CELLULAR GROWTH 3 Reasons Why Cells Are Small
... than the surface area. The surface area to volume ratio decreases. Cells would have difficulty moving materials across the cell. 2. Transport of Substance- Once inside the cell materials move by diffusion and transport proteins. Cells remain small to maximize the ability to transport nutrients and w ...
... than the surface area. The surface area to volume ratio decreases. Cells would have difficulty moving materials across the cell. 2. Transport of Substance- Once inside the cell materials move by diffusion and transport proteins. Cells remain small to maximize the ability to transport nutrients and w ...
Name School Class Date Laboratory Investigation on Cells Observing Plant Cells
... microscope slide. The piece of onion should be no bigger than 1cm . Cover this with one drop of iodine solution and place the cover slip over this. Observe the cells using the x10 objective lens. ...
... microscope slide. The piece of onion should be no bigger than 1cm . Cover this with one drop of iodine solution and place the cover slip over this. Observe the cells using the x10 objective lens. ...
Biology Notes 3-2
... 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (SA:V) in order to function efficiently. Cell Featur ...
... 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (SA:V) in order to function efficiently. Cell Featur ...
CELL: the smallest unit of life. CHLOROPHYLL: a material in plants
... CHLOROPHYLL: a material in plants that helps them takes in sunlight. BIOTIC FACTOR: a living part of the ecosystem. ABIOTIC FACTORS: a nonliving part of the ecosystem ENVIRONMENT: all the living and nonliving things that surround an organism. TISSUE: similar cells acting to perform a specific functi ...
... CHLOROPHYLL: a material in plants that helps them takes in sunlight. BIOTIC FACTOR: a living part of the ecosystem. ABIOTIC FACTORS: a nonliving part of the ecosystem ENVIRONMENT: all the living and nonliving things that surround an organism. TISSUE: similar cells acting to perform a specific functi ...
Osmosis and Mitosis - Perth Grammar School
... Remember to save your work as you go along!! Either type answers into field or choose using drop down boxes.. Name two substances important to cells, which can diffuse into the cell. When a membrane is described as selectively permeable, what does this mean? What is the main differences between and ...
... Remember to save your work as you go along!! Either type answers into field or choose using drop down boxes.. Name two substances important to cells, which can diffuse into the cell. When a membrane is described as selectively permeable, what does this mean? What is the main differences between and ...
Lecture Quiz 2, Biol-1, C. Briggs, ver 9.13 (1pt each, unless noted
... b. Why does the order of these subunits matter in proteins? ...
... b. Why does the order of these subunits matter in proteins? ...
ADVANCED BIOLOGY Exam III (Chapter 3: Cell Structure and
... 3. Know the various types of organelles within both the animal and plant cells and their function(s). (Refer to Cell Function Wkshts) 4. What are the functions of all organelles within both the animal and plant cells. 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic c ...
... 3. Know the various types of organelles within both the animal and plant cells and their function(s). (Refer to Cell Function Wkshts) 4. What are the functions of all organelles within both the animal and plant cells. 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic c ...
3-cell-cycle-and-division-mitosis-16-17
... too many tasks to do (such as making proteins) and not enough DNA to get the job done efficiently. ...
... too many tasks to do (such as making proteins) and not enough DNA to get the job done efficiently. ...
Bio07_TR_U03_CH10.QXD
... 1. What happens to the cells at the edges of an injury when a cut in the skin or a break in a bone occurs? 2. What happens to the rapidly dividing cells when the healing process nears completion? ...
... 1. What happens to the cells at the edges of an injury when a cut in the skin or a break in a bone occurs? 2. What happens to the rapidly dividing cells when the healing process nears completion? ...
powerpoint jeopardy
... In an animal with 90 chromosomes, it is the number of chromosomes contributed by the mother. ...
... In an animal with 90 chromosomes, it is the number of chromosomes contributed by the mother. ...
