Honors Chemistry
... 8. What is a line-emission spectrum and how is it different from a continuous spectrum? A line-emission spectrum is emitted light that gives off separated frequencies of electromagnetic radiation when passed through a prism. A continues spectrum is an emission of a continuous range of frequency of ...
... 8. What is a line-emission spectrum and how is it different from a continuous spectrum? A line-emission spectrum is emitted light that gives off separated frequencies of electromagnetic radiation when passed through a prism. A continues spectrum is an emission of a continuous range of frequency of ...
brief answers - Inside Mines
... causes electrons to be ejected. The number of electrons ejected is proportional to the intensity, while their kinetic energy is proportional to the frequency minus a constant that depends on the material. This is surprising because classically one expects the energy to increase with intensity and no ...
... causes electrons to be ejected. The number of electrons ejected is proportional to the intensity, while their kinetic energy is proportional to the frequency minus a constant that depends on the material. This is surprising because classically one expects the energy to increase with intensity and no ...
Gamma Decay Supplement - Inside Mines
... electron conversion to decrease the energy of the nucleus. The transitions can occur between two excited states or an excited state and the ground state. This decrease in energy does not change the isotope, it merely reconfigures the nucleons within the nucleus. In the γ-decay process, electromagnet ...
... electron conversion to decrease the energy of the nucleus. The transitions can occur between two excited states or an excited state and the ground state. This decrease in energy does not change the isotope, it merely reconfigures the nucleons within the nucleus. In the γ-decay process, electromagnet ...
Honors Chemistry
... 8. What is a line-emission spectrum and how is it different from a continuous spectrum? A line-emission spectrum is emitted light that gives off separated frequencies of electromagnetic radiation when passed through a prism. A continues spectrum is an emission of a continuous range of frequency of ...
... 8. What is a line-emission spectrum and how is it different from a continuous spectrum? A line-emission spectrum is emitted light that gives off separated frequencies of electromagnetic radiation when passed through a prism. A continues spectrum is an emission of a continuous range of frequency of ...
Chapter8_notes
... • Line widths due to pressure broadening are two to three orders of magnitude greater than natural line widths (10-2 Å to 10-1 Å). ...
... • Line widths due to pressure broadening are two to three orders of magnitude greater than natural line widths (10-2 Å to 10-1 Å). ...
Document
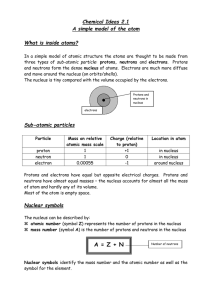
... The nuclei of all atoms of a particular element must contain the same number of protons. They may contain varying numbers of neutrons. Isotopes of an element have the same Z but differing N and A values. Example: 11 12 13 14 ...
... The nuclei of all atoms of a particular element must contain the same number of protons. They may contain varying numbers of neutrons. Isotopes of an element have the same Z but differing N and A values. Example: 11 12 13 14 ...
revised preliminary introduction of spectroscopy
... of the species. Peaks resulting from n → π* transitions are shifted to shorter wavelengths (blue shift) with increasing solvent polarity because of increased solvation of the lone pair in the ground state, which lowers the energy of the n orbital. Often the reverse (i.e. red shift) is seen for π → π ...
... of the species. Peaks resulting from n → π* transitions are shifted to shorter wavelengths (blue shift) with increasing solvent polarity because of increased solvation of the lone pair in the ground state, which lowers the energy of the n orbital. Often the reverse (i.e. red shift) is seen for π → π ...
Introduction to spectroscopy
... Spectrum: A plot of the intensity as a function light or particle energy (frequency, wavelength) ...
... Spectrum: A plot of the intensity as a function light or particle energy (frequency, wavelength) ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
... • In some inst., the freq. of the source is held constant while the strength of the field is scanned. • CW spectroscopy is inefficient in comparison to FT NMR, as it probes the NMR response at individual frequencies in succession. As the NMR signal is intrinsically weak, the observed spectra suffer ...
... • In some inst., the freq. of the source is held constant while the strength of the field is scanned. • CW spectroscopy is inefficient in comparison to FT NMR, as it probes the NMR response at individual frequencies in succession. As the NMR signal is intrinsically weak, the observed spectra suffer ...
