Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... The theory that all living things are made from cells and come only from pre-existing cells; cells are the basic structural and functional unit of life. ...
... The theory that all living things are made from cells and come only from pre-existing cells; cells are the basic structural and functional unit of life. ...
Cell Growth
... B. Forms of DNA and eukaryotic chromosomes (xsomes) 1. the chemical structure of DNA is always the same, changes are only physical 2. (**chromatin)- thin uncoiled strands of DNA in the nucleus (spaghetti in a TIN can) 3. (**chromosome) (xsome)- one long piece of double stranded DNA coiled into a rod ...
... B. Forms of DNA and eukaryotic chromosomes (xsomes) 1. the chemical structure of DNA is always the same, changes are only physical 2. (**chromatin)- thin uncoiled strands of DNA in the nucleus (spaghetti in a TIN can) 3. (**chromosome) (xsome)- one long piece of double stranded DNA coiled into a rod ...
Cellular Reproduction Study Guide
... pair) align in the middle? 12) How any cells result from meiosis? What is their chromosome number? Are they identical to the parent cell? 13) Draw telophase for a 2N=2 cell. 14) When are the chromosomes doubled and DNA replicated? 15) Does crossing over occur? Why or why not? 16) Be able to explain ...
... pair) align in the middle? 12) How any cells result from meiosis? What is their chromosome number? Are they identical to the parent cell? 13) Draw telophase for a 2N=2 cell. 14) When are the chromosomes doubled and DNA replicated? 15) Does crossing over occur? Why or why not? 16) Be able to explain ...
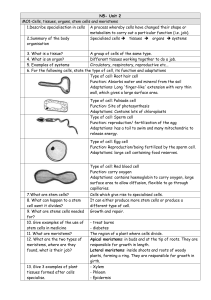
N5- Unit 2 MO1-Cells, tissues, organs, stem cells and meristems 1
... It can either produce more stem cells or produce a different type of cell. Growth and repair. - treat burns - diabetes The region of a plant where cells divide. Apical meristems: in buds and at the tip of roots. They are responsible for growth in length. Lateral meristems: inside shoots and roots of ...
... It can either produce more stem cells or produce a different type of cell. Growth and repair. - treat burns - diabetes The region of a plant where cells divide. Apical meristems: in buds and at the tip of roots. They are responsible for growth in length. Lateral meristems: inside shoots and roots of ...
Cell Structure Review
... 15. The _________________ is the smallest unit that can carry out all of the processes of life. The basic unit of life. 16. The maximum size to which a cell may grow is limited mainly by the cell's ___________________ ____________________. 17. Organisms whose cells never contain a membrane bound nuc ...
... 15. The _________________ is the smallest unit that can carry out all of the processes of life. The basic unit of life. 16. The maximum size to which a cell may grow is limited mainly by the cell's ___________________ ____________________. 17. Organisms whose cells never contain a membrane bound nuc ...
Welcome Back!!
... plant cells and provides protection and support? 2. Which cell part controls all the cell’s activities? 3. Which part allows water, food, and oxygen to enter the cell and carbon dioxide to leave the cell? ...
... plant cells and provides protection and support? 2. Which cell part controls all the cell’s activities? 3. Which part allows water, food, and oxygen to enter the cell and carbon dioxide to leave the cell? ...
Cell cycle and mitosis PowerPoint
... Interphase – Cell grows, carries out normal cell functions, and replicates (makes copies of) its DNA, and prepares for mitosis Mitosis – Cell division: nucleus and DNA divide ...
... Interphase – Cell grows, carries out normal cell functions, and replicates (makes copies of) its DNA, and prepares for mitosis Mitosis – Cell division: nucleus and DNA divide ...
MLAB 1415- Hematology Keri Brophy-Martinez Hematopoiesis
... EPO - Stimulate erythrocyte production, Used to treat chronic anemia caused by renal failure, increase RBC prior to surgery which may cause blood loss, illegally by athletes to boost performance. Trade name is Epogen or Procrit. ...
... EPO - Stimulate erythrocyte production, Used to treat chronic anemia caused by renal failure, increase RBC prior to surgery which may cause blood loss, illegally by athletes to boost performance. Trade name is Epogen or Procrit. ...
Aim: How can we apply our knowledge of cells?
... 1. Label the picture with each phase of mitosis. 2. Write a description of each phase of mitosis. 3. Identify the part of the cell cycle being discussed. a. b. c. d. ...
... 1. Label the picture with each phase of mitosis. 2. Write a description of each phase of mitosis. 3. Identify the part of the cell cycle being discussed. a. b. c. d. ...
The NUCLEUS (“mayor of city hall”)
... The ribosomes carry out manual labor in the form of protein synthesis for the nucleus. They bring together all the raw ingredients such as RNA (copies of the original DNA blueprints) and amino acids to assemble proteins. The proteins created are essential to cell and organismal function. Think of pr ...
... The ribosomes carry out manual labor in the form of protein synthesis for the nucleus. They bring together all the raw ingredients such as RNA (copies of the original DNA blueprints) and amino acids to assemble proteins. The proteins created are essential to cell and organismal function. Think of pr ...
Cells
... Question: How do plant and animal cells differ? Hypothesis: If we study a plant cell and an animal cell, then we will see that they are different from each other because______ _________________________________________________ Materials: light microscope, 2 glass slides, 2 coverslips, dropper, Methyl ...
