Homo-coupling of terminal alkynes on a noble metal surface
... reestablishment of the linear butadiyne bridge are almost spontaneous with barriers below B0.15 eV. The reaction barrier of B1.4 eV may be too high to match the experimental fact that dimerization readily takes place at TB330 K. However, the employed reaction intermediate geometry was obtained by st ...
... reestablishment of the linear butadiyne bridge are almost spontaneous with barriers below B0.15 eV. The reaction barrier of B1.4 eV may be too high to match the experimental fact that dimerization readily takes place at TB330 K. However, the employed reaction intermediate geometry was obtained by st ...
CH 4 Notes
... The neutral Ca has lost two electrons to 2 H1+ to become Ca2+ We say Ca has been oxidized to Ca2+ When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction: 2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) ---> 2 CaO (s) In this reaction the neutral O2 has gained electrons from the Ca to become O2- in CaO. We say O2 has ...
... The neutral Ca has lost two electrons to 2 H1+ to become Ca2+ We say Ca has been oxidized to Ca2+ When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction: 2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) ---> 2 CaO (s) In this reaction the neutral O2 has gained electrons from the Ca to become O2- in CaO. We say O2 has ...
AP Chemistry: Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... We say Ca has been oxidized to Ca When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction: 2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) ---> 2 CaO (s) 2In this reaction the neutral O2 has gained electrons from the Ca to become O in CaO. 2We say O2 has been reduced to O . In all reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions, one spec ...
... We say Ca has been oxidized to Ca When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction: 2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) ---> 2 CaO (s) 2In this reaction the neutral O2 has gained electrons from the Ca to become O in CaO. 2We say O2 has been reduced to O . In all reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions, one spec ...
Shifting Equilibrium
... Changes in Temperature Reversible reactions are exothermic in one direction and endothermic in the other. Remember, equilibrium constants are for a given temperature, because changing the temperature changes the relative amounts of reactants and products. Increasing the temperature is, in effect, th ...
... Changes in Temperature Reversible reactions are exothermic in one direction and endothermic in the other. Remember, equilibrium constants are for a given temperature, because changing the temperature changes the relative amounts of reactants and products. Increasing the temperature is, in effect, th ...
Acids-bases and Organic Review
... indicators to test the pH of distilled water and five aqueous household solutions. Then the student used a pH meter to measure the pH of the distilled water and each solution. The results of the student's work are recorded in the accompanying table. ...
... indicators to test the pH of distilled water and five aqueous household solutions. Then the student used a pH meter to measure the pH of the distilled water and each solution. The results of the student's work are recorded in the accompanying table. ...
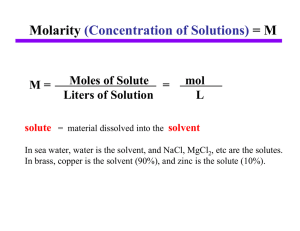
Molarity = M (Concentration of Solutions)
... Later R = 8.314 J / (mol K) = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 An ideal gas is one for which both the volume of molecules and forces between the molecules are so small that they have insignificant effect on its P-V-T behavior. Independent of substance, in the limit that n/V →0, all gases behave ideally. Usually tr ...
... Later R = 8.314 J / (mol K) = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 An ideal gas is one for which both the volume of molecules and forces between the molecules are so small that they have insignificant effect on its P-V-T behavior. Independent of substance, in the limit that n/V →0, all gases behave ideally. Usually tr ...
Entropy geometric construction of a pure substance with normal
... Figure 1 shows generic p − T diagrams of (a) a normal substance and (b) a quantum one. Although stylized for didactical purposes, those diagrams are based on the experimental phase diagrams of Ar and 4 He [3–6]. According to the Gibbs phase rule, areas in a phase diagram correspond to a unique phase ...
... Figure 1 shows generic p − T diagrams of (a) a normal substance and (b) a quantum one. Although stylized for didactical purposes, those diagrams are based on the experimental phase diagrams of Ar and 4 He [3–6]. According to the Gibbs phase rule, areas in a phase diagram correspond to a unique phase ...
Redox I
... 3. The oxidation number of oxygen in a compound is usually -2 (exception is peroxide, O22-, where the oxidation number is -1). 4. The oxidation number of hydrogen in a compound is 1 when bonded to nonmetals and -1 when bonded to metals. 5. The oxidation number of fluoride is always -1. 6. The sum of ...
