Models of the Atom - Red Hook Central Schools
... When you try to look to see where an eactually is, you must give it energy. If you give it energy, it moves. ...
... When you try to look to see where an eactually is, you must give it energy. If you give it energy, it moves. ...
N/Z = 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, 126
... These values of neutron and proton number are anomalously stable with respect to the average – the pattern must therefore reflect something important about the average nuclear potential V(r) that the neutrons and protons are bound in.... (NB, the most stable nucleus of all is 56Fe, which has Z = 28, ...
... These values of neutron and proton number are anomalously stable with respect to the average – the pattern must therefore reflect something important about the average nuclear potential V(r) that the neutrons and protons are bound in.... (NB, the most stable nucleus of all is 56Fe, which has Z = 28, ...
Document
... build first mass spectrometers, establish source of isotopes, measure atomic charge, mass & dimensions ...
... build first mass spectrometers, establish source of isotopes, measure atomic charge, mass & dimensions ...
chapter 8
... Suppose the parent and daughter nuclei have spins of quantum number jp and jD. The total angular momentum must be conserved. If jP≠jD the α-particle must emerge with relative orbital angular momentum (with quantum number l) with respect to the recoiling daughter nucleus. With the zero spin of the α- ...
... Suppose the parent and daughter nuclei have spins of quantum number jp and jD. The total angular momentum must be conserved. If jP≠jD the α-particle must emerge with relative orbital angular momentum (with quantum number l) with respect to the recoiling daughter nucleus. With the zero spin of the α- ...
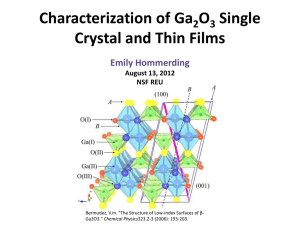
Characterization of Ga 2 0 3 Single Crystal and Thin Films
... Fadley, Charles S. "X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: From Origins to Future Directions." Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment 601.1-2 (2009): ...
... Fadley, Charles S. "X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: From Origins to Future Directions." Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment 601.1-2 (2009): ...
X-ray diffraction techniques X
... 2. Ink, dyes and paints which reflects the complementary colors when a light falls on it. 3. Astronomy: Most research telescopes have spectrographs. The measured spectra are used to determine the chemical composition and physical properties of astronomical objects (such as their temperature and velo ...
... 2. Ink, dyes and paints which reflects the complementary colors when a light falls on it. 3. Astronomy: Most research telescopes have spectrographs. The measured spectra are used to determine the chemical composition and physical properties of astronomical objects (such as their temperature and velo ...
Unit 8: Electron Configuration
... They both carve out space in a sphere, but a 2s ehas more energy than a 1s e- and therefore is further from the nucleus. ...
... They both carve out space in a sphere, but a 2s ehas more energy than a 1s e- and therefore is further from the nucleus. ...
nuc_alchemy_talk-fgs-dec07
... atomic ‘vacancies’ i.e. holes in the electron shells around the atom. Quantum mechanics means that the electron orbits are fixed in energy…. X-rays come from an electron ‘dropping’ from one energy level to a lower one ...
... atomic ‘vacancies’ i.e. holes in the electron shells around the atom. Quantum mechanics means that the electron orbits are fixed in energy…. X-rays come from an electron ‘dropping’ from one energy level to a lower one ...
Which frequency of light has the most energy
... What color of light is emitted when an electron moves from the third energy level to the second energy level? A. red B. yellow C. blue-green D. violet ...
... What color of light is emitted when an electron moves from the third energy level to the second energy level? A. red B. yellow C. blue-green D. violet ...
Nuclear Forces and Mesons
... Since Planck told us that E = h∙f there are only certain permitted energies E that the electron can occupy! Spectral lines from excited hydrogen atoms ...
... Since Planck told us that E = h∙f there are only certain permitted energies E that the electron can occupy! Spectral lines from excited hydrogen atoms ...
Level 3 Distance Learning
... more widely the knowledge and insights that you will be gaining. High resolution NMR in the study of solutions of inorganic compounds. ...
... more widely the knowledge and insights that you will be gaining. High resolution NMR in the study of solutions of inorganic compounds. ...
Orientation of the electric field gradient and ellipticity of the magnetic
... Oxygen octahedron rotation and iron atom displacement lead to differentiation of the iron – oxygen distances in the nearest neighbour shell of the oxygen’s surrounding iron. Oxygens octahedra rotate in the opposite way in adjacent chemical cells joint by the line along the 〈1 1 1〉 direction. Hence, ...
... Oxygen octahedron rotation and iron atom displacement lead to differentiation of the iron – oxygen distances in the nearest neighbour shell of the oxygen’s surrounding iron. Oxygens octahedra rotate in the opposite way in adjacent chemical cells joint by the line along the 〈1 1 1〉 direction. Hence, ...
Study of the self-diffusion coefficient in the water
... Self-diffusion coefficient in the water-methanol binary mixture was measured by NMR diffusion-order spectroscopy (DOSY) experiment [1] at different concentrations. The selfdiffusion coefficient of both water and methanol decreases exponentially as methanol mole fraction increases. This behavior is s ...
... Self-diffusion coefficient in the water-methanol binary mixture was measured by NMR diffusion-order spectroscopy (DOSY) experiment [1] at different concentrations. The selfdiffusion coefficient of both water and methanol decreases exponentially as methanol mole fraction increases. This behavior is s ...
