Chapter 4 Student Notes
... Elements have an oxidation number of 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the same as its charge. Oxygen has an oxidation number of 2- (except peroxides, O22-) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of 1+ (except hydrides, H1-) The sum of the oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is 0. The sum ...
... Elements have an oxidation number of 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the same as its charge. Oxygen has an oxidation number of 2- (except peroxides, O22-) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of 1+ (except hydrides, H1-) The sum of the oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is 0. The sum ...
CHEM 150
... 7. For the reaction 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O which of the following can be answered only using the coefficients of the balanced equation? a. What weight of water is produced when 2.5 grams of hydrogen react completely? b. What weight of water is produced when 2.5 moles of hydrogen react completely? c. How ma ...
... 7. For the reaction 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O which of the following can be answered only using the coefficients of the balanced equation? a. What weight of water is produced when 2.5 grams of hydrogen react completely? b. What weight of water is produced when 2.5 moles of hydrogen react completely? c. How ma ...
Complete ionic equation
... Rules for Balancing Reactions • For each element, the number of atoms on the reactant side must equal the number of atoms on the product side. • The subscripts cannot change. Only ...
... Rules for Balancing Reactions • For each element, the number of atoms on the reactant side must equal the number of atoms on the product side. • The subscripts cannot change. Only ...
ZOONO TECHNICAL OVERVIEW
... of chemical reactions including trans-esterification, acetylation, halogenation, condensation and hydrolysis to name but a few. The most important of these reactions are hydrolysis (which is used to prepare Zoono) and condensation, (which is required for Zoono to bond to surfaces and form polymeric ...
... of chemical reactions including trans-esterification, acetylation, halogenation, condensation and hydrolysis to name but a few. The most important of these reactions are hydrolysis (which is used to prepare Zoono) and condensation, (which is required for Zoono to bond to surfaces and form polymeric ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions can be classified into one of four categories depending on what type and how many reactants are present. We can use a generalized equation to represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose el ...
... Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions can be classified into one of four categories depending on what type and how many reactants are present. We can use a generalized equation to represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose el ...
m/z
... • Not Tandem MS, but useful fragmentation technique: Post-source decay (PSD) combined with MALDI ...
... • Not Tandem MS, but useful fragmentation technique: Post-source decay (PSD) combined with MALDI ...
File
... A reversible reaction. The reaction can occur in both directions. Acetic acid is a weak electrolyte because its ionization in water is incomplete. ...
... A reversible reaction. The reaction can occur in both directions. Acetic acid is a weak electrolyte because its ionization in water is incomplete. ...
Lecture 12
... 2. Photosynthesis is endothermic. This means it requires energy from an outside source. In this case the energy source is the sun. Essentially plants convert the photo energy from the sun into high energy C - C bonds. This conversion happens in the plants photosystems. Respiration is exothermic. Thi ...
... 2. Photosynthesis is endothermic. This means it requires energy from an outside source. In this case the energy source is the sun. Essentially plants convert the photo energy from the sun into high energy C - C bonds. This conversion happens in the plants photosystems. Respiration is exothermic. Thi ...
Balancing Chemical Equations Academic Success Center Science Tutoring Area *
... charges within a molecule not to balance the number of atoms on each side of an equation 3.Balance the number of atoms on each side of the equation by changing the coefficient in front of the different reactants and products ...
... charges within a molecule not to balance the number of atoms on each side of an equation 3.Balance the number of atoms on each side of the equation by changing the coefficient in front of the different reactants and products ...
ic199p5a
... to being the same size (as r+/r- -> 1) and the ZnS structure when the ions are most different in size. This rule, along with the fact that the sizes increase with incr. negative charge and decrease with incr. positive charge, along with the general dependance of atom sizes on their position in the p ...
... to being the same size (as r+/r- -> 1) and the ZnS structure when the ions are most different in size. This rule, along with the fact that the sizes increase with incr. negative charge and decrease with incr. positive charge, along with the general dependance of atom sizes on their position in the p ...
Chemical Equations
... compare for each element. If any of these numbers do not match, the equation is not balanced and you will need proceed to the following steps 3. Balance by placing coefficients in front of the formulae. Do not change the actual formula. If the substance is present as an element, leave the balancing ...
... compare for each element. If any of these numbers do not match, the equation is not balanced and you will need proceed to the following steps 3. Balance by placing coefficients in front of the formulae. Do not change the actual formula. If the substance is present as an element, leave the balancing ...
Dry Friction
... will be used. F is tangent to the surface and opposite to P N is found from the distribution of Nn and is upward to balance W N acts at a distance X right to W line of action X is necessary for the tipping effect Take moment about O WX = Ph X = Ph / W The block will be on the verge of tipping if ...
... will be used. F is tangent to the surface and opposite to P N is found from the distribution of Nn and is upward to balance W N acts at a distance X right to W line of action X is necessary for the tipping effect Take moment about O WX = Ph X = Ph / W The block will be on the verge of tipping if ...
transcript - American Chemical Society
... Today, law enforcement officials say that the Amerithrax incident, as the FBI named it, was actually perpetrated by a misguided government research scientist. He may have been trying to call attention to our vulnerability to such attacks. Whether that was really his intention will never be known. Th ...
... Today, law enforcement officials say that the Amerithrax incident, as the FBI named it, was actually perpetrated by a misguided government research scientist. He may have been trying to call attention to our vulnerability to such attacks. Whether that was really his intention will never be known. Th ...
