Math Review
... the other blue atom and then back to the first blue atom, you would have a triangular shape. Thus, we describe the geometry as trigonal planar. ...
... the other blue atom and then back to the first blue atom, you would have a triangular shape. Thus, we describe the geometry as trigonal planar. ...
text
... is favorable). A reaction at equilibrium has a ∆G of zero. As a reaction moves from its initial, non-equilibrium condition to its equilibrium position, its value of ∆G approaches zero. At the same time, the chemical species in the reaction experience a change in their concentrations. The Gibb's free ...
... is favorable). A reaction at equilibrium has a ∆G of zero. As a reaction moves from its initial, non-equilibrium condition to its equilibrium position, its value of ∆G approaches zero. At the same time, the chemical species in the reaction experience a change in their concentrations. The Gibb's free ...
Thermal Physics Concepts and Practice
... 12.1 Variable particle number . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.1.1 Thermodynamics and particle number 12.1.2 The open system: formalities . . . . . 12.1.3 Open system thermodynamics . . . . . 12.1.4 Grand partition function . . . . . . . . 12.1.5 Grand potential . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.1.6 G, Ω gr an ...
... 12.1 Variable particle number . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.1.1 Thermodynamics and particle number 12.1.2 The open system: formalities . . . . . 12.1.3 Open system thermodynamics . . . . . 12.1.4 Grand partition function . . . . . . . . 12.1.5 Grand potential . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.1.6 G, Ω gr an ...
Reactions of Plutonium Dioxide with Water and Oxygen
... to 50, 100, 150, and 250°C over a period in excess of 110 hours. Water vapor was introduced into the evacuated balantxtchamber via a gas manifold system and was maintained at a constant pressure with a water reservoir held at a fixed temperature. A constant sample temperature was maintained with a p ...
... to 50, 100, 150, and 250°C over a period in excess of 110 hours. Water vapor was introduced into the evacuated balantxtchamber via a gas manifold system and was maintained at a constant pressure with a water reservoir held at a fixed temperature. A constant sample temperature was maintained with a p ...
Symmetry axis n
... An equivalent configuration is the one which cannot be distinguished from the original one but need not be identical with it. 1.4. SYMMETRY OPERATION A symmetry operation is a movement of the molecule such that the resulting configuration of the molecule is indistinguishable from the original. 1.5. ...
... An equivalent configuration is the one which cannot be distinguished from the original one but need not be identical with it. 1.4. SYMMETRY OPERATION A symmetry operation is a movement of the molecule such that the resulting configuration of the molecule is indistinguishable from the original. 1.5. ...
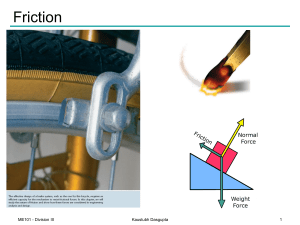
Friction
... Determine the maximum angle Ө before the block begins to slip. μs = Coefficient of static friction between the block and the inclined surface Solution: Draw the FBD of the block ...
... Determine the maximum angle Ө before the block begins to slip. μs = Coefficient of static friction between the block and the inclined surface Solution: Draw the FBD of the block ...
04 Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The ions crossed out are called spectator ions, K+ and NO3−, in this example. • The remaining ions are the reactants that form the product—an insoluble salt in a precipitation reaction, as in this example. ...
... that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The ions crossed out are called spectator ions, K+ and NO3−, in this example. • The remaining ions are the reactants that form the product—an insoluble salt in a precipitation reaction, as in this example. ...
Chapter 4: Reaction Stoichiometry Reaction Stoichiometry
... CaCl2(aq) + Li2 SO4(aq) → CaSO4(s) + 2 LiCl(aq) Ionic Equation Ca+2(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) + 2 Li+(aq) + SO4-2(aq) → CaSO4(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) Net Ionic Equation Ca+2(aq) + SO4-2(aq) → CaSO4(s) ...
... CaCl2(aq) + Li2 SO4(aq) → CaSO4(s) + 2 LiCl(aq) Ionic Equation Ca+2(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) + 2 Li+(aq) + SO4-2(aq) → CaSO4(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) Net Ionic Equation Ca+2(aq) + SO4-2(aq) → CaSO4(s) ...
Molecules, Moles and Chemical Equations File
... the explosion to occur becomes shorter, the power of the explosion will increase. Modern explosives are generally solids. But that was not always true; liquid nitroglycerin was one of the first widely used explosives. Liquids are much harder to transport and handle than solids, though, and early use ...
... the explosion to occur becomes shorter, the power of the explosion will increase. Modern explosives are generally solids. But that was not always true; liquid nitroglycerin was one of the first widely used explosives. Liquids are much harder to transport and handle than solids, though, and early use ...
