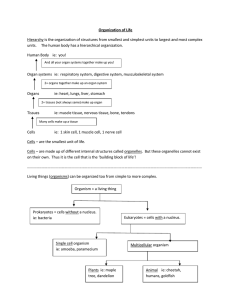
Organization of Life Hierarchy is the organization of structures from
... Organization of Life Hierarchy is the organization of structures from smallest and simplest units to largest and most complex units. The human body has a hierarchical organization. Human Body ie: you! And all your organ systems together make up you! ...
... Organization of Life Hierarchy is the organization of structures from smallest and simplest units to largest and most complex units. The human body has a hierarchical organization. Human Body ie: you! And all your organ systems together make up you! ...
Do Animal Cells have a Cell Wall? What are cells walls made of
... Do Animal Cells have a What are tiny cell structures that carry out specific Cell Wall? functions with a cell? ...
... Do Animal Cells have a What are tiny cell structures that carry out specific Cell Wall? functions with a cell? ...
Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7 “I can…” state discuss
... Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7) ...
... Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7) ...
Cell Membrane Animal Cell Controls what enters and leaves the cell
... Animal Cell Controls activity within the cell (“brain” of the cell) ...
... Animal Cell Controls activity within the cell (“brain” of the cell) ...
Question Before the video After the video How many cells are there
... does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do genes have to do with cells? How many chromosomes do you have and how do you get them? How many cells are there in an egg? Why do they call red blood cells “red”. Explain What do white blood cells do? What is osmosis? What is unusual ...
... does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do genes have to do with cells? How many chromosomes do you have and how do you get them? How many cells are there in an egg? Why do they call red blood cells “red”. Explain What do white blood cells do? What is osmosis? What is unusual ...
Section 9.2 * Mitosis and Cytokinesis
... • During mitosis, the cells’ copied genetic material separates and the cell prepares to split into two cells • This allows the cell’s genetic material to pass into the new cells – The resulting daughter cells are genetically identical!! ...
... • During mitosis, the cells’ copied genetic material separates and the cell prepares to split into two cells • This allows the cell’s genetic material to pass into the new cells – The resulting daughter cells are genetically identical!! ...
Cell Unit Project (Chapters 1-2)
... Contributions to the Study of Cells 1. Comparisons between the 3 types of microscopes: Light, SEM, TEM 2. Discoveries made by Louis Pasteur 3. The theory of spontaneous generation Domains (Provide a description of each domain and state whether organisms found in each domain are prokaryotes or eukary ...
... Contributions to the Study of Cells 1. Comparisons between the 3 types of microscopes: Light, SEM, TEM 2. Discoveries made by Louis Pasteur 3. The theory of spontaneous generation Domains (Provide a description of each domain and state whether organisms found in each domain are prokaryotes or eukary ...
Cell Structure Cloze - Science
... All living organisms are composed of microscopic building blocks called _________________. These cells have many different basic structures in common called _________________. For example, cells are surrounded by a cell _________________ which controls the materials that move in and out of a cell. A ...
... All living organisms are composed of microscopic building blocks called _________________. These cells have many different basic structures in common called _________________. For example, cells are surrounded by a cell _________________ which controls the materials that move in and out of a cell. A ...
Cell theory + structure
... Describe the contributions of the following scientists: Robert Hooke – Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Matthias Schleiden – Theodor Schwann – Rudolph Virchow – All cells come from pre-existing cells The Cell Theory State the three components of the cell theory: 1. ___________________________________________ ...
... Describe the contributions of the following scientists: Robert Hooke – Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Matthias Schleiden – Theodor Schwann – Rudolph Virchow – All cells come from pre-existing cells The Cell Theory State the three components of the cell theory: 1. ___________________________________________ ...
mitosis veg prop - Hicksville Public Schools
... The body cells of all organisms have a special way of dividing. The dividing of a cell to form two new cells that are exactly alike is called mitosis. The dividing cell is called the parent cell, & the 2 new cells are called the daughter cells. Before the parent cell divides it makes a copy of its n ...
