops near charged surfaces (or another charged objects) in aqueous solutions. Within this double layer, the first layer corresponds to the charged surface. These charges may originate from tightly adsorbed ions, dissociated surface groups, or substituted ions within the crystal lattice. The second layer corresponds to the diffuse layer, which contains the neutralizing charge consisting of accumulated counterions and depleted coions. The resulting potential profile between these two objects leads to differences in the ionic concentrations within the gap between these objects with respect to the bulk solution. These differences generate an osmotic pressure, which generates a force between these objects.These forces are easily experienced when hands are washed with soap. Adsorbing soap molecules make the skin negatively charged, and the slippery feeling is caused by the strongly repulsive double layer forces. These forces are further relevant in many colloidal or biological systems, and may be responsible for their stability, formation of colloidal crystals, or their rheological properties.