Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3)
... • allows for cell differentiation • allows organism to be more complex. Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems, limited to: • communication between cells (nervous system) • supplying the cells with nutrients (digestive system) • controlling exchanges with the e ...
... • allows for cell differentiation • allows organism to be more complex. Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems, limited to: • communication between cells (nervous system) • supplying the cells with nutrients (digestive system) • controlling exchanges with the e ...
B cells in Type 1 diabetes: Studies on cell surface antibody binding
... Innate and adaptive immune system The innate immune system is present at birth and provides an immediate response to foreign molecules and organisms. Its components treat all foreign substances in a generic but specific manner and respond to a defined number of antigens and structures, both from pat ...
... Innate and adaptive immune system The innate immune system is present at birth and provides an immediate response to foreign molecules and organisms. Its components treat all foreign substances in a generic but specific manner and respond to a defined number of antigens and structures, both from pat ...
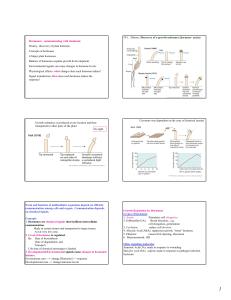
Hormones: communicating with chemicals History
... Balance of hormones regulate growth & development. Environmental signals can cause changes in hormone levels. Physiological effects- what changes does each hormone induce? Signal transduction- How does each hormone induce the response? ...
... Balance of hormones regulate growth & development. Environmental signals can cause changes in hormone levels. Physiological effects- what changes does each hormone induce? Signal transduction- How does each hormone induce the response? ...
Anillin, a Contractile Ring Protein That Cycles from the Nucleus to
... sembles metaphase furrow formation, as the plasma membrane invaginates down around each nucleus. The final stage consists of a contraction at the base of the invagination that results in the pinching off of individual cells though these remain attached to the yolk center by thin necks until gastrula ...
... sembles metaphase furrow formation, as the plasma membrane invaginates down around each nucleus. The final stage consists of a contraction at the base of the invagination that results in the pinching off of individual cells though these remain attached to the yolk center by thin necks until gastrula ...
Cells
... Reactions of Photosynthesis Light dependent reactions • Grana are stacks of thylakoids in the chloroplast that contain the chlorophyll which captures sunlight • Light dependent reactions take place in the thylakoids ...
... Reactions of Photosynthesis Light dependent reactions • Grana are stacks of thylakoids in the chloroplast that contain the chlorophyll which captures sunlight • Light dependent reactions take place in the thylakoids ...
The Balance between Cell Division and Endoreplication Depends
... retinoblastoma (RBR)/E2F/DP pathway. Arabidopsis thaliana DPB is regulated by phosphorylation and targeted to proteasome-mediated proteolysis by the SCFSKP2A complex. In addition, DPB interacts in vivo with E2FC, because ectopic coexpression of E2FC and DPB produces severe developmental defects. To ...
... retinoblastoma (RBR)/E2F/DP pathway. Arabidopsis thaliana DPB is regulated by phosphorylation and targeted to proteasome-mediated proteolysis by the SCFSKP2A complex. In addition, DPB interacts in vivo with E2FC, because ectopic coexpression of E2FC and DPB produces severe developmental defects. To ...
Epithelial repair is a two-stage process driven first by dying cells and
... (Rosenblatt et al., 2001). Following the induction of cell death by UV exposure, the dying cell signals through sphingosine 1phosphate (Gu et al., 2011). Immunostaining studies and liveimaging studies of wound healing after single-cell ablation within monolayers have revealed that this signal leads ...
... (Rosenblatt et al., 2001). Following the induction of cell death by UV exposure, the dying cell signals through sphingosine 1phosphate (Gu et al., 2011). Immunostaining studies and liveimaging studies of wound healing after single-cell ablation within monolayers have revealed that this signal leads ...