Topic 7: Atomic and nuclear physics 7.1 The atom
... elements are different in some fundamental way or ways. – Chemical compounds are formed when atoms combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. – Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms-changes in the way they are bound together. T ...
... elements are different in some fundamental way or ways. – Chemical compounds are formed when atoms combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. – Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms-changes in the way they are bound together. T ...
Quantum Mechanics Physics
... Introduction and theory • Atomic Spectroscopy is the analytical measurement of the quantum energy level jumps of different electron energy states. • It is a spectral analysis of the colors (frequencies or wavelengths) that an atom gives off when it changes energy levels. • Formulas: c = f and 1/ ...
... Introduction and theory • Atomic Spectroscopy is the analytical measurement of the quantum energy level jumps of different electron energy states. • It is a spectral analysis of the colors (frequencies or wavelengths) that an atom gives off when it changes energy levels. • Formulas: c = f and 1/ ...
II. Radioactive Decay
... Isotopes - atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons Radioisotopes – isotope with an unstable nucleus that emits radiation to become a more stable nucleus ...
... Isotopes - atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons Radioisotopes – isotope with an unstable nucleus that emits radiation to become a more stable nucleus ...
HW8 not graded v3 - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... a) Which of the two semiconductors will absorb a greater fraction of the sun’s light? ...
... a) Which of the two semiconductors will absorb a greater fraction of the sun’s light? ...
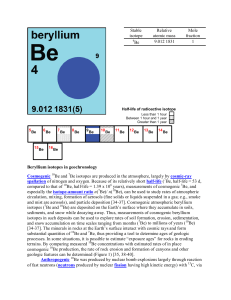
Beryllium isotopes in geochronology Cosmogenic Be and Be
... Cosmogenic 10Be and 7Be isotopes are produced in the atmosphere, largely by cosmic-ray spallation of nitrogen and oxygen. Because of its relatively short half-life (7 Be, half-life = 53 d, compared to that of 10Be, half-life = 1.39 x 106 years), measurements of cosmogenic 7Be, and especially the iso ...
... Cosmogenic 10Be and 7Be isotopes are produced in the atmosphere, largely by cosmic-ray spallation of nitrogen and oxygen. Because of its relatively short half-life (7 Be, half-life = 53 d, compared to that of 10Be, half-life = 1.39 x 106 years), measurements of cosmogenic 7Be, and especially the iso ...
3/27 Lecture Slides
... at a frequency of 750 MHz. This is in the radio frequency and Hz = s-1. What is the wavelength of this light? An infrared absorption band occurs at a wavenumber of 812 cm-1. What is the wavelength (in mm) and energy (J/photon) of that light? What type of light involves transitions of inner shell ele ...
... at a frequency of 750 MHz. This is in the radio frequency and Hz = s-1. What is the wavelength of this light? An infrared absorption band occurs at a wavenumber of 812 cm-1. What is the wavelength (in mm) and energy (J/photon) of that light? What type of light involves transitions of inner shell ele ...
Work sheet –chapter 2 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Structure of Atom
... 5. What did Einstein explain about photoelectric effect? 6. What is the relation between kinetic energy and frequency of the photoelectrons? 7. Calculate energy of 2mole of photons of radiation whose frequency is 51014Hz. 8. What is emission and absorption spectra? 9. What transition in the hydroge ...
... 5. What did Einstein explain about photoelectric effect? 6. What is the relation between kinetic energy and frequency of the photoelectrons? 7. Calculate energy of 2mole of photons of radiation whose frequency is 51014Hz. 8. What is emission and absorption spectra? 9. What transition in the hydroge ...
Chem 1st Sem Rev Ch2
... c. father of the modern atomic theory, everything made of atoms d. planetary model of the atom, electrons move around the nucleus like planets around sun. e. plum pudding model of the atom: atom looks like chocolate chip cookie f. gold foil experiment – atoms have a dense core called nucleus g. he g ...
... c. father of the modern atomic theory, everything made of atoms d. planetary model of the atom, electrons move around the nucleus like planets around sun. e. plum pudding model of the atom: atom looks like chocolate chip cookie f. gold foil experiment – atoms have a dense core called nucleus g. he g ...