... The body cells of all organisms have a special way of dividing. The dividing of a cell to form two new cells that are exactly alike is called mitosis. The dividing cell is called the parent cell, & the 2 new cells are called the daughter cells. Before the parent cell divides it makes a copy of its n ...
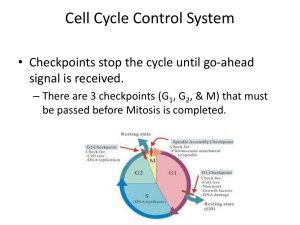
Cell Cycle Control System - Santa Susana High School
... • Checkpoints stop the cycle until go-ahead signal is received. – There are 3 checkpoints (G1, G2, & M) that must be passed before Mitosis is completed. ...
... • Checkpoints stop the cycle until go-ahead signal is received. – There are 3 checkpoints (G1, G2, & M) that must be passed before Mitosis is completed. ...
Unit 2 Part 1: The Cell Test Review 1. What is the function of a cell`s
... 13. What does the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum look like? 14. How does the cell membrane function like a security gate? 15. What gets energy by absorbing materials and does not have chloroplast? 16. What part of the phospholipid is attracted to water? Which part repels water? 17. What did ...
... 13. What does the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum look like? 14. How does the cell membrane function like a security gate? 15. What gets energy by absorbing materials and does not have chloroplast? 16. What part of the phospholipid is attracted to water? Which part repels water? 17. What did ...
Cell membrane
... The gel-like fluid inside of a cell made of mostly water. The other organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm. Nucleus ...
... The gel-like fluid inside of a cell made of mostly water. The other organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm. Nucleus ...
Mitosis Meiosis
... • The diploid mother cell (diploid means it has 2 sets of chromosomes) doubles its DNA so that it has one set for each new cell. This means that each daughter cell has a full set of chromosomes. ...
... • The diploid mother cell (diploid means it has 2 sets of chromosomes) doubles its DNA so that it has one set for each new cell. This means that each daughter cell has a full set of chromosomes. ...
How are new cells made? - Social Circle City Schools
... copy of its DNA called replication. 3. The cell prepares to divide into two cells. Page 96 ...
... copy of its DNA called replication. 3. The cell prepares to divide into two cells. Page 96 ...
L3 I Have, Who Has? Cards
... Who has the basic unit of structure and function in all living things? ...
... Who has the basic unit of structure and function in all living things? ...
Mitosis Online Lab
... Use the following formula to calculate the duration of each stage: % of cells in stage x 1440 minutes (24 hours) = ___________ minutes of cell cycle spent in stage Analysis Questions ...
... Use the following formula to calculate the duration of each stage: % of cells in stage x 1440 minutes (24 hours) = ___________ minutes of cell cycle spent in stage Analysis Questions ...
Biology Play Dough Mitosis Use your notes to answer the following
... Biology Play Dough Mitosis Use your notes to answer the following questions about cell division. Use complete sentences. ...
... Biology Play Dough Mitosis Use your notes to answer the following questions about cell division. Use complete sentences. ...
CHAPTER 12 THE CELL CYCLE
... 1. Understand that cell division functions in reproduction, growth, renewal and repair. 2. Explain how chromatin, chromosomes and genomes relate to one another 3. Describe the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete. The Mitotic Cell Cycle 1. Describe the process of binary fission in bacteria ...
... 1. Understand that cell division functions in reproduction, growth, renewal and repair. 2. Explain how chromatin, chromosomes and genomes relate to one another 3. Describe the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete. The Mitotic Cell Cycle 1. Describe the process of binary fission in bacteria ...
Ch. 22 Cell Reproduction
... Cell Cycle • The life of a cell is called the cell cycle • It has five main phases – G1: this phase is for GROWTH and making new organelles. – S phase: this phase for SYNTHESIZING chromosomes. – G2: this phase is a second GROWTH phase dedicated to growing in size to prepare for cell division. – Mit ...
... Cell Cycle • The life of a cell is called the cell cycle • It has five main phases – G1: this phase is for GROWTH and making new organelles. – S phase: this phase for SYNTHESIZING chromosomes. – G2: this phase is a second GROWTH phase dedicated to growing in size to prepare for cell division. – Mit ...