The plasma membrane recycling pathway and cell polarity in plants
... (PVCs). PVCs are randomly distributed within cells (Bolte et al., 2004a). They possibly function in the regulation of trafficking events between the Golgi stacks and lytic vacuoles (Bolte et al., 2004a; Kotzer et al., 2004). PVCs are essentially defined by the presence of specific vacuolar sorting r ...
... (PVCs). PVCs are randomly distributed within cells (Bolte et al., 2004a). They possibly function in the regulation of trafficking events between the Golgi stacks and lytic vacuoles (Bolte et al., 2004a; Kotzer et al., 2004). PVCs are essentially defined by the presence of specific vacuolar sorting r ...
PDF
... bitscore values) Dh showed maximum similarity with P. edulis (temperate bamboo) proteins compared to other species. Transcription factors act as molecular control of gene expression, regulating spatial, and temporal expression during various kinds of environmental responses (Nakashima et al., 2009; ...
... bitscore values) Dh showed maximum similarity with P. edulis (temperate bamboo) proteins compared to other species. Transcription factors act as molecular control of gene expression, regulating spatial, and temporal expression during various kinds of environmental responses (Nakashima et al., 2009; ...
lengthened g1 phase indicates differentiation status in
... Cyclin E and Cyclin D1; the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) CDK2 and CDK4; the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKI) p27 and p21; and the retinoblastoma protein (pRb). G1 can be divided into two phases: early G1 when pRb is un/hypophosphorylated and active and late G1 when pRb is hyperphosphorylat ...
... Cyclin E and Cyclin D1; the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) CDK2 and CDK4; the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKI) p27 and p21; and the retinoblastoma protein (pRb). G1 can be divided into two phases: early G1 when pRb is un/hypophosphorylated and active and late G1 when pRb is hyperphosphorylat ...
Osmosis and Diffusion Passive Transport
... • In the real world………. – In humans, osmosis occurs in the kidneys to recover the water form waste materials of the body. The kidneys regulate the concentration of water in the blood plasma. ...
... • In the real world………. – In humans, osmosis occurs in the kidneys to recover the water form waste materials of the body. The kidneys regulate the concentration of water in the blood plasma. ...
DNA double-strand breaks: signaling, repair and the cancer
... acetylases17 and the association of BRCA1 with a chromatin remodeling complex20 and with histone deacetylases17—is that BRCA1 and BRCA2 participate in HR by modulating chromatin structure. BRCA1 also appears to interact with another repair protein complex, RAD50/MRE11/NBS1, and co-localizes with it ...
... acetylases17 and the association of BRCA1 with a chromatin remodeling complex20 and with histone deacetylases17—is that BRCA1 and BRCA2 participate in HR by modulating chromatin structure. BRCA1 also appears to interact with another repair protein complex, RAD50/MRE11/NBS1, and co-localizes with it ...
Structure–function relationships during secondary phloem
... Fusiform cambial cells possessed a reticulate arrangement of randomly oriented CMTs, but there was no obviously preferred angle of orientation to the component microtubules (Figures 6 and 7). In elements of the secondary phloem at their earliest stages of development, i.e., in cells within the cambi ...
... Fusiform cambial cells possessed a reticulate arrangement of randomly oriented CMTs, but there was no obviously preferred angle of orientation to the component microtubules (Figures 6 and 7). In elements of the secondary phloem at their earliest stages of development, i.e., in cells within the cambi ...
4)Cell wall
... 1-They are heterotrophs. That is, they cannot manufacture their own food from simple compounds as plants are able to do. So they are dependent on other organisms to produce their foods, e.g., sugars, starches, proteins, fats, etc. Fungi can be further divided into saprobes, parasites, symbionts, fac ...
... 1-They are heterotrophs. That is, they cannot manufacture their own food from simple compounds as plants are able to do. So they are dependent on other organisms to produce their foods, e.g., sugars, starches, proteins, fats, etc. Fungi can be further divided into saprobes, parasites, symbionts, fac ...