... Question: How do plant and animal cells differ? Hypothesis: If we study a plant cell and an animal cell, then we will see that they are different from each other because______ _________________________________________________ Materials: light microscope, 2 glass slides, 2 coverslips, dropper, Methyl ...
Sizing Up Cells - Cloudfront.net
... Main steps for analysis techniques Background information Sample product(s) Student handouts for data collection & analysis (if provided); may be electronic ...
... Main steps for analysis techniques Background information Sample product(s) Student handouts for data collection & analysis (if provided); may be electronic ...
NAME - Issaquah Connect
... 4. Describe how your pond changed over time. The leaves and hay broke down, more living things were present, number of Lemna, amount of water. 5. Explain how organisms got into your pond. They were attached to the leaves, straw, and soil in their cyst form, when they had the right conditions they ca ...
... 4. Describe how your pond changed over time. The leaves and hay broke down, more living things were present, number of Lemna, amount of water. 5. Explain how organisms got into your pond. They were attached to the leaves, straw, and soil in their cyst form, when they had the right conditions they ca ...
Cell Organelles
... • A cell is like a factory. It has many machines inside to make it work correctly. • The “machines” in a cell are called organelles ...
... • A cell is like a factory. It has many machines inside to make it work correctly. • The “machines” in a cell are called organelles ...
Cell Organelle Table
... Machines that makes proteins according to the directions of the DNA – not bound by membrane Modify and sorts proteins from RER, Loads them into vesicles and sends them to destinations Transport proteins (enzymes), lipids (steroids) and carbohydrates to specific locations Single membrane bound struct ...
... Machines that makes proteins according to the directions of the DNA – not bound by membrane Modify and sorts proteins from RER, Loads them into vesicles and sends them to destinations Transport proteins (enzymes), lipids (steroids) and carbohydrates to specific locations Single membrane bound struct ...
Parts of an Animal Cell - Hicksville Public Schools
... Parts of a Cell A- nucleus -directs all cell activities N -the nucleolus makes ribosomes L -chromatin contains DNA (genes) M -the nuclear membrane surrounds the nucleus. B- cell membrane -outer boundary of the cell, allows materials to move in and out of the cell, it is a selectively permeable membr ...
... Parts of a Cell A- nucleus -directs all cell activities N -the nucleolus makes ribosomes L -chromatin contains DNA (genes) M -the nuclear membrane surrounds the nucleus. B- cell membrane -outer boundary of the cell, allows materials to move in and out of the cell, it is a selectively permeable membr ...
BILL Standards Unit 2 - Cells! Textbook Chapters: 7.1, 7.2, 20.1
... 1. Describe characteristics all living things have in common 2. List the following levels of organization in order from simplest to most complex (molecule, cell, atom, organelle, organism, organ, tissue, organ system) Viruses (4) 1. Describe why viruses are not considered living things and how they ...
... 1. Describe characteristics all living things have in common 2. List the following levels of organization in order from simplest to most complex (molecule, cell, atom, organelle, organism, organ, tissue, organ system) Viruses (4) 1. Describe why viruses are not considered living things and how they ...
Scientists not found in the book: Zacharias Janssen 1590: Janssen`s
... 3. Include 5 pictures of the scientists or their contribution 4. BE NEAT & LEGIBLE!! With the final product posted in your spiral ...
... 3. Include 5 pictures of the scientists or their contribution 4. BE NEAT & LEGIBLE!! With the final product posted in your spiral ...
Performance Indicator 7.L.3A.3
... • Act as temporary storage centers. • Some store water: others store waste products until they can be eliminated from the cell. • Plant cells have fewer and larger vacuoles than animal cells. ...
... • Act as temporary storage centers. • Some store water: others store waste products until they can be eliminated from the cell. • Plant cells have fewer and larger vacuoles than animal cells. ...
Biology LP 11.14-12.2
... -single celled organisms -process of binary vision What are the advantages and disadvantages of binary fission? ...
... -single celled organisms -process of binary vision What are the advantages and disadvantages of binary fission? ...
4 A closer look at animal and plant cells KEY_2
... 1. How did scientists discover the common structure of cells? Scientists used microscope to observe many kids of cells 2. What are some of the common structures of a cell? Common cell structures include the cell membrane and cytoplasm. 3. Why is the nucleus an important part of most cells? The nucle ...
... 1. How did scientists discover the common structure of cells? Scientists used microscope to observe many kids of cells 2. What are some of the common structures of a cell? Common cell structures include the cell membrane and cytoplasm. 3. Why is the nucleus an important part of most cells? The nucle ...
Handout: Organelle List
... “Handout: Organelle List” Using Microsoft Word, create a document showing the name of the organelle, its location and its function. That document might look like the example shown here. Organelle ...
... “Handout: Organelle List” Using Microsoft Word, create a document showing the name of the organelle, its location and its function. That document might look like the example shown here. Organelle ...
Section 3.2 – Moving Cellular Materials Selectively Permeable
... Section 3.2 – Moving Cellular Materials ...
... Section 3.2 – Moving Cellular Materials ...
Solution - Glencoe
... 3. fluid-filled space within the cytoplasm; temporarily stores food ______________________ ...
... 3. fluid-filled space within the cytoplasm; temporarily stores food ______________________ ...