Cell division (mitosis) lab
... The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes. For example, each human cell possesses 46 chromosomes, while each cell of an onion possesses 8 chromosomes. All cells must replicate their DNA when dividin ...
... The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes. For example, each human cell possesses 46 chromosomes, while each cell of an onion possesses 8 chromosomes. All cells must replicate their DNA when dividin ...
File
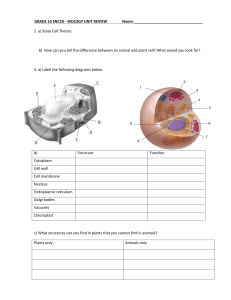
... Directions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the differences between plant cells and animal cells? 2. How do waste products, such as carbon dioxide leave cells? 3. What are cells? 4. Which part of a plant cell provides rigid support for t ...
... Directions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the differences between plant cells and animal cells? 2. How do waste products, such as carbon dioxide leave cells? 3. What are cells? 4. Which part of a plant cell provides rigid support for t ...
Organic Molecules - Riverdale Middle School
... • Long term energy storage – body uses last • Makes up most of the cell membrane • Fats, oils, and waxes • Whole milk, ice cream, and fried foods • Examples: – Cholesterol – found in your blood – Phosopholipids – make up cell membrane ...
... • Long term energy storage – body uses last • Makes up most of the cell membrane • Fats, oils, and waxes • Whole milk, ice cream, and fried foods • Examples: – Cholesterol – found in your blood – Phosopholipids – make up cell membrane ...
Cell Division
... 9. C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are log-like structures that appear near the nucleus during cell division in an animal cell and move to opposite poles to pull the chromosomes apart. 10. The S __ __ __ __ __ __ fibers are made of M __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ and connect each chromosome to the ...
... 9. C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are log-like structures that appear near the nucleus during cell division in an animal cell and move to opposite poles to pull the chromosomes apart. 10. The S __ __ __ __ __ __ fibers are made of M __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ and connect each chromosome to the ...
High
... What is the name of the element that the respiratory system takes in (Inhale) and transfers to cells for survival? ...
... What is the name of the element that the respiratory system takes in (Inhale) and transfers to cells for survival? ...
BIOLOGY EXAM REVIEW
... b) Explain what is happening in the diagram above and use the following terms in your explanation: Red blood cell, bronchioles, alveoli, bronchi, mouth, trachea, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ...
... b) Explain what is happening in the diagram above and use the following terms in your explanation: Red blood cell, bronchioles, alveoli, bronchi, mouth, trachea, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... 4. The goo of water and proteins that the organelles float in and where metabolic activities occur. 5. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions, only found in a eukaryotic cell 6. Converts sugar to energy in both plant and animal cells 7. Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food ...
... 4. The goo of water and proteins that the organelles float in and where metabolic activities occur. 5. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions, only found in a eukaryotic cell 6. Converts sugar to energy in both plant and animal cells 7. Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food ...
What do I need to know for Monday`s test? Prokaryotes Single cell
... Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)- Covered with ribosomes, the RER processes the proteins created by the ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) = makes lipids and breaks down toxins Golgi body – packages proteins into vesicles and ships them out of the cell. Mitochondria = the power ho ...
... Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)- Covered with ribosomes, the RER processes the proteins created by the ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) = makes lipids and breaks down toxins Golgi body – packages proteins into vesicles and ships them out of the cell. Mitochondria = the power ho ...
Characteristics of Cancer Cells
... a. Loss of inhibitors to prevent overcrowding in tissues b. Cell population increases at high densities…… tumor c. Proteins form that trigger an increase in blood capillaries that service the growing mass ...
... a. Loss of inhibitors to prevent overcrowding in tissues b. Cell population increases at high densities…… tumor c. Proteins form that trigger an increase in blood capillaries that service the growing mass ...
Mitosis Name: Background Concepts *What organelle contains the
... ---we can see chromosomes, if a cell is going through ______________________ ...
... ---we can see chromosomes, if a cell is going through ______________________ ...
Chap 7 HW Biology Due Date: Please compl
... 1. What are the two major parts of the cell? 2. What is the difference between the smooth ER and rough ER? 3. What is the function of the mitochondria? 4. You examine an unknown cell under a microscope and discover that the cell contains chloroplasts. From what type of organism does the cell li ...
... 1. What are the two major parts of the cell? 2. What is the difference between the smooth ER and rough ER? 3. What is the function of the mitochondria? 4. You examine an unknown cell under a microscope and discover that the cell contains chloroplasts. From what type of organism does the cell li ...
What is the Chapter 4 Test Like
... 1. Activity: Why Don’t Cells Grow Indefinitely? AND Review Worksheet: Cell Growth o How do you calculate surface area to volume ratios? o What is the significance of surface area to volume ratios? o Is a small cell or a large cell more efficient? 2. Activity: The Cell Theory o What were the contribu ...
... 1. Activity: Why Don’t Cells Grow Indefinitely? AND Review Worksheet: Cell Growth o How do you calculate surface area to volume ratios? o What is the significance of surface area to volume ratios? o Is a small cell or a large cell more efficient? 2. Activity: The Cell Theory o What were the contribu ...
The Eukaryotic Cell
... All eukaryotic cells have linear DNA, a nucleus, and membrane-bound organelles All eukaryotic cells have the following organelles in ...
... All eukaryotic cells have linear DNA, a nucleus, and membrane-bound organelles All eukaryotic cells have the following organelles in ...
2/11 Cloning and Transformation
... introduced into a cell – Has features that make it easier to insert DNA and select for presence of vector in cell. • Origin of replication • Antibiotic resistance gene • Cloning site ...
... introduced into a cell – Has features that make it easier to insert DNA and select for presence of vector in cell. • Origin of replication • Antibiotic resistance gene • Cloning site ...
PARTS OF THE CELL CELL ORGANELLES
... NUCLEUS: controls most cell processes and contains DNA (code for all proteins and other molecules made by cells) ...
... NUCLEUS: controls most cell processes and contains DNA (code for all proteins and other molecules made by cells) ...
Type of Cell Diversity
... Skeletal Muscle – elongated shape which allow cells to shorten (contract) moving our skeleton. They contain long protein fibers. Smooth Muscle – elongated shape too which allow our internal organs to change size ...
... Skeletal Muscle – elongated shape which allow cells to shorten (contract) moving our skeleton. They contain long protein fibers. Smooth Muscle – elongated shape too which allow our internal organs to change size ...
Cells
... – Rough endoplasmic reticulum (ribosomes are attached) – Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (no ribosomes) ...
... – Rough endoplasmic reticulum (ribosomes are attached) – Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (no ribosomes) ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.