THE ORGANELLLE/ORGAN SHOW
... tissues are usually coordinated so that they can perform specific functions for the whole animal. Specific tissue types can be created by cells that produce the same proteins and perform the same functions. (muscle cells have special proteins and nerve cells have special lipids, both cell types have ...
... tissues are usually coordinated so that they can perform specific functions for the whole animal. Specific tissue types can be created by cells that produce the same proteins and perform the same functions. (muscle cells have special proteins and nerve cells have special lipids, both cell types have ...
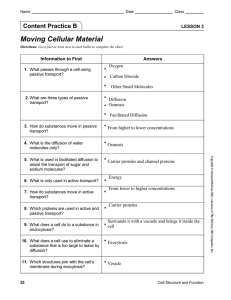
Moving Cellular Material
... 6. What is only used in active transport? 7. How do substances move in active transport? 8. Which proteins are used in active and passive transport? 9. What does a cell do to a substance in endocytosis? 10. What does a cell use to eliminate a substance that is too large to leave by diffusion? 11. Wh ...
... 6. What is only used in active transport? 7. How do substances move in active transport? 8. Which proteins are used in active and passive transport? 9. What does a cell do to a substance in endocytosis? 10. What does a cell use to eliminate a substance that is too large to leave by diffusion? 11. Wh ...
Cell Structure and Function: Review
... C. old age D. harmful microorganisms 7. In chloroplasts, energy from the sun is used to make food in a process called? (pg. 200-203) A. photosynthesis B. mitosis C. respiration D. inflammation ***Directions: Use the terms in the box to complete each sentence. If you need help, you may use your TEXTB ...
... C. old age D. harmful microorganisms 7. In chloroplasts, energy from the sun is used to make food in a process called? (pg. 200-203) A. photosynthesis B. mitosis C. respiration D. inflammation ***Directions: Use the terms in the box to complete each sentence. If you need help, you may use your TEXTB ...
Cells and Structure
... Schleiden, Schwann and Virchow - 1800s The cell is the basic and smallest unit of life All cells arise from pre-existing cells The cell is the working unit of organisms ...
... Schleiden, Schwann and Virchow - 1800s The cell is the basic and smallest unit of life All cells arise from pre-existing cells The cell is the working unit of organisms ...
1. All living things are made of cell
... 9. What is the ability of the cell membrane to block some substances, but allow others to pass into the cell? Selective permeability (semi-permeable) 10. Contrast osmosis and diffusion? -Osmosis is the passive movement of water across a cell membrane -Diffusion is the passive movement of substances ...
... 9. What is the ability of the cell membrane to block some substances, but allow others to pass into the cell? Selective permeability (semi-permeable) 10. Contrast osmosis and diffusion? -Osmosis is the passive movement of water across a cell membrane -Diffusion is the passive movement of substances ...
This organelle looks like a stack of
... Powerhouse of the cell with its own DNA that burns glucose for energy and stores it as ATP ...
... Powerhouse of the cell with its own DNA that burns glucose for energy and stores it as ATP ...
cell structures - Learn District 196
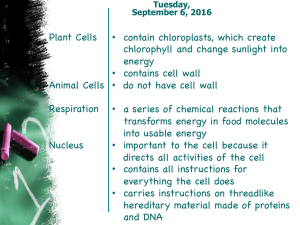
... FOUND ONLY IN PLANT CELLS GREEN PIGMENTED STRUCTURES THAT CONTAIN CHLOROPHYLL THAT IS NEEDED TO MAKE FOOD FOR THE CELL ...
... FOUND ONLY IN PLANT CELLS GREEN PIGMENTED STRUCTURES THAT CONTAIN CHLOROPHYLL THAT IS NEEDED TO MAKE FOOD FOR THE CELL ...
ppt - University of Kentucky
... • Cells are divded into two categories depending on their complexities: Prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells: Simpler, smaller, have no membrane bound nucleus or organelles. Have outer cell wall enclosing a fluid cytoplasm. E.g. bacteria (E. coli). ...
