Lecture 12: Review.
... Hund's first rule: for every atomic ground state, the total electron spin has maximum value tolerated by the Pauli principle. Hund's second rule: for a given spin, the term with the largest value of the total orbital angular momentum quantum number L, consistent with overall antisymmetrization, has ...
... Hund's first rule: for every atomic ground state, the total electron spin has maximum value tolerated by the Pauli principle. Hund's second rule: for a given spin, the term with the largest value of the total orbital angular momentum quantum number L, consistent with overall antisymmetrization, has ...
CHM 101 - Academic Computer Center
... Cold packs, whose temperatures are lowered when ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, are carried by athletic trainers when transporting ice is not possible. Which of the following is true of this reaction? A. H < 0, process is exothermic B. H > 0, process is exothermic C. H < 0, process is endoth ...
... Cold packs, whose temperatures are lowered when ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, are carried by athletic trainers when transporting ice is not possible. Which of the following is true of this reaction? A. H < 0, process is exothermic B. H > 0, process is exothermic C. H < 0, process is endoth ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... Cause transmutation of elements with the release of a large amount of energy These reactions are the source of electric energy at nuclear power plants as well as the energy from the Sun and stars This immense amount of energy comes from the conversion of matter to energy ...
... Cause transmutation of elements with the release of a large amount of energy These reactions are the source of electric energy at nuclear power plants as well as the energy from the Sun and stars This immense amount of energy comes from the conversion of matter to energy ...
Spectrophotometry Chapter 18
... • Ground State: The state of least possible energy in a physical system, as of elementary particles. – Also called ground level. • Excited State: Being at an energy level higher than the ground state Absorption • A photon of light hits a molecule or atom. • If the energy of the photon is “right”, it ...
... • Ground State: The state of least possible energy in a physical system, as of elementary particles. – Also called ground level. • Excited State: Being at an energy level higher than the ground state Absorption • A photon of light hits a molecule or atom. • If the energy of the photon is “right”, it ...
Emission Spectroscopy Lab
... 2. Note: Be sure that the wire loop is correctly matched to the correct chemical before using it! a. If the chemical (salt) is solid, moisten the wire loop in some distilled water. Then dip the loop in the solid chemical so that some of the chemical sticks to the loop of the wire. b. If the chemical ...
... 2. Note: Be sure that the wire loop is correctly matched to the correct chemical before using it! a. If the chemical (salt) is solid, moisten the wire loop in some distilled water. Then dip the loop in the solid chemical so that some of the chemical sticks to the loop of the wire. b. If the chemical ...
Physics 12 Assignmen.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
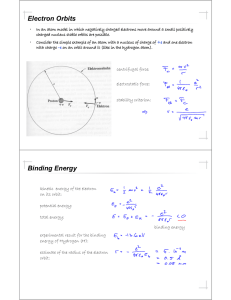
... 2. In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, what keeps the electrons from flying off into space? In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, the Coulomb (or electrostatic) force keeps the electrons from flying off into space. Since the protons in the center are positively charged, the negativel ...
... 2. In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, what keeps the electrons from flying off into space? In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, the Coulomb (or electrostatic) force keeps the electrons from flying off into space. Since the protons in the center are positively charged, the negativel ...
Relativity Problem Set 7 - Solutions Prof. J. Gerton October 24, 2011
... In Bohr’s model , the velocity of the electron is quantized as vn = α c/n, where α = 1/137 is the fine structure constant. Since αc = 2.19 × 106 m/s, we see that only the velocities in (b) and (d) are allowed, being given by the above relation with n = 1 and n = 2 respectively. The quantities in (a) ...
... In Bohr’s model , the velocity of the electron is quantized as vn = α c/n, where α = 1/137 is the fine structure constant. Since αc = 2.19 × 106 m/s, we see that only the velocities in (b) and (d) are allowed, being given by the above relation with n = 1 and n = 2 respectively. The quantities in (a) ...