Mechanistic Studies on the Galvanic Replacement Reaction
... 1C). Two types of multiple twinned structures, decahedron and icosahedron, commonly referred to as MTPs, were revealed from the HRTEM images (Figure S2), consistent with the observation for small Ag nanoparticles reported by various research groups.10,26 Both MTPs can be considered as the twinned as ...
... 1C). Two types of multiple twinned structures, decahedron and icosahedron, commonly referred to as MTPs, were revealed from the HRTEM images (Figure S2), consistent with the observation for small Ag nanoparticles reported by various research groups.10,26 Both MTPs can be considered as the twinned as ...
Unit 8: Reactions
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
Supplemental information
... to a carbon-coated copper grid and then drying the grid, which was then measured in a JEM-2010 TEM (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). For particle size analysis, nanoparticle size in the TEM images was compared with a nanometer scale bar. TEM images of bare HFO particles were obtained by the above procedure ...
... to a carbon-coated copper grid and then drying the grid, which was then measured in a JEM-2010 TEM (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). For particle size analysis, nanoparticle size in the TEM images was compared with a nanometer scale bar. TEM images of bare HFO particles were obtained by the above procedure ...
Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization, and Electro
... (4) Diethyl [5-[4-[[4-[(6-Hydroxyhexyl)thio]phenyl]azo]phenyl]pentoxy]phosphonate. In a 100 mL round-bottom flask containing 70 mL of absolute ethanol was placed 0.39 g (1.2 mmol) of 4-[[4-[(6-hydroxyhexyl)thio]phenyl]azo]phenol. The mixture was heated with stirring to dissolve all of the solid. To ...
... (4) Diethyl [5-[4-[[4-[(6-Hydroxyhexyl)thio]phenyl]azo]phenyl]pentoxy]phosphonate. In a 100 mL round-bottom flask containing 70 mL of absolute ethanol was placed 0.39 g (1.2 mmol) of 4-[[4-[(6-hydroxyhexyl)thio]phenyl]azo]phenol. The mixture was heated with stirring to dissolve all of the solid. To ...
Development of lactate sensor based on an extended gate FET with
... biosensor is usually performed by employing immobilized enzymes such as lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) or lactate oxidase (LOx) because of their simple enzymatic reaction and relatively easy sensor design configuration [1, 2]. Lactate oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of L-lactate to pyruvate and formed ...
... biosensor is usually performed by employing immobilized enzymes such as lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) or lactate oxidase (LOx) because of their simple enzymatic reaction and relatively easy sensor design configuration [1, 2]. Lactate oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of L-lactate to pyruvate and formed ...
Chemical Reactions
... they merely shift from one substance to another. Thus all the atoms present at the start of the reaction (on the left side of the equation) must still be present at the end (on the right side of the equation). In the equation we have just written, there are three carbon atoms on the left but only on ...
... they merely shift from one substance to another. Thus all the atoms present at the start of the reaction (on the left side of the equation) must still be present at the end (on the right side of the equation). In the equation we have just written, there are three carbon atoms on the left but only on ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... must be above normal. Many reactions are speeded up and can take place at lower temperatures in the presence of a catalyst. A catalyst is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction but can be recovered unchanged. To show that a catalyst is present, the formula for the catalyst or the w ...
... must be above normal. Many reactions are speeded up and can take place at lower temperatures in the presence of a catalyst. A catalyst is a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction but can be recovered unchanged. To show that a catalyst is present, the formula for the catalyst or the w ...
KEY + + - UIC Department of Chemistry
... H2(g) 4. Identify the limiting reactant when 5.0 g of Fe react with 5.0 g of water. (a) Fe (b) H2 O 5. What mass of Fe2 O4 can be produced from the amounts of Fe and water in question 4? (a) 48.8 g (b) 49 g (c) 7.86 g (d) 7.9 g (e) 12 g 6. Given the answer in question 5, what is the actual yield of ...
... H2(g) 4. Identify the limiting reactant when 5.0 g of Fe react with 5.0 g of water. (a) Fe (b) H2 O 5. What mass of Fe2 O4 can be produced from the amounts of Fe and water in question 4? (a) 48.8 g (b) 49 g (c) 7.86 g (d) 7.9 g (e) 12 g 6. Given the answer in question 5, what is the actual yield of ...
Equilibrium STUDY GUIDE by Keshara Senanayake ---
... Since the Q for this reaction is Q = [N2O4]/[NO2]^2 --> And if you increase NO2 the denominator increases resulting in a lower Q value, so Q < Keq and because of this in order to reach equilibrium now it must shift to the right. The opposite happens when you increase the numerator. (then Q > Keq and ...