... • Cells are divded into two categories depending on their complexities: Prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells: Simpler, smaller, have no membrane bound nucleus or organelles. Have outer cell wall enclosing a fluid cytoplasm. E.g. bacteria (E. coli). ...
Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes
... • Ends of proteins are hydrophyllic • Center is hydrophobic • Integral proteins go through membrane • Peripheral proteins are only on surface • Proteins have many functions (later) ...
... • Ends of proteins are hydrophyllic • Center is hydrophobic • Integral proteins go through membrane • Peripheral proteins are only on surface • Proteins have many functions (later) ...
Organelle - wiltseswall
... Captures and stores the sun’s energy in plants to make sugar through photosynthesis. Houses DNA, the directions for everything the cell does ...
... Captures and stores the sun’s energy in plants to make sugar through photosynthesis. Houses DNA, the directions for everything the cell does ...
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW
... • THE CELLS WOULD SWELL DUE TO THE HYPOTONIC SOLUTION SURROUNDING THEM- WATER WOULD MOVE INTO THE CELL. ...
... • THE CELLS WOULD SWELL DUE TO THE HYPOTONIC SOLUTION SURROUNDING THEM- WATER WOULD MOVE INTO THE CELL. ...
Biochemistry Review Sheet
... 10. What is diffusion? 11. What is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion? 12. What is osmosis? 13. Draw three cells: one surrounded by hypotonic solution, one surrounded by hypertonic solution, and one surrounded by isotonic solution. Label the direction of solute movement and wate ...
... 10. What is diffusion? 11. What is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion? 12. What is osmosis? 13. Draw three cells: one surrounded by hypotonic solution, one surrounded by hypertonic solution, and one surrounded by isotonic solution. Label the direction of solute movement and wate ...
The Cell
... secretions from salt that gets trapped inside cells that draws moisture inside. Movement through the Cell Membrane Diffusion – movement from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (example – oxygen/carbon dioxide) Facilitated Diffusion – Special carrier molecule moves substanc ...
... secretions from salt that gets trapped inside cells that draws moisture inside. Movement through the Cell Membrane Diffusion – movement from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (example – oxygen/carbon dioxide) Facilitated Diffusion – Special carrier molecule moves substanc ...
Biology Midterm Review Handouts
... 2. When scientists are "evaluating results" as a part of scientific thinking, they mainly ...
... 2. When scientists are "evaluating results" as a part of scientific thinking, they mainly ...
Slide 1
... Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine - 1974 For “the structure and functional organization of the cell” ...
... Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine - 1974 For “the structure and functional organization of the cell” ...
Name - Humble ISD
... Centrosome cytoplasm Mitochondria nucleus Concentration gradient Metabolism mitosis ...
... Centrosome cytoplasm Mitochondria nucleus Concentration gradient Metabolism mitosis ...
Topic Organizer # 3
... 14. Be able to recognize specialized human cells and know their functions in relation to their structure. ...
... 14. Be able to recognize specialized human cells and know their functions in relation to their structure. ...
1. The drawing shows part of a root hair cell. (a) Use words from the
... Name the process by which these gases move into and out of the cell. ...
... Name the process by which these gases move into and out of the cell. ...
Cell Study Guide - Miss Gleason`s Science
... structure: The basic framework of the cell membrane consists of a double layer of _________________ _________________ are found in the cell membrane, including some which are transmembrane and some that are peripheral membrane. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm consists of a clear liquid called ____________ ...
... structure: The basic framework of the cell membrane consists of a double layer of _________________ _________________ are found in the cell membrane, including some which are transmembrane and some that are peripheral membrane. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm consists of a clear liquid called ____________ ...
Chapter 6
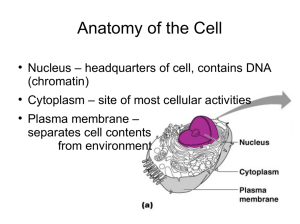
... • Function: control center of cell • Contains DNA • Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) ...
... • Function: control center of cell • Contains DNA • Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.