... 3. The oxidation number of oxygen in a compound is usually -2 (exception is peroxide, O22-, where the oxidation number is -1). 4. The oxidation number of hydrogen in a compound is 1 when bonded to nonmetals and -1 when bonded to metals. 5. The oxidation number of fluoride is always -1. 6. The sum of ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... The Rules 1. The rule is that the cation is written first in a formula, followed by the anion. Example: in NaH, the H is H-; in HCl, the H is H+. + + 2. The oxidation number of a free element is always 0. Example: The atoms in He and N2, for example, have oxidation numbers of 0. 3. The oxidation nu ...
... The Rules 1. The rule is that the cation is written first in a formula, followed by the anion. Example: in NaH, the H is H-; in HCl, the H is H+. + + 2. The oxidation number of a free element is always 0. Example: The atoms in He and N2, for example, have oxidation numbers of 0. 3. The oxidation nu ...
Chemistry workbook
... 1. consist of a metal and a nonmetal (cation and an anion) 2. charges must balance in the final formula to form a neutral compound 3. List the characteristics of an ionic compound. 4. Write the formula for the following: a. lithium chloride b. magnesium fluoride c. scandium sulfide d. calcium nitrid ...
... 1. consist of a metal and a nonmetal (cation and an anion) 2. charges must balance in the final formula to form a neutral compound 3. List the characteristics of an ionic compound. 4. Write the formula for the following: a. lithium chloride b. magnesium fluoride c. scandium sulfide d. calcium nitrid ...
1 R R 1Ch Ro_ R___ + ____ ____ + _+ S ___y → +
... compound is broken down into two or more simpler substances. ...
... compound is broken down into two or more simpler substances. ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... Solutions solute: component present in smaller amount solvent: component present in greater amount The formation of a solution: As a solute crystal is dropped into a solution, the water molecules begin to pull apart the ionic compound ion by ion Solvent molecules surround the solute particles, form ...
... Solutions solute: component present in smaller amount solvent: component present in greater amount The formation of a solution: As a solute crystal is dropped into a solution, the water molecules begin to pull apart the ionic compound ion by ion Solvent molecules surround the solute particles, form ...
4.1 Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
... Precipitation Reactions and Solubility Rules A precipitation reaction is one in which dissolved substances react to form one (or more) solid products. Many reactions of this type involve the exchange of ions between ionic compounds in aqueous solution and are sometimes referred to as double displace ...
... Precipitation Reactions and Solubility Rules A precipitation reaction is one in which dissolved substances react to form one (or more) solid products. Many reactions of this type involve the exchange of ions between ionic compounds in aqueous solution and are sometimes referred to as double displace ...
Balancing Reaction Equations Oxidation State Reduction
... Oxidation: Loss of electrons from an element ….oxidation number increases Reduction: Gain of electrons by an element ….oxidation number decreases ...
... Oxidation: Loss of electrons from an element ….oxidation number increases Reduction: Gain of electrons by an element ….oxidation number decreases ...
Module 2
... Entropy (S) is a quantity that is a measure of the disorder of the particles (atoms and molecules) that make up the system and the dispersal of energy associated with these particles. The disorder in a system depends only on the conditions that determine the state of the system, such as composition, ...
... Entropy (S) is a quantity that is a measure of the disorder of the particles (atoms and molecules) that make up the system and the dispersal of energy associated with these particles. The disorder in a system depends only on the conditions that determine the state of the system, such as composition, ...
Chapter 8 and 9 homework
... 2. What property of water enables its molecules to interact with ions in solution? A. Water is a polarized compound and can hydrate both positive and negative ions. B. The low molecular weight of water enables it to interact with ions in solution. C. Water is ionic and therefore interacts with ions ...
... 2. What property of water enables its molecules to interact with ions in solution? A. Water is a polarized compound and can hydrate both positive and negative ions. B. The low molecular weight of water enables it to interact with ions in solution. C. Water is ionic and therefore interacts with ions ...
Ceramics for catalysis
... Once the reactant is bound to the surface, it can readily undergo reactions which take place only with difficulty in the gas or liquid phases. This may result from the close proximity of reactant molecules on the surface and/or the changes in bonding consequent upon chemisorption; both are essential ...
