Domain Bacteria
... These are your EXTREME ENVIRONMENT organisms. Although they are unicellular, they are probably more closely related to humans than they are to Eubacteria. ...
... These are your EXTREME ENVIRONMENT organisms. Although they are unicellular, they are probably more closely related to humans than they are to Eubacteria. ...
Ch. 10 Flip Book
... This is why cells do not grow much bigger even if the organism of which they are a part of does. Quick Lab (p. 242) Analyze & conclude 1-2 ...
... This is why cells do not grow much bigger even if the organism of which they are a part of does. Quick Lab (p. 242) Analyze & conclude 1-2 ...
Unit 7 Cheek Cell Lab
... • Our cheek cells are clear. Iodine is a brown color. It is also a stain. I will turn our cheek cells a brown color so that we will see them. ...
... • Our cheek cells are clear. Iodine is a brown color. It is also a stain. I will turn our cheek cells a brown color so that we will see them. ...
Compare the size of these organisms
... • What does replication mean? • To make an exact copy of the chromosome. ...
... • What does replication mean? • To make an exact copy of the chromosome. ...
ppt - University of Kentucky
... • Prokaryotic cells: Simpler, smaller, have no membrane bound nucleus or organelles. Have outer cell wall enclosing a fluid cytoplasm. E.g. bacteria (E. coli). ...
... • Prokaryotic cells: Simpler, smaller, have no membrane bound nucleus or organelles. Have outer cell wall enclosing a fluid cytoplasm. E.g. bacteria (E. coli). ...
Ch 4 quiz - TESADVBiology
... ____ 6.Which scientist determined that cells come only from other cells? a.van Leeuwenhoek b. Schleiden c. Schwann d. Virchow ____ 7.Which of the following is NOT part of the cell theory? a.All living things are made of one or more cells. b.All cells contain the same organelles. c.Cells are the basi ...
... ____ 6.Which scientist determined that cells come only from other cells? a.van Leeuwenhoek b. Schleiden c. Schwann d. Virchow ____ 7.Which of the following is NOT part of the cell theory? a.All living things are made of one or more cells. b.All cells contain the same organelles. c.Cells are the basi ...
CELL DIVISION
... Chromosomes • Chromosomes are the structures that contain genetic material we are passing from generation to generation in our cells. • Chromatin is the relaxed form of DNA in a cell’s nucleus. • Chromosomes are much more organized than chromatin. ...
... Chromosomes • Chromosomes are the structures that contain genetic material we are passing from generation to generation in our cells. • Chromatin is the relaxed form of DNA in a cell’s nucleus. • Chromosomes are much more organized than chromatin. ...
A View of the Cell
... are composed of many cells. And are said to be multicellular. Some organisms such as bacteria, yeast and protozoans are only single celled. ...
... are composed of many cells. And are said to be multicellular. Some organisms such as bacteria, yeast and protozoans are only single celled. ...
Mitosis ppt
... Multicellular organisms are made of cells and cell products Multicellular organisms have divided from a single cell Most cells are specialized ...
... Multicellular organisms are made of cells and cell products Multicellular organisms have divided from a single cell Most cells are specialized ...
9.1 CELLULAR GROWTH - Olathe School District
... How more sophisticated microscopes have allowed scientists to advance their knowledge of cells. -cells must stay small to function properly -cells use cell cycle to stay small -cells actively growing in interphase -when a growing cell reaches its max size, it keeps small by dividing into two smaller ...
... How more sophisticated microscopes have allowed scientists to advance their knowledge of cells. -cells must stay small to function properly -cells use cell cycle to stay small -cells actively growing in interphase -when a growing cell reaches its max size, it keeps small by dividing into two smaller ...
1.2.2 MITOSIS
... Third stage of cell division when the chromosomes begin to divide into two sister chromatids and go to opposite ends of the cell. 5.Telophase & Cytokinesis: Final stage where the cytoplasm divides completely in to two, the nuclear envelopes reform, and the nuclei begin to reform resulting in two new ...
... Third stage of cell division when the chromosomes begin to divide into two sister chromatids and go to opposite ends of the cell. 5.Telophase & Cytokinesis: Final stage where the cytoplasm divides completely in to two, the nuclear envelopes reform, and the nuclei begin to reform resulting in two new ...
Research into human body cell behaviour reveals
... allows us to have more complex functions than single cell organisms like yeast and bacteria. Cell specialization allows us to do things like hear, Provided by University of Western Australia pump blood and walk. "To make all of this work the human body has evolved protein messages that are used to c ...
... allows us to have more complex functions than single cell organisms like yeast and bacteria. Cell specialization allows us to do things like hear, Provided by University of Western Australia pump blood and walk. "To make all of this work the human body has evolved protein messages that are used to c ...