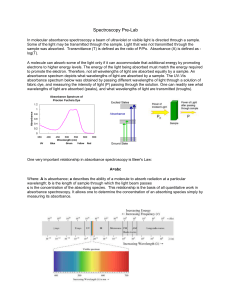
About UV-Vis Molecular Absorbance Spectroscopy
... Where: A is absorbance; a describes the ability of a molecule to absorb radiation at a particular wavelength; b is the length of sample through which the light beam passes c is the concentration of the absorbing species. This relationship is the basis of all quantitative work in absorbance spectrosc ...
... Where: A is absorbance; a describes the ability of a molecule to absorb radiation at a particular wavelength; b is the length of sample through which the light beam passes c is the concentration of the absorbing species. This relationship is the basis of all quantitative work in absorbance spectrosc ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... average mass of the isotopes of that element. o Example: Element X has two isotopes X-6 (6.015 amu) and X-7 (7.016 amu). X-6 comprises 7.5% of all of element X. X-7 makes up the remaining 92.5%. What is the atomic mass? o NOTE: The % needs to be divided by 100 BEFORE putting it into the equation!! ...
... average mass of the isotopes of that element. o Example: Element X has two isotopes X-6 (6.015 amu) and X-7 (7.016 amu). X-6 comprises 7.5% of all of element X. X-7 makes up the remaining 92.5%. What is the atomic mass? o NOTE: The % needs to be divided by 100 BEFORE putting it into the equation!! ...
Atomic and Molecular S Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy
... q is the molecular partition function (see HT Stat. Mech. notes) gi is the degeneracy of the i th level (the no. states with same energy) Ei is the energy is the energy of the i of the i th level k is the Boltzmann constant ( = R/NA= 1.381 x 10‐23 J K‐1) T is the Kelvin temperature ...
... q is the molecular partition function (see HT Stat. Mech. notes) gi is the degeneracy of the i th level (the no. states with same energy) Ei is the energy is the energy of the i of the i th level k is the Boltzmann constant ( = R/NA= 1.381 x 10‐23 J K‐1) T is the Kelvin temperature ...
constructive - Purdue Physics
... therefore know for example the intensity of the radiation that it can produce is by counting the number of decays in a second. This is known as the activity of the radioactive source and depends on the half-life of the nucleus and also on how many nucleus are present. It is measured in Curies or Bec ...
... therefore know for example the intensity of the radiation that it can produce is by counting the number of decays in a second. This is known as the activity of the radioactive source and depends on the half-life of the nucleus and also on how many nucleus are present. It is measured in Curies or Bec ...
Atomic and Molecular Physics for Physicists Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
... angular momentum J, and as JZ=LZ+SZ, and as, when calculating the distances and therefore the forces one has to take into account that g for the orbital motion is gL=1 while for the spin is gS=2, we will have the following forces acting on the atoms: F(LZ=+1, SZ=+1/2), F(LZ=+0, SZ=+1/2), F(LZ=-1, SZ ...
... angular momentum J, and as JZ=LZ+SZ, and as, when calculating the distances and therefore the forces one has to take into account that g for the orbital motion is gL=1 while for the spin is gS=2, we will have the following forces acting on the atoms: F(LZ=+1, SZ=+1/2), F(LZ=+0, SZ=+1/2), F(LZ=-1, SZ ...
Harmonic oscillator - Vibration energy of molecules 1. Definitions
... The optical spectroscopy, i.e. the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with atoms or molecules, is one of the most important experimental techniques for investigating the structure of atoms and molecules. Indeed, essential informations are given by the absorption properties of molecules in di↵e ...
... The optical spectroscopy, i.e. the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with atoms or molecules, is one of the most important experimental techniques for investigating the structure of atoms and molecules. Indeed, essential informations are given by the absorption properties of molecules in di↵e ...
Chemistry Questions
... 4. What is the total number of electrons in the nucleus of an atom of potassium-42? 5. Which of the following elements have the greatest number of neutrons? a. 37Cl b. 39K 4. An atomic mass unit is defined as exactly a. 1/16 the mass of 12C atom b. 1/12 the mass of 12C atom 5. The total number of el ...