University of Groningen How to get (a)round Pinho, Mariana
... cells to curved, spiral or even square bacteria, implies that there are different mechanisms guiding proper cell growth and division. In most bacteria, cell shape is maintained by the cell wall peptidoglycan sacculus, a sack-like macromolecule that encases the cytoplasmic membrane and is composed of ...
... cells to curved, spiral or even square bacteria, implies that there are different mechanisms guiding proper cell growth and division. In most bacteria, cell shape is maintained by the cell wall peptidoglycan sacculus, a sack-like macromolecule that encases the cytoplasmic membrane and is composed of ...
IUG - CELL BIO - E
... with the electron microscope. The freeze-etching technique has been used to cleave membranes down the center of the lipid bilayer, splitting them in half and exposing the interior. In this way it has been discovered that many membranes, including the plasma membrane, have a complex internal structur ...
... with the electron microscope. The freeze-etching technique has been used to cleave membranes down the center of the lipid bilayer, splitting them in half and exposing the interior. In this way it has been discovered that many membranes, including the plasma membrane, have a complex internal structur ...
Expansion of the phragmoplast during plant cytokinesis: a MAPK
... These findings suggest a role for NPK1 in cytokinesis. Indeed, inhibition of NPK1 signaling has been shown to result in a defect in cytokinesis [39••]. Overexpression of a kinase-negative mutant of NPK1 (NPK1KW) induces the formation of multinucleate cells that contain incomplete disc-shaped cell pl ...
... These findings suggest a role for NPK1 in cytokinesis. Indeed, inhibition of NPK1 signaling has been shown to result in a defect in cytokinesis [39••]. Overexpression of a kinase-negative mutant of NPK1 (NPK1KW) induces the formation of multinucleate cells that contain incomplete disc-shaped cell pl ...
PDF
... blastocyst attachment during implantation prevents any further influx of polar cells into the mural region and so is responsible for the initiation of egg-cylinder formation. When mouse blastocysts outgrow in vitro, a trophoblastic giant-cell monolayer is formed on which the ICM can be seen as a com ...
... blastocyst attachment during implantation prevents any further influx of polar cells into the mural region and so is responsible for the initiation of egg-cylinder formation. When mouse blastocysts outgrow in vitro, a trophoblastic giant-cell monolayer is formed on which the ICM can be seen as a com ...
Nondestructive Manipulation of Single Live Plant Cell by Laser
... 2. Nondestructive separation of living fission yeast cell The cell division of the fission yeast cell was conducted symmetrically and two daughter cells of the same size were produced. When the laser was focused directly on the interface between the pair of cells as shown in Fig. 3 (a), the pair was ...
... 2. Nondestructive separation of living fission yeast cell The cell division of the fission yeast cell was conducted symmetrically and two daughter cells of the same size were produced. When the laser was focused directly on the interface between the pair of cells as shown in Fig. 3 (a), the pair was ...
PDF
... consecutive confocal slices through the embryo between clonal ages ~50-65 hours (Fig. 3A-C). Older segments (anterior) contained mesoderm that was shifted ventrally with respect to the neuroectoderm, while in younger (posterior) segments, neuroectoderm was positioned ventral with respect to mesoderm ...
... consecutive confocal slices through the embryo between clonal ages ~50-65 hours (Fig. 3A-C). Older segments (anterior) contained mesoderm that was shifted ventrally with respect to the neuroectoderm, while in younger (posterior) segments, neuroectoderm was positioned ventral with respect to mesoderm ...
1 a dictyostelium mutant with reduced lysozyme levels compensates
... particles. The lysosome is the most potent degradative organelle within the eukaryotic cell. It contains hydrolytic enzymes that fulfill essential functions. In humans, many mutations affecting its constituents lead to the diseased state, often with dramatic consequences. Mutations of this sort fall ...
... particles. The lysosome is the most potent degradative organelle within the eukaryotic cell. It contains hydrolytic enzymes that fulfill essential functions. In humans, many mutations affecting its constituents lead to the diseased state, often with dramatic consequences. Mutations of this sort fall ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.