Spectra and atomic structure
... When an electron drops from one level to another a quantum of radiant energy is emitted and this gives a line in the hydrogen spectrum. The energy of this quantum is given by the formula: Quantum energy: E = hf where h is Planck’s constant and f is the frequency The bigger the energy difference the ...
... When an electron drops from one level to another a quantum of radiant energy is emitted and this gives a line in the hydrogen spectrum. The energy of this quantum is given by the formula: Quantum energy: E = hf where h is Planck’s constant and f is the frequency The bigger the energy difference the ...
Modern physics
... We already have the angular part of the wavefunctions for any radial potential in the spherical Schrödinger equation: Y (r ,q , ) R(r )Ylm (q , ) where ...
... We already have the angular part of the wavefunctions for any radial potential in the spherical Schrödinger equation: Y (r ,q , ) R(r )Ylm (q , ) where ...
Photoreflectance of Semiconductors
... Majority of Defects on the Surface Defects cause strain on the surface Cracks form Periodicity lost ...
... Majority of Defects on the Surface Defects cause strain on the surface Cracks form Periodicity lost ...
Radioactive Reactions
... • When an atom emits part of its NUCLEUS (protons or neutrons) this is called radiation • This happens because the nucleus is unstable. • When an atom emits protons its identity changes • This can happen naturally (sun) or through man made isotopes in a lab ...
... • When an atom emits part of its NUCLEUS (protons or neutrons) this is called radiation • This happens because the nucleus is unstable. • When an atom emits protons its identity changes • This can happen naturally (sun) or through man made isotopes in a lab ...
Document
... Some isotopes of some elements are unstable, so their nuclei break down spontaneously and emit rays and particles called emissions. They are radioactive. This breakdown or RADIOACTIVE DECAY occurs without any need to be triggered off by something. There are 3 different kinds of emissions identified: ...
... Some isotopes of some elements are unstable, so their nuclei break down spontaneously and emit rays and particles called emissions. They are radioactive. This breakdown or RADIOACTIVE DECAY occurs without any need to be triggered off by something. There are 3 different kinds of emissions identified: ...
Atomic Theory Handout CNS 8
... Bohr began to work on the problem of the atom's structure. Ernest Rutherford had recently suggested the atom had a miniature, dense nucleus surrounded by a cloud of nearly weightless electrons. There were a few problems with the model, however. For example, according to classical physics, the electr ...
... Bohr began to work on the problem of the atom's structure. Ernest Rutherford had recently suggested the atom had a miniature, dense nucleus surrounded by a cloud of nearly weightless electrons. There were a few problems with the model, however. For example, according to classical physics, the electr ...
File
... 19. What is the name of the process in which the nucleus of an atom of one element is changed into the nucleus of an atom of a different element? A) decomposition C) substitution ...
... 19. What is the name of the process in which the nucleus of an atom of one element is changed into the nucleus of an atom of a different element? A) decomposition C) substitution ...
Optical pumping of nuclear polarization in a single
... levels. This Overhauser shift has been observed in interface GaAs QDs[1] and in a selfassembled InAlAs QD[2] and InAs QD[3]. Figure shows the Zeeman spectra of the excitonic emissions split by 645 eV in linearly-polarized excitation and by 750 eV in circularly-polarized excitation (-) at 5 T. The ...
... levels. This Overhauser shift has been observed in interface GaAs QDs[1] and in a selfassembled InAlAs QD[2] and InAs QD[3]. Figure shows the Zeeman spectra of the excitonic emissions split by 645 eV in linearly-polarized excitation and by 750 eV in circularly-polarized excitation (-) at 5 T. The ...
Mössbauer spectroscopy

Mössbauer spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique based on the Mössbauer effect. This effect, discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1957, consists in the recoil-free, resonant absorption and emission of gamma rays in solids.Like NMR spectroscopy, Mössbauer spectroscopy probes tiny changes in the energy levels of an atomic nucleus in response to its environment. Typically, three types of nuclear interactions may be observed: an isomeric shift, also known as a chemical shift; quadrupole splitting; and magnetic or hyperfine splitting, also known as the Zeeman effect. Due to the high energy and extremely narrow line widths of gamma rays, Mössbauer spectroscopy is a very sensitive technique in terms of energy (and hence frequency) resolution, capable of detecting change in just a few parts per 1011.