eukaryote: cell that has a membrane
... Nervous tissue composed of nerve cells called neurons. Nucleus: contains the cell's genetic information that is passed on to future generations. It controls the activities of the cell. May contain nucleoli, which function in ...
... Nervous tissue composed of nerve cells called neurons. Nucleus: contains the cell's genetic information that is passed on to future generations. It controls the activities of the cell. May contain nucleoli, which function in ...
The spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to
... replacement of hard parts with minerals (or from casts and impressions or, by preservation when no decay occurs). ...
... replacement of hard parts with minerals (or from casts and impressions or, by preservation when no decay occurs). ...
Cell Structure Transport Review
... Unit 2 Cell and Cell Structure REVIEW 1. Plant and animal cells are types of _______________, because they contain a nucleus. 2. List the objectives on a microscope that you should use to find a specimen in order of magnification. 3. Name two structures that help an animal cell move. 4. What does ER ...
... Unit 2 Cell and Cell Structure REVIEW 1. Plant and animal cells are types of _______________, because they contain a nucleus. 2. List the objectives on a microscope that you should use to find a specimen in order of magnification. 3. Name two structures that help an animal cell move. 4. What does ER ...
Name
... 14. Sketch a simple drawing of an animal cell below. Include and label the following cell features in your drawing: -nucleus, nuclear envelope, nucleoulus, nuclear pore, mitochondria, microfilaments, lysosomes, golgi apparatus, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum, microtbules, ...
... 14. Sketch a simple drawing of an animal cell below. Include and label the following cell features in your drawing: -nucleus, nuclear envelope, nucleoulus, nuclear pore, mitochondria, microfilaments, lysosomes, golgi apparatus, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum, microtbules, ...
File - GarzScience!
... cytokinesis you will have 2 distinct cells. Cytokinesis starts with the creation of the cleavage furrow during telophase. In plants, cytokinesis can’t pinch in the cell wall, so a cell plate is formed within that cell. In animals, the cell membrane can be pinched so it forms a cleavage furrow to pin ...
... cytokinesis you will have 2 distinct cells. Cytokinesis starts with the creation of the cleavage furrow during telophase. In plants, cytokinesis can’t pinch in the cell wall, so a cell plate is formed within that cell. In animals, the cell membrane can be pinched so it forms a cleavage furrow to pin ...
Plant and Animal Cell Lab
... 5. Why were no chloroplasts found in the onion cells? (hint: think about where you find onions) ...
... 5. Why were no chloroplasts found in the onion cells? (hint: think about where you find onions) ...
FORMATIVE Cell Test 1 Answers 2015
... Without lipids: the cell would be missing a very important molecule for storing energy; it would be missing key molecules that make up its cell membrane! Without carbohydrates: the cell would be missing a very important molecule for storing energy or for use in respiration to make usable ATP energy; ...
... Without lipids: the cell would be missing a very important molecule for storing energy; it would be missing key molecules that make up its cell membrane! Without carbohydrates: the cell would be missing a very important molecule for storing energy or for use in respiration to make usable ATP energy; ...
Cells and Heredity
... Every living thing is made of one or more cells. Cells carry out the functions needed to support life. Cells come only from other living cells. ...
... Every living thing is made of one or more cells. Cells carry out the functions needed to support life. Cells come only from other living cells. ...
Northeast High School GHSGT Junior Academy
... Anton van Leewenhoek Robert Brown Matthias Schleiden Theodor Schwann Rudolph Virchow ...
... Anton van Leewenhoek Robert Brown Matthias Schleiden Theodor Schwann Rudolph Virchow ...
UPcellprepro.10131154
... At the end of this unit you will be able to: 1. Describe each phase of the cell cycle 2. Describe the structure of a chromosome. 3. Compare prokaryotic chromosomes with eukaryotic chromosomes. 4. Explain the differences between sex chromosomes and autosomes. 5. Give examples of diploid and haploid c ...
... At the end of this unit you will be able to: 1. Describe each phase of the cell cycle 2. Describe the structure of a chromosome. 3. Compare prokaryotic chromosomes with eukaryotic chromosomes. 4. Explain the differences between sex chromosomes and autosomes. 5. Give examples of diploid and haploid c ...
cell plate
... Prophase is over when the chromosomes begin to move toward the equator of the cell ...
... Prophase is over when the chromosomes begin to move toward the equator of the cell ...
Crucial step in cell division discovered
... published in Developmental Cell today. revealing the secrets of cell division and in 2001, Sir Paul Nurse and Sir Tim Hunt received a Nobel The team, based at Cancer Research UK's London Prize for Medicine for their work in this area. Research Institute, discovered that a protein called Ect2 gathers ...
... published in Developmental Cell today. revealing the secrets of cell division and in 2001, Sir Paul Nurse and Sir Tim Hunt received a Nobel The team, based at Cancer Research UK's London Prize for Medicine for their work in this area. Research Institute, discovered that a protein called Ect2 gathers ...
Vocab and Functions
... digestive enzymes – are responsible for digesting inside a cell; Found mainly in animal cells . They destroy worn-out or damaged organelles, get rid of waste materials and “swallow” ...
... digestive enzymes – are responsible for digesting inside a cell; Found mainly in animal cells . They destroy worn-out or damaged organelles, get rid of waste materials and “swallow” ...
Document
... ___ 19.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ___ 20.Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ___ 21.Chloroplasts ...
... ___ 19.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ___ 20.Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ___ 21.Chloroplasts ...
Plants and Animal Cells Under the Light Microscope
... The structure that controls all of the cells functions and contains the genetic information (cromosomes). The thin film that controls the movement of molecules in and out of the cell, such as nutrients and waste. The watery fluid that fills the cell ...
... The structure that controls all of the cells functions and contains the genetic information (cromosomes). The thin film that controls the movement of molecules in and out of the cell, such as nutrients and waste. The watery fluid that fills the cell ...
Scientists – Microscopes
... Observations: observed “animalcules” (wee beasties) in a drop of pond water 2. Robert Hooke When: 1665 Discovery: Named the cell Observations: Looked at cork under microscope (also spiders, insects, flowers, etc.) Observed that cork was made of empty little boxes he named cells 3. Robert Brown W ...
... Observations: observed “animalcules” (wee beasties) in a drop of pond water 2. Robert Hooke When: 1665 Discovery: Named the cell Observations: Looked at cork under microscope (also spiders, insects, flowers, etc.) Observed that cork was made of empty little boxes he named cells 3. Robert Brown W ...
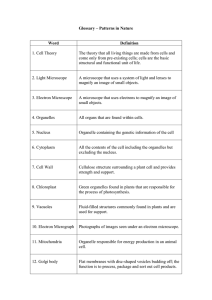
Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... The theory that all living things are made from cells and come only from pre-existing cells; cells are the basic structural and functional unit of life. ...
... The theory that all living things are made from cells and come only from pre-existing cells; cells are the basic structural and functional unit of life. ...