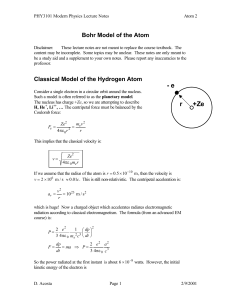
Atom 2 - UF Physics
... Bohr’s Postulates In 1913, Bohr proposed several postulates in an attempt to describe the atom. 1. Atoms have stationary states of definite energy. These states do not radiate any energy, as is necessary to explain the stability of atoms. 2. The emission and absorption of electromagnetic energy can ...
... Bohr’s Postulates In 1913, Bohr proposed several postulates in an attempt to describe the atom. 1. Atoms have stationary states of definite energy. These states do not radiate any energy, as is necessary to explain the stability of atoms. 2. The emission and absorption of electromagnetic energy can ...
Lesson7
... • The previous slide shows a potential energy diagram for a typical diatomic molecule. • The x axis is the inter-nuclear separation r, and the y axis is the potential energy. • As the two atoms come together the electrons of each overlap and produce a binding force which stabilizes the molecule. • H ...
... • The previous slide shows a potential energy diagram for a typical diatomic molecule. • The x axis is the inter-nuclear separation r, and the y axis is the potential energy. • As the two atoms come together the electrons of each overlap and produce a binding force which stabilizes the molecule. • H ...
Abstract - nanopia 2015
... School of Science and Laboratory of Optical Information Technology Wuhan Institute of Technology Wuhan 430205, China Email: [email protected] ...
... School of Science and Laboratory of Optical Information Technology Wuhan Institute of Technology Wuhan 430205, China Email: [email protected] ...
EXAM # 1
... structure of this compound. F. __2__ You want to measure the relative air quality in Lincoln by monitoring the concentration of ozone and NO2 at various locations in the city. G. __1__ You want to monitor the enzyme mechanism involved in a redox reaction H. __8__ You want to compare DNA fragments co ...
... structure of this compound. F. __2__ You want to measure the relative air quality in Lincoln by monitoring the concentration of ozone and NO2 at various locations in the city. G. __1__ You want to monitor the enzyme mechanism involved in a redox reaction H. __8__ You want to compare DNA fragments co ...
Atoms and Nuclei
... • One must add energy to the motion of an electron to move it to a higher energy (i.e., larger) orbit. If one removes energy, the electron must move closer to the nucleus. This energy can be in the form of electromagnetic radiation (“light”) or it can be associated with collisions with other atoms. ...
... • One must add energy to the motion of an electron to move it to a higher energy (i.e., larger) orbit. If one removes energy, the electron must move closer to the nucleus. This energy can be in the form of electromagnetic radiation (“light”) or it can be associated with collisions with other atoms. ...
10. Molecules and Solids
... The positions and intensities of the observed bands are ruled by quantum mechanics. Note two features in particular: 1) The relative intensities of the bands are due to different transition probabilities. 2) Some transitions are forbidden by the selection rule that ...
... The positions and intensities of the observed bands are ruled by quantum mechanics. Note two features in particular: 1) The relative intensities of the bands are due to different transition probabilities. 2) Some transitions are forbidden by the selection rule that ...
Random Laser - Department of Physics
... important material features. In brief, CL occurs when a sample absorbs electrons and emits light at a specific frequency corresponding to the material’s specific structure, composition and quality. The theory of cathodoluminescence, in relation to semiconductor materials, and its use in understandin ...
... important material features. In brief, CL occurs when a sample absorbs electrons and emits light at a specific frequency corresponding to the material’s specific structure, composition and quality. The theory of cathodoluminescence, in relation to semiconductor materials, and its use in understandin ...
File
... Periodic Trends (Chapter 5) Atomic Radius – distance from nucleus to outer electrons (PreIB only) Shielding – inner electrons “blocking” or “shielding” the valence electrons from the pull of the nucleus. Ionization Energy – energy needed to remove an electron Electronegativity – ability of an ...
... Periodic Trends (Chapter 5) Atomic Radius – distance from nucleus to outer electrons (PreIB only) Shielding – inner electrons “blocking” or “shielding” the valence electrons from the pull of the nucleus. Ionization Energy – energy needed to remove an electron Electronegativity – ability of an ...
Nuclear(1).
... Can be stopped by several cm of lead or several meters of concrete. The nucleus goes from an excited state to a normal (unexcited) state. Almost always occurs with alpha or beta decay. Does not change mass number or atomic number. No new element is created ...
... Can be stopped by several cm of lead or several meters of concrete. The nucleus goes from an excited state to a normal (unexcited) state. Almost always occurs with alpha or beta decay. Does not change mass number or atomic number. No new element is created ...
Condensed Plasmoids – The Intermediate State of LENR
... 4. Ab Initio Simulations of CP and Numerical Results Based on the theory above the author is undertaking ab initio (i.e. derived only from first principles) quantummechanical simulations of CPs. This is the subject of ongoing research. The goal is to obtain the quantitative properties of CP, such as ...
... 4. Ab Initio Simulations of CP and Numerical Results Based on the theory above the author is undertaking ab initio (i.e. derived only from first principles) quantummechanical simulations of CPs. This is the subject of ongoing research. The goal is to obtain the quantitative properties of CP, such as ...
Mössbauer spectroscopy

Mössbauer spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique based on the Mössbauer effect. This effect, discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1957, consists in the recoil-free, resonant absorption and emission of gamma rays in solids.Like NMR spectroscopy, Mössbauer spectroscopy probes tiny changes in the energy levels of an atomic nucleus in response to its environment. Typically, three types of nuclear interactions may be observed: an isomeric shift, also known as a chemical shift; quadrupole splitting; and magnetic or hyperfine splitting, also known as the Zeeman effect. Due to the high energy and extremely narrow line widths of gamma rays, Mössbauer spectroscopy is a very sensitive technique in terms of energy (and hence frequency) resolution, capable of detecting change in just a few parts per 1011.