... Once the reactant is bound to the surface, it can readily undergo reactions which take place only with difficulty in the gas or liquid phases. This may result from the close proximity of reactant molecules on the surface and/or the changes in bonding consequent upon chemisorption; both are essential ...
SAMPLE EXERCISE 4.5 Comparing Acid Strengths
... present in solution. Plan: We first need to write the chemical formulas of the reactants and products and to determine which product is insoluble. Then we write and balance the molecular equation. Next, we write each soluble strong electrolyte as separated ions to obtain the complete ionic equation. ...
... present in solution. Plan: We first need to write the chemical formulas of the reactants and products and to determine which product is insoluble. Then we write and balance the molecular equation. Next, we write each soluble strong electrolyte as separated ions to obtain the complete ionic equation. ...
Document
... present in solution. Plan: We first need to write the chemical formulas of the reactants and products and to determine which product is insoluble. Then we write and balance the molecular equation. Next, we write each soluble strong electrolyte as separated ions to obtain the complete ionic equation. ...
... present in solution. Plan: We first need to write the chemical formulas of the reactants and products and to determine which product is insoluble. Then we write and balance the molecular equation. Next, we write each soluble strong electrolyte as separated ions to obtain the complete ionic equation. ...
Silicon Carbide Coating for Carbon Materials Produced by a
... A lot of gaseous precursors have been already used to synthesize S i c by CVD 11-31. Actual trends involve organometallic precursors, the most common being certainly the trichloromethylsilane C13SiCH3 appropriately diluted in hydrogen gas. More and more authors try to create and use "single precurso ...
... A lot of gaseous precursors have been already used to synthesize S i c by CVD 11-31. Actual trends involve organometallic precursors, the most common being certainly the trichloromethylsilane C13SiCH3 appropriately diluted in hydrogen gas. More and more authors try to create and use "single precurso ...
Powerpoints - Holy Cross Collegiate
... • Stoichiometry calculations can be used to predict the maximum quantity of product expected from a reaction. This quantity is known as the predicted yield (which is also known as the theoretical yield). • The predicted yield is calculated on the assumption that all the limiting reactant reacts to m ...
... • Stoichiometry calculations can be used to predict the maximum quantity of product expected from a reaction. This quantity is known as the predicted yield (which is also known as the theoretical yield). • The predicted yield is calculated on the assumption that all the limiting reactant reacts to m ...
Precipitation Reactions
... Assigning Oxidation Numbers: All atoms have an “oxidation number” regardless of whether it carries an ionic charge. 1. An atom in its elemental state has an oxidation number of zero. ...
... Assigning Oxidation Numbers: All atoms have an “oxidation number” regardless of whether it carries an ionic charge. 1. An atom in its elemental state has an oxidation number of zero. ...
Double layer forces

Double layer forces occur between charged objects across liquids, typically water. This force acts over distances that are comparable to the Debye length, which is on the order of one to a few tenths of nanometers. The strength of these forces increases with the magnitude of the surface charge density (or the electrical surface potential). For two similarly charged objects, this force is repulsive and decays exponentially at larger distances, see figure. For unequally charged objects and eventually at shorted distances, these forces may also be attractive. The theory due to Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DLVO) combines such double layer forces together with Van der Waals forces in order to estimate the actual interaction potential between colloidal particles.An electrical double layer develops near charged surfaces (or another charged objects) in aqueous solutions. Within this double layer, the first layer corresponds to the charged surface. These charges may originate from tightly adsorbed ions, dissociated surface groups, or substituted ions within the crystal lattice. The second layer corresponds to the diffuse layer, which contains the neutralizing charge consisting of accumulated counterions and depleted coions. The resulting potential profile between these two objects leads to differences in the ionic concentrations within the gap between these objects with respect to the bulk solution. These differences generate an osmotic pressure, which generates a force between these objects.These forces are easily experienced when hands are washed with soap. Adsorbing soap molecules make the skin negatively charged, and the slippery feeling is caused by the strongly repulsive double layer forces. These forces are further relevant in many colloidal or biological systems, and may be responsible for their stability, formation of colloidal crystals, or their rheological properties.