... 4. What is the total number of electrons in the nucleus of an atom of potassium-42? 5. Which of the following elements have the greatest number of neutrons? a. 37Cl b. 39K 4. An atomic mass unit is defined as exactly a. 1/16 the mass of 12C atom b. 1/12 the mass of 12C atom 5. The total number of el ...
Rotational and Vibrational Spectra
... 3. Calculate the ratio of the number NJ of molecules in a sample of HCl at (a) 300º K and (b) 1000º K having rotational quantum numbers of J = 5 and J = 0. (c) Calculate the values of J at the maximum NJ at these temperatures. (d) From this information, construct relative intensities of the lines in ...
... 3. Calculate the ratio of the number NJ of molecules in a sample of HCl at (a) 300º K and (b) 1000º K having rotational quantum numbers of J = 5 and J = 0. (c) Calculate the values of J at the maximum NJ at these temperatures. (d) From this information, construct relative intensities of the lines in ...
Material since exam 3
... a p-shell (except for He). How many electrons do next two inert gas atoms after helium ( neon (Ne) and argon (Ar) ) have. In this range of atomic number the subshells fill in order of increasing angular momentum. ...
... a p-shell (except for He). How many electrons do next two inert gas atoms after helium ( neon (Ne) and argon (Ar) ) have. In this range of atomic number the subshells fill in order of increasing angular momentum. ...
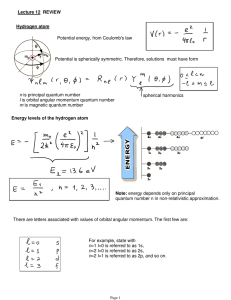
energy levels
... – Tells you how far away the electron is from the nucleus – There are 1-7 energy levels, correlates with period numbers – Each level has same n number of sublevels – Maximum number of 2n2 electrons per level ...
... – Tells you how far away the electron is from the nucleus – There are 1-7 energy levels, correlates with period numbers – Each level has same n number of sublevels – Maximum number of 2n2 electrons per level ...
No Slide Title
... are randomly distributed and cancel out. For the ones in z, we get a net magnetization proportional to Na - Nb. • Since this is (more or less) the situation in a real sample, we will from now on use Mo in all further descriptions/examples. • There is an important difference between a m and Mo. While ...
... are randomly distributed and cancel out. For the ones in z, we get a net magnetization proportional to Na - Nb. • Since this is (more or less) the situation in a real sample, we will from now on use Mo in all further descriptions/examples. • There is an important difference between a m and Mo. While ...
Matter and Energy
... ◦ Protons – found in nucleus, + charge, 1 AMU ◦ Neutrons – found in nucleus, no charge, 1 AMU ◦ Electrons – found orbiting nucleus, - charge, approximately 1/1836 AMU ...
... ◦ Protons – found in nucleus, + charge, 1 AMU ◦ Neutrons – found in nucleus, no charge, 1 AMU ◦ Electrons – found orbiting nucleus, - charge, approximately 1/1836 AMU ...
CHAPTER 11 – NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... - A new element is produced 2. Beta Decay: - nucleus decays and gives off a beta particle - beta particle is a high speed electron (0e) - symbol is Ex: ...
... - A new element is produced 2. Beta Decay: - nucleus decays and gives off a beta particle - beta particle is a high speed electron (0e) - symbol is Ex: ...
Mössbauer spectroscopy

Mössbauer spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique based on the Mössbauer effect. This effect, discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1957, consists in the recoil-free, resonant absorption and emission of gamma rays in solids.Like NMR spectroscopy, Mössbauer spectroscopy probes tiny changes in the energy levels of an atomic nucleus in response to its environment. Typically, three types of nuclear interactions may be observed: an isomeric shift, also known as a chemical shift; quadrupole splitting; and magnetic or hyperfine splitting, also known as the Zeeman effect. Due to the high energy and extremely narrow line widths of gamma rays, Mössbauer spectroscopy is a very sensitive technique in terms of energy (and hence frequency) resolution, capable of detecting change in just a few parts per 1011.