Chapter 4 Eukaryotic Cell
... Free in the cytoplasm Show up as dots in a micrograph. Made up of two subunits. Each subunit is made up of proteins and ribosomal RNA. • Eukaryotic cell has 80s ribosomes. • Larger and denser than prokarytoic ribosomes. ...
... Free in the cytoplasm Show up as dots in a micrograph. Made up of two subunits. Each subunit is made up of proteins and ribosomal RNA. • Eukaryotic cell has 80s ribosomes. • Larger and denser than prokarytoic ribosomes. ...
Mitosis Notes
... • 1 cell ÷ into 2 identical daughter cells (same genetic info) • Eukaryotes (cells w/ nucleus) go through 2 stages of ÷ • Mitosis – ÷ of nucleus – Cytokinesis – ÷ of cytoplasm ...
... • 1 cell ÷ into 2 identical daughter cells (same genetic info) • Eukaryotes (cells w/ nucleus) go through 2 stages of ÷ • Mitosis – ÷ of nucleus – Cytokinesis – ÷ of cytoplasm ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Body Systems
... Cilia: tiny hairs that can move some cells or the surrounding environment ...
... Cilia: tiny hairs that can move some cells or the surrounding environment ...
Which step of the design process is exemplified below:
... the nucleus of the cell. · Mitosis enables a cell to make an exact copy of it. · Mitosis is a process of cell division, which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. · The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. · Mitosis is nee ...
... the nucleus of the cell. · Mitosis enables a cell to make an exact copy of it. · Mitosis is a process of cell division, which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. · The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. · Mitosis is nee ...
The cell is the smallest unit of life
... Cells contain tiny structures that perform specific functions that are called ___________. The ________ ________ is a rigid layer of non-living material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. The cell wall is made of a tough, yet flexible, material called __________________. Th ...
... Cells contain tiny structures that perform specific functions that are called ___________. The ________ ________ is a rigid layer of non-living material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. The cell wall is made of a tough, yet flexible, material called __________________. Th ...
Eukaryotic cells Section review model answers Ribosomes are
... animal cells do not have. Plant cells do not seem to have small lysosomes (they have large vacuoles instead), which animal cells do have. 5. Ribosomes are the organelles where proteins are made. All cells need protein in order to live. 6. Mitochondria are organelles that produce most of a cell’s ene ...
... animal cells do not have. Plant cells do not seem to have small lysosomes (they have large vacuoles instead), which animal cells do have. 5. Ribosomes are the organelles where proteins are made. All cells need protein in order to live. 6. Mitochondria are organelles that produce most of a cell’s ene ...
Study Guide for AP Biology Mid-term Biochemistry What is
... 2. Why is ATP a common energy source for organisms? 3. What factors affect the rate of an enzyme mediated reaction? 4. How do enzymes affect biochemical reactions? ...
... 2. Why is ATP a common energy source for organisms? 3. What factors affect the rate of an enzyme mediated reaction? 4. How do enzymes affect biochemical reactions? ...
AP Bio - Chapter 6.4 Presentation
... Cell sap inside, different than cytosol Holds reserve organic and inorganic compounds, metabolic byproducts, pigmentation, and toxins. More H2O in vacuole, bigger plant cell ...
... Cell sap inside, different than cytosol Holds reserve organic and inorganic compounds, metabolic byproducts, pigmentation, and toxins. More H2O in vacuole, bigger plant cell ...
Structure and Function of Cells
... transporting materials, storing and releasing energy, getting rid of waste materials, and increasing in number. The following diagrams show two typical cells. Identify whether the cell is a plant or animal cell, and then label the following structures. ...
... transporting materials, storing and releasing energy, getting rid of waste materials, and increasing in number. The following diagrams show two typical cells. Identify whether the cell is a plant or animal cell, and then label the following structures. ...
Assessment
... a. a long, hairlike structure that enables a cell to move b. a distinct group of cells that have a similar structure and function c. a collection of tissues of different types that function together to carry out a specific function ...
... a. a long, hairlike structure that enables a cell to move b. a distinct group of cells that have a similar structure and function c. a collection of tissues of different types that function together to carry out a specific function ...
Year 8 Science
... Bacterial cells are microscopic unicellular organisms with no membrane around their nucleoid DNA (prokaryotic). ...
... Bacterial cells are microscopic unicellular organisms with no membrane around their nucleoid DNA (prokaryotic). ...
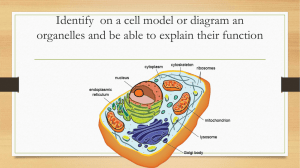
Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to
... Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to explain their function ...
... Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to explain their function ...
Parts of the Eukaryotic Cell
... Parts of the Eukaryotic Cell Cell Membrane Selectively permeable = only certain things can enter/exit the cell Cytoplasm Contain the organelles of the cell Nucleus stores the hereditary information in its DNA; controls the cell Nuclear Membrane Double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, has nuclear ...
... Parts of the Eukaryotic Cell Cell Membrane Selectively permeable = only certain things can enter/exit the cell Cytoplasm Contain the organelles of the cell Nucleus stores the hereditary information in its DNA; controls the cell Nuclear Membrane Double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, has nuclear ...
logcsscibap_2_1_2_d_..
... Choose one of these structures and explain why it is not found in animal cells. (1 mark) ...
... Choose one of these structures and explain why it is not found in animal cells. (1 mark) ...
Cell Motility - Cochran`s Half Acre
... Components of the Cytoskeleton: • Intermediate Filaments – Only in animal cells of specific tissues – Mechanically strengthen cells or cell parts and help maintain shape ...
... Components of the Cytoskeleton: • Intermediate Filaments – Only in animal cells of specific tissues – Mechanically strengthen cells or cell parts and help maintain shape ...
Answers for extension worksheet – Chapter 2
... Membranes all have similar structures but cells (such as endocrine cells) that take in or secrete many different substances will have a greater proportion of protein channels. A red blood cell does not do this so will have a lower proportion of protein compared with other cells. ...
... Membranes all have similar structures but cells (such as endocrine cells) that take in or secrete many different substances will have a greater proportion of protein channels. A red blood cell does not do this so will have a lower proportion of protein compared with other cells. ...
Cell Analogy Paper
... 1. The different parts and activities of a cell can be compared to a factory. 2. The parts of a cell are called organelles. 3. The activities that a cell does are called functions. 4. Like a fence, the cell membrane controls what goes in and out of the cell. 5. Like a computer holding instructions, ...
... 1. The different parts and activities of a cell can be compared to a factory. 2. The parts of a cell are called organelles. 3. The activities that a cell does are called functions. 4. Like a fence, the cell membrane controls what goes in and out of the cell. 5. Like a computer holding instructions, ...
Ch. 6 Section 3 Directed Reading/Quiz
... b. A nuclear envelope forms around the chromatids at each pole. c. Chromosomes coil up and become visible. d. The two chromatids move toward opposite poles as the spindle fibers attached to them shorten. ...
... b. A nuclear envelope forms around the chromatids at each pole. c. Chromosomes coil up and become visible. d. The two chromatids move toward opposite poles as the spindle fibers attached to them shorten. ...
Cell Theory Timeline
... He is the first to call the spaces in the cork “cells” which means little rooms. ...
... He is the first to call the spaces in the cork “cells” which means little rooms. ...