Cell Reproduction
... PROPHASE The first phase = ____________ This is the ________ longest phase (OF MITOSIS) During this phase, chromatin coils to form visible _____________ chromosomes Each chromosome is made up of ___ 2 sister chromatids and are held together by a __________ centromere *Remember: The chromoso ...
... PROPHASE The first phase = ____________ This is the ________ longest phase (OF MITOSIS) During this phase, chromatin coils to form visible _____________ chromosomes Each chromosome is made up of ___ 2 sister chromatids and are held together by a __________ centromere *Remember: The chromoso ...
Mitosis
... ● Spindle fibers pull on chromosomes ● Centromere breaks, sister chromatids move to opposite centrioles ...
... ● Spindle fibers pull on chromosomes ● Centromere breaks, sister chromatids move to opposite centrioles ...
Allium Mitosis Lab ppt
... Metaphase Cell prepares chromosomes for division by: • aligning chromosomes at cell equator • attaching spindle fibers to sister chromatids of each chromosome ...
... Metaphase Cell prepares chromosomes for division by: • aligning chromosomes at cell equator • attaching spindle fibers to sister chromatids of each chromosome ...
Starter Activity
... Starter Activity • Name 4 differences between plant and animal cells. ANSWERS 1. Shape (plant cells are rectangular and animal cells are generally round) 2. Plant cells have a large vacuole 3. Plant cells have a cell wall (to provide extra structure) 4. Plant cells have chroloplasts (where photosynt ...
... Starter Activity • Name 4 differences between plant and animal cells. ANSWERS 1. Shape (plant cells are rectangular and animal cells are generally round) 2. Plant cells have a large vacuole 3. Plant cells have a cell wall (to provide extra structure) 4. Plant cells have chroloplasts (where photosynt ...
Document
... cells, each cell keeps one of the two halves and grows a smaller half within it. • After each division cycle the average size of diatom cells in the population gets smaller. • When a certain minimum size is reached, they reverse this decline by expanding in size to give rise to a much larger cell – ...
... cells, each cell keeps one of the two halves and grows a smaller half within it. • After each division cycle the average size of diatom cells in the population gets smaller. • When a certain minimum size is reached, they reverse this decline by expanding in size to give rise to a much larger cell – ...
Chapter 1 (C) Review
... b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, long life, and cell specialization. b. generalized cells, longer ...
... b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, long life, and cell specialization. b. generalized cells, longer ...
Cells specialize to carry out different jobs
... You started out as an unspecialized cell – a single cell, a fertilized egg. Really soon after an egg is fertilized by a sperm cell, it begins to divide. The single cell divides by mitosis until it forms a ball of cells called an embryo. At some early point in the life of this embryo, the cells begin ...
... You started out as an unspecialized cell – a single cell, a fertilized egg. Really soon after an egg is fertilized by a sperm cell, it begins to divide. The single cell divides by mitosis until it forms a ball of cells called an embryo. At some early point in the life of this embryo, the cells begin ...
UNICELLULAR MULTICELLULAR
... organisms and moves them into the REPRODUCE vacuoles Digest-enzymes move into the GROW AND REPAIR vacuole in order to break down food into nutrients that can be used INGEST by the cell Reproduce-binary fission-divides DIGEST into two cells that are identical to EXCRETE the original cell Excrete-wast ...
... organisms and moves them into the REPRODUCE vacuoles Digest-enzymes move into the GROW AND REPAIR vacuole in order to break down food into nutrients that can be used INGEST by the cell Reproduce-binary fission-divides DIGEST into two cells that are identical to EXCRETE the original cell Excrete-wast ...
Gametogenesis - NCEA Level 2 Biology
... Oogenesis differs from spermatogenesis in a number of ways. ...
... Oogenesis differs from spermatogenesis in a number of ways. ...
Study guide
... 1. State the three major principles of the cell theory. 2. Why is there a limit to cell size? Describe two types of problems that would be encountered if cell was significantly larger than they actually are. 3. What four features of cells do all organisms (i.e. both prokaryotes and eukaryotes) conta ...
... 1. State the three major principles of the cell theory. 2. Why is there a limit to cell size? Describe two types of problems that would be encountered if cell was significantly larger than they actually are. 3. What four features of cells do all organisms (i.e. both prokaryotes and eukaryotes) conta ...
Sc 8 Unit 2 Topic 3 Notes WD
... -Cannot grow very large, must take in all materials they need through cell membranes so most can only live in watery, food-rich surroundings Multicellular (many-celled): -Made up of 2 or more cells -Bigger and more complex -May look different because they are specialized for specific functions -Can ...
... -Cannot grow very large, must take in all materials they need through cell membranes so most can only live in watery, food-rich surroundings Multicellular (many-celled): -Made up of 2 or more cells -Bigger and more complex -May look different because they are specialized for specific functions -Can ...
No Slide Title
... hemophilia. They are pregnant with a boy. What are the chances that the boy will have hemophilia? ...
... hemophilia. They are pregnant with a boy. What are the chances that the boy will have hemophilia? ...
name date ______ period
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle the correct answer for each question that follows. The nucleus includes all of the following EXCEPT ____________________ A. cytoplasm B. nuclear envelope C. DNA D. nucleolus E. chromatin Cells like muscle cells which require lots of energy would probably have many ___________ ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle the correct answer for each question that follows. The nucleus includes all of the following EXCEPT ____________________ A. cytoplasm B. nuclear envelope C. DNA D. nucleolus E. chromatin Cells like muscle cells which require lots of energy would probably have many ___________ ...
Research Scientist, Molecular and Cell Biology
... biologist to join the team. The successful candidate will join active drug discovery programmes and can expect to be involved with a broad range of different activities but particularly: ...
... biologist to join the team. The successful candidate will join active drug discovery programmes and can expect to be involved with a broad range of different activities but particularly: ...
Cell Physiology
... • Requires ATP input from cell • Solute pumps – Specialized protein carriers – Most move from low to high concentration ...
... • Requires ATP input from cell • Solute pumps – Specialized protein carriers – Most move from low to high concentration ...
Biology Notes 1 and 2
... 1. What is the difference between a chromosome and gene? 2. What happen in the nucleus before it can undergo mitosis? 3. What is the function of mitosis? 4. Look up “cell interphase”. What happens during this stage of the cell cycle? 5. Why does the nuclear membrane break down in mitosis? 6. What ce ...
... 1. What is the difference between a chromosome and gene? 2. What happen in the nucleus before it can undergo mitosis? 3. What is the function of mitosis? 4. Look up “cell interphase”. What happens during this stage of the cell cycle? 5. Why does the nuclear membrane break down in mitosis? 6. What ce ...
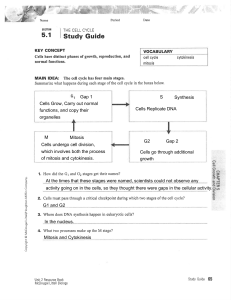
5.1 Study Guide KEY
... The rate of cell division is linked to the body's need for that type of cell. Skin cells are typically exposed to more damaging conditions and must be replaced more often than liver cells. ...
... The rate of cell division is linked to the body's need for that type of cell. Skin cells are typically exposed to more damaging conditions and must be replaced more often than liver cells. ...
Cell biology - Central Magnet School
... Cells display organization Obtain and use energy to perform chemical reactions (metabolism) Change through time (adapt) Respond to their environment/stimulus Reproduce Growth and development Homeostasis ...
... Cells display organization Obtain and use energy to perform chemical reactions (metabolism) Change through time (adapt) Respond to their environment/stimulus Reproduce Growth and development Homeostasis ...