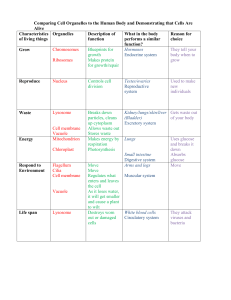
Comparing Cell Organelles to the Human Body and
... Endocrine system body when to Ribosomes Makes protein grow for growth/repair ...
... Endocrine system body when to Ribosomes Makes protein grow for growth/repair ...
Cells and Organelles Chart
... Match the function cards by writing or gluing them into the correct locations in the chart below. Include the household object you used to represent your organelle. Organelle Function/Description Household object Cell Membrane Cell Wall ...
... Match the function cards by writing or gluing them into the correct locations in the chart below. Include the household object you used to represent your organelle. Organelle Function/Description Household object Cell Membrane Cell Wall ...
Grade 6 Spelling
... Science1. Photosynthesis- process by which plants and other autotrophs capture and use light energy to make food from carbon dioxide and water 2. Autotroph- an organism that is able to capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food 3. Heterotroph- organism that cannot m ...
... Science1. Photosynthesis- process by which plants and other autotrophs capture and use light energy to make food from carbon dioxide and water 2. Autotroph- an organism that is able to capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food 3. Heterotroph- organism that cannot m ...
2.2 – Prokaryotic Cells
... must pass Cell Wall - Protects against mechanical and hypertonic stress, rupture caused by osmosis and possible harm from other organisms. Plasmid - Aid DNA exchange. These are DNA molecule capable of replicating. ...
... must pass Cell Wall - Protects against mechanical and hypertonic stress, rupture caused by osmosis and possible harm from other organisms. Plasmid - Aid DNA exchange. These are DNA molecule capable of replicating. ...
Cellular Level of Organization
... Use book/internet/handouts to fill in the information about cell organelles. Color back side diagram of parts. Memory clue: reminder of function Cell Organelle/ Location and Function How will you remember this info? Station/color Cell Wall/1 (plant cell only) Light green Cell membrane/1 Dark blue Cy ...
... Use book/internet/handouts to fill in the information about cell organelles. Color back side diagram of parts. Memory clue: reminder of function Cell Organelle/ Location and Function How will you remember this info? Station/color Cell Wall/1 (plant cell only) Light green Cell membrane/1 Dark blue Cy ...
2.3 Cell Division
... The sequence of growth and division cells undergo 3 main stages Parent cell divides to form two identical daughter cells ...
... The sequence of growth and division cells undergo 3 main stages Parent cell divides to form two identical daughter cells ...
Cell Organelle Function Matching Quiz (One of the terms below is
... Cell Organelle Function Matching Quiz (One of the terms below is not used) cell wall plasma (cell) membrane nucleus ribosome lysosome cilia chromosome cytosol ...
... Cell Organelle Function Matching Quiz (One of the terms below is not used) cell wall plasma (cell) membrane nucleus ribosome lysosome cilia chromosome cytosol ...
Morphogenesis – the process of cell development.
... Morphogenesis – the process of cell development. 1. All cells begin as a single cell 2. A horse grows and develops into an adult with millions of cells through: a. Cell growth b. Mitosis c. Cell division 3. Many different types of cells in full grown horses. a. Differences in cell is controlled by g ...
... Morphogenesis – the process of cell development. 1. All cells begin as a single cell 2. A horse grows and develops into an adult with millions of cells through: a. Cell growth b. Mitosis c. Cell division 3. Many different types of cells in full grown horses. a. Differences in cell is controlled by g ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... Be prepared to know the location and key words to define the cell parts. Use your worksheet from class to study the parts. You must be able to identify the following organelles by shape so you can label each part. You must also know the function of each cell part. Cell wall Mitochondria Chloroplast ...
... Be prepared to know the location and key words to define the cell parts. Use your worksheet from class to study the parts. You must be able to identify the following organelles by shape so you can label each part. You must also know the function of each cell part. Cell wall Mitochondria Chloroplast ...