... Since the Q for this reaction is Q = [N2O4]/[NO2]^2 --> And if you increase NO2 the denominator increases resulting in a lower Q value, so Q < Keq and because of this in order to reach equilibrium now it must shift to the right. The opposite happens when you increase the numerator. (then Q > Keq and ...
EFFLORESCENCE: A simple Explanation, A Simple Solution
... What is Efflorescence? Efflorescence is a deposit of soluble salts, usually white in color, which sometimes appears on the surface of masonry or concrete construction. Often efflorescence is apparent just after the structure is completed, when the builder, architect and owner are most concerned with ...
... What is Efflorescence? Efflorescence is a deposit of soluble salts, usually white in color, which sometimes appears on the surface of masonry or concrete construction. Often efflorescence is apparent just after the structure is completed, when the builder, architect and owner are most concerned with ...
Chapter 4 Student Presentation
... a) FeCl2 (aq) + K2S (aq) b) AlBr3 (aq) + NaOH (aq) c) (NH4)3PO4 (aq) + Ca(NO3)2 (aq) d) Aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and sodium carbonate react. e) Aqueous solutions of barium chloride and potassium sulfate react. ...
... a) FeCl2 (aq) + K2S (aq) b) AlBr3 (aq) + NaOH (aq) c) (NH4)3PO4 (aq) + Ca(NO3)2 (aq) d) Aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and sodium carbonate react. e) Aqueous solutions of barium chloride and potassium sulfate react. ...
2(g)
... Excess and limiting reagents refer to the reactant that will run out first and stop more product from forming. ...
... Excess and limiting reagents refer to the reactant that will run out first and stop more product from forming. ...
File
... - Similarly, in heterogeneous reactions that involve pure liquids and another phase, the concentration of the pure _______ is ________ (fixed density) and can also be incorporated into the equilibrium constant. - The equilibrium constant reported in reference tables for heterogeneous equilibria will ...
... - Similarly, in heterogeneous reactions that involve pure liquids and another phase, the concentration of the pure _______ is ________ (fixed density) and can also be incorporated into the equilibrium constant. - The equilibrium constant reported in reference tables for heterogeneous equilibria will ...
Mnemonic Devices - Free WonderKids-e
... Iodine – is a weak oxidizing agent. A dilute solution of iodine in alcohol, known as tincture of iodine, is an effective antiseptic for minor wounds. Because it is a weak oxidizing agent, iodine can be used in reaction mixtures when chemists want to oxidize only the more active reducing agents that ...
... Iodine – is a weak oxidizing agent. A dilute solution of iodine in alcohol, known as tincture of iodine, is an effective antiseptic for minor wounds. Because it is a weak oxidizing agent, iodine can be used in reaction mixtures when chemists want to oxidize only the more active reducing agents that ...
U6B _13-14
... Molecular Equation: the typical equation you are use to writing keeping all molecules together Complete Ionic Equation: shows all the particles in a solution as they really exist, as IONS or MOLECULES. Anything aqueous needs to be split apart into the cation and anion Anything solid stays intact ...
... Molecular Equation: the typical equation you are use to writing keeping all molecules together Complete Ionic Equation: shows all the particles in a solution as they really exist, as IONS or MOLECULES. Anything aqueous needs to be split apart into the cation and anion Anything solid stays intact ...
Double layer forces

Double layer forces occur between charged objects across liquids, typically water. This force acts over distances that are comparable to the Debye length, which is on the order of one to a few tenths of nanometers. The strength of these forces increases with the magnitude of the surface charge density (or the electrical surface potential). For two similarly charged objects, this force is repulsive and decays exponentially at larger distances, see figure. For unequally charged objects and eventually at shorted distances, these forces may also be attractive. The theory due to Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DLVO) combines such double layer forces together with Van der Waals forces in order to estimate the actual interaction potential between colloidal particles.An electrical double layer develops near charged surfaces (or another charged objects) in aqueous solutions. Within this double layer, the first layer corresponds to the charged surface. These charges may originate from tightly adsorbed ions, dissociated surface groups, or substituted ions within the crystal lattice. The second layer corresponds to the diffuse layer, which contains the neutralizing charge consisting of accumulated counterions and depleted coions. The resulting potential profile between these two objects leads to differences in the ionic concentrations within the gap between these objects with respect to the bulk solution. These differences generate an osmotic pressure, which generates a force between these objects.These forces are easily experienced when hands are washed with soap. Adsorbing soap molecules make the skin negatively charged, and the slippery feeling is caused by the strongly repulsive double layer forces. These forces are further relevant in many colloidal or biological systems, and may be responsible for their stability, formation of colloidal crystals, or their rheological properties.