The Function of Organelles
... Energy released by mitochondria is stored in ATP Most of cell’s ATP made here Animal cells can’t make own food so we need these to break down sugar for energy ...
... Energy released by mitochondria is stored in ATP Most of cell’s ATP made here Animal cells can’t make own food so we need these to break down sugar for energy ...
Cells are organized into.
... • This is the maintenance of the normal operating conditions of an organism. • Control of body temperature, pulse rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, urine output, digestive absorption, metabolism rate, growth rate and hormone levels all need to be maintained. ...
... • This is the maintenance of the normal operating conditions of an organism. • Control of body temperature, pulse rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, urine output, digestive absorption, metabolism rate, growth rate and hormone levels all need to be maintained. ...
People creditied for discovering the cell theory
... o Theodore Schwann- 1838- german zoologist who concluded all animals and animal parts are composed of cells o Rudolph Virchow- 1858- german physician who concluded all cells must come from other cells CELL THEORY: o 1. All living things are composed of cells o Cells are the basic unit of life o Al ...
... o Theodore Schwann- 1838- german zoologist who concluded all animals and animal parts are composed of cells o Rudolph Virchow- 1858- german physician who concluded all cells must come from other cells CELL THEORY: o 1. All living things are composed of cells o Cells are the basic unit of life o Al ...
KEY WORDS/
... c. Diploid: Cells that have two sets of DNA – one set from each parent. Often designated as 2n...where n stands for the amount of DNA in a set and the 2 means you have 2 sets. d. Haploid: Cells that have one set of DNA. Often designated as “n”. AKA gametes e. Somatic Cell: AKA body cells – any diplo ...
... c. Diploid: Cells that have two sets of DNA – one set from each parent. Often designated as 2n...where n stands for the amount of DNA in a set and the 2 means you have 2 sets. d. Haploid: Cells that have one set of DNA. Often designated as “n”. AKA gametes e. Somatic Cell: AKA body cells – any diplo ...
Cell Structure Guided Notes
... 4. Which is largest, a plant cell, an animal cell, or a bacterial cell? 5. Cells in multicellular organisms often specialize or DIFFERENTIATE. What does this mean? ...
... 4. Which is largest, a plant cell, an animal cell, or a bacterial cell? 5. Cells in multicellular organisms often specialize or DIFFERENTIATE. What does this mean? ...
Mitosis PowerPoint
... Description of Stage The final phase of mitosis. Two distinct daughter cells are formed and the cells begin to separate. This stage is indicated by the formation of a cell plate in plant cells and a cleavage furrow in animal cells. ...
... Description of Stage The final phase of mitosis. Two distinct daughter cells are formed and the cells begin to separate. This stage is indicated by the formation of a cell plate in plant cells and a cleavage furrow in animal cells. ...
Biology Review
... 5. What is the basic unit of all living things? 6. Where is the cell’s genetic information found? ...
... 5. What is the basic unit of all living things? 6. Where is the cell’s genetic information found? ...
Chapter 9 PowerPoint Lecture
... • Cellulose deposits begin to form at the cell plate, forming a crosswall that divides the parent cell into two daughter cells. ...
... • Cellulose deposits begin to form at the cell plate, forming a crosswall that divides the parent cell into two daughter cells. ...
Cell wall Single large vacuole Chloroplasts
... The contents of an animal cell, meanwhile, are held by the cell membrane alone. Animals tend to rely on endo- and exo-skeletons for support. ...
... The contents of an animal cell, meanwhile, are held by the cell membrane alone. Animals tend to rely on endo- and exo-skeletons for support. ...
Slide 1
... How do Molecules form Living, Moving, Reproducing Cells? 1683, Leeuwenhoek: “An unbelievably great company of living animalcules, a-swimming more nimbly than any I had ever seen up to this time. The biggest sort bent their body into curves in going forwards." ...
... How do Molecules form Living, Moving, Reproducing Cells? 1683, Leeuwenhoek: “An unbelievably great company of living animalcules, a-swimming more nimbly than any I had ever seen up to this time. The biggest sort bent their body into curves in going forwards." ...
The cell cycle - U of L Class Index
... • Forming of nuclear envelope • Chromatin is less condensed • Mitosis is complete • Cytokinesis: formation of cleavage furrow and separation of two daughter cells Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells • Cytokinesis begins during telophase of mitosis • It is different in plants and animals. • In anim ...
... • Forming of nuclear envelope • Chromatin is less condensed • Mitosis is complete • Cytokinesis: formation of cleavage furrow and separation of two daughter cells Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells • Cytokinesis begins during telophase of mitosis • It is different in plants and animals. • In anim ...
The “brains” of the cell, that directs cell activities and contains
... plant cells than in animal cells ...
... plant cells than in animal cells ...
Cells: The Basic Units of Life
... All living things are made up of one or more cells. The compound microscope is an instrument used to see cells and can help us learn more about the structure and function of cells. Microscopes and the skills of scientific inquiry can be used to learn more about the structure of cells. Plant and anim ...
... All living things are made up of one or more cells. The compound microscope is an instrument used to see cells and can help us learn more about the structure and function of cells. Microscopes and the skills of scientific inquiry can be used to learn more about the structure of cells. Plant and anim ...
Name
... 13. The structures that hold together sister chromatids are _______________________. 14. The structures that carry genetic material are ______________________. 15. The uncontrolled division of cells is ___________________________. 16. The two halves of a doubled chromosome structure are called _____ ...
... 13. The structures that hold together sister chromatids are _______________________. 14. The structures that carry genetic material are ______________________. 15. The uncontrolled division of cells is ___________________________. 16. The two halves of a doubled chromosome structure are called _____ ...
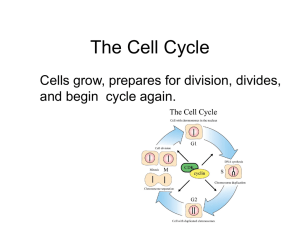
Stages of the cell cycle
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
Centriole organelles made of microtubules involved in cell division
... Maintains cell shape, works with central vacuole to maintain turgor pressure ...
... Maintains cell shape, works with central vacuole to maintain turgor pressure ...
The Cell Cycle (2009).
... Cell Growth DNA Replication (in preparation for cell division) Preparation for the M phase ...
... Cell Growth DNA Replication (in preparation for cell division) Preparation for the M phase ...
Cell Processes Study Guide
... Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight -------- Glucose + Oxygen Cellular Respiration – this process takes place in the mitochondrion of the cell Glucose + Oxygen ---------Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (useable cell energy) Know the “chemical” representations for each of the chemicals in BOTH equations Fe ...
... Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight -------- Glucose + Oxygen Cellular Respiration – this process takes place in the mitochondrion of the cell Glucose + Oxygen ---------Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (useable cell energy) Know the “chemical” representations for each of the chemicals in BOTH equations Fe ...