Cell Vocabulary
... substances to enter and exit cell. 4. Cytoplasm- Jelly like fluid between nucleus and cell membrane; holds organelles. 5. Mitochondria- Both cells- “powerhouse of cells”. Produces energy for cells. 6. Nucleus- Both cells- Control center or “Brain” of Cell. Directs the Cell activities. Both Cells 7. ...
... substances to enter and exit cell. 4. Cytoplasm- Jelly like fluid between nucleus and cell membrane; holds organelles. 5. Mitochondria- Both cells- “powerhouse of cells”. Produces energy for cells. 6. Nucleus- Both cells- Control center or “Brain” of Cell. Directs the Cell activities. Both Cells 7. ...
013368718X_CH10_143
... Controls on Cell Division Dozens of proteins regulate the cell cycle. Cyclins are proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. Regulatory proteins work both inside and outside of the cell. Internal regulators allow the cell cycle to proceed when certain events have occu ...
... Controls on Cell Division Dozens of proteins regulate the cell cycle. Cyclins are proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. Regulatory proteins work both inside and outside of the cell. Internal regulators allow the cell cycle to proceed when certain events have occu ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Eukaryotes (eu “true”; karyon “nucleus”) are cells that have a nucleus. • Prokaryotes (pro “before”) do not contain nuclei. • Nucleus – large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. ...
... • Eukaryotes (eu “true”; karyon “nucleus”) are cells that have a nucleus. • Prokaryotes (pro “before”) do not contain nuclei. • Nucleus – large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. ...
Unit 3 Test Review
... Answers do not need to be in complete sentences. 1. What is a prokaryote? 2. What is an example of an organism that has prokaryotic cells? 3. What is a eukaryote? 4. What is an example of an organism that has eukaryotic cells? 5. What is an organelle? 6. List 4 ways that prokaryotes are different fr ...
... Answers do not need to be in complete sentences. 1. What is a prokaryote? 2. What is an example of an organism that has prokaryotic cells? 3. What is a eukaryote? 4. What is an example of an organism that has eukaryotic cells? 5. What is an organelle? 6. List 4 ways that prokaryotes are different fr ...
Skeletal System Activities – Chapter 7
... 3.1.1 Summarize the principles of the cell theory. 3.1.2 Differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. 3.1.3 Identify the structure and function of the parts of a typical eukaryotic cell. 3.1.4 Compare and contrast structures of plant and animal cells. 3.1.5 Describe how a cell’s plasma m ...
... 3.1.1 Summarize the principles of the cell theory. 3.1.2 Differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. 3.1.3 Identify the structure and function of the parts of a typical eukaryotic cell. 3.1.4 Compare and contrast structures of plant and animal cells. 3.1.5 Describe how a cell’s plasma m ...
Cell Chart Review
... Embryonic Stem Cells Eukaryotic cells, found in animals. In early development these cells have the potential to become any cell in the body. Currently stem cells can be harvested from embryos, cord blood, and now some adult cells can be induced to turn back the clock and become stem cells. Stem cel ...
... Embryonic Stem Cells Eukaryotic cells, found in animals. In early development these cells have the potential to become any cell in the body. Currently stem cells can be harvested from embryos, cord blood, and now some adult cells can be induced to turn back the clock and become stem cells. Stem cel ...
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis
... – At some point, the cell would be unable to exchange enough materials to maintain cell ...
... – At some point, the cell would be unable to exchange enough materials to maintain cell ...
Name: Date: Block: Science 8 Chapter 1 Review Answer the
... 1. What are the 5 characteristics of living things? 2. What is the cell theory? 3. What is the field of view? Which objective lens will show you the greatest field of view? 4. What is the nucleus of a cell? 5. Explain the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? 6. What are chromosomes a ...
... 1. What are the 5 characteristics of living things? 2. What is the cell theory? 3. What is the field of view? Which objective lens will show you the greatest field of view? 4. What is the nucleus of a cell? 5. Explain the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? 6. What are chromosomes a ...
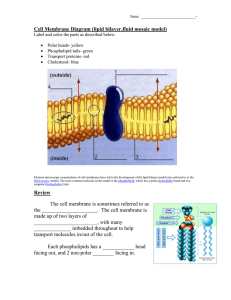
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... Polar heads- yellow Phospholipid tails- green Transport proteins- red Cholesterol- blue ...
... Polar heads- yellow Phospholipid tails- green Transport proteins- red Cholesterol- blue ...
Genetic lab 1
... Homologous Chromosome • In diploid (2n) organisms, the genome is composed of homologous chromosomes. • One chromosome of each homologous pair comes from the mother (called a maternal chromosome) and one comes from the father (paternal chromosome). ...
... Homologous Chromosome • In diploid (2n) organisms, the genome is composed of homologous chromosomes. • One chromosome of each homologous pair comes from the mother (called a maternal chromosome) and one comes from the father (paternal chromosome). ...
Cell Comparison *All in the Family*
... They are were energy (food) is produced so it can be used by all parts of the family (cell). ...
... They are were energy (food) is produced so it can be used by all parts of the family (cell). ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.