Ch06 BalancingChemRxns
... Solid aluminum metal reacts with oxygen gas to produce solid aluminum oxide. 1. Write the formulas of the reactants and products. ...
... Solid aluminum metal reacts with oxygen gas to produce solid aluminum oxide. 1. Write the formulas of the reactants and products. ...
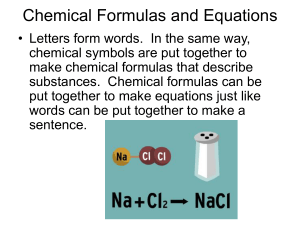
Chemical Formulas and Equations
... Chemical Formulas and Equations • Letters form words. In the same way, chemical symbols are put together to make chemical formulas that describe substances. Chemical formulas can be put together to make equations just like words can be put together to make a sentence. ...
... Chemical Formulas and Equations • Letters form words. In the same way, chemical symbols are put together to make chemical formulas that describe substances. Chemical formulas can be put together to make equations just like words can be put together to make a sentence. ...
Unit- 5.pmd
... or residual attractive forces. These forces of the adsorbent are responsible for attracting the adsorbate particles on its surface.The extent of adsorption increases with the increase of surface area per unit mass of the adsorbent at a given temperature and pressure. Another important factor featuri ...
... or residual attractive forces. These forces of the adsorbent are responsible for attracting the adsorbate particles on its surface.The extent of adsorption increases with the increase of surface area per unit mass of the adsorbent at a given temperature and pressure. Another important factor featuri ...
chemical reaction
... not always. Be careful what is actually changing color. If acid/base indicator, may not be a chemical reaction. ...
... not always. Be careful what is actually changing color. If acid/base indicator, may not be a chemical reaction. ...
PowerPoint Lectures - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry ...
... Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry ...
Equations - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... (balanced symbol equations), and you might need to add state symbols to an equation. This unit will help you to write these types of equation and to get information from equations. ...
... (balanced symbol equations), and you might need to add state symbols to an equation. This unit will help you to write these types of equation and to get information from equations. ...
chapter 9: aqueous solutions
... I. Dissociation Equations: Can be written for ionic compounds or strong acids dissolving in water. Show that the ions separate from each other in solution. Steps: 1. write the separate aqueous ions (including their correct charges) on the right side 2. write the formula of the compound followed ...
... I. Dissociation Equations: Can be written for ionic compounds or strong acids dissolving in water. Show that the ions separate from each other in solution. Steps: 1. write the separate aqueous ions (including their correct charges) on the right side 2. write the formula of the compound followed ...
Topological Analysis of Electron Density
... Jyväskylä Summer School on Charge Density August 2007 ...
... Jyväskylä Summer School on Charge Density August 2007 ...
homework_#1_10
... Interpret the balanced equation in terms of relative numbers of moles, volumes of gases at STP and masses of reactants and products. 2C2H2(g) + 5O2 (g) ...
... Interpret the balanced equation in terms of relative numbers of moles, volumes of gases at STP and masses of reactants and products. 2C2H2(g) + 5O2 (g) ...
Chapter 4 Nomenclature and Chemical Equations
... Ionic equations require balancing of both the number of atoms and the number of charges. In the previous example, there are one copper atom and two silver atoms on both sides. For the charges, two Ag+ give rise to a total of 2 units of positive charges on the left while one Cu2+ io ...
... Ionic equations require balancing of both the number of atoms and the number of charges. In the previous example, there are one copper atom and two silver atoms on both sides. For the charges, two Ag+ give rise to a total of 2 units of positive charges on the left while one Cu2+ io ...
Chem 5336_Potentiometry
... Ecell = const + 0.0592 log (a1) Ecell = const - 0.0592 pH In practice, pH meter incorporates these equations And relates them to measurements with standard buffer, And the output is a direct measurement of pH: pH = pHstd + F (Ecell - Estd)/2.303 RT, R = gas const, T = abs. ...
... Ecell = const + 0.0592 log (a1) Ecell = const - 0.0592 pH In practice, pH meter incorporates these equations And relates them to measurements with standard buffer, And the output is a direct measurement of pH: pH = pHstd + F (Ecell - Estd)/2.303 RT, R = gas const, T = abs. ...
Double layer forces

Double layer forces occur between charged objects across liquids, typically water. This force acts over distances that are comparable to the Debye length, which is on the order of one to a few tenths of nanometers. The strength of these forces increases with the magnitude of the surface charge density (or the electrical surface potential). For two similarly charged objects, this force is repulsive and decays exponentially at larger distances, see figure. For unequally charged objects and eventually at shorted distances, these forces may also be attractive. The theory due to Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DLVO) combines such double layer forces together with Van der Waals forces in order to estimate the actual interaction potential between colloidal particles.An electrical double layer develops near charged surfaces (or another charged objects) in aqueous solutions. Within this double layer, the first layer corresponds to the charged surface. These charges may originate from tightly adsorbed ions, dissociated surface groups, or substituted ions within the crystal lattice. The second layer corresponds to the diffuse layer, which contains the neutralizing charge consisting of accumulated counterions and depleted coions. The resulting potential profile between these two objects leads to differences in the ionic concentrations within the gap between these objects with respect to the bulk solution. These differences generate an osmotic pressure, which generates a force between these objects.These forces are easily experienced when hands are washed with soap. Adsorbing soap molecules make the skin negatively charged, and the slippery feeling is caused by the strongly repulsive double layer forces. These forces are further relevant in many colloidal or biological systems, and may be responsible for their stability, formation of colloidal crystals, or their rheological properties.