Name: Period________ General Biology First Semester Study
... 79. Name, in order, the phases of mitosis AND briefly tell what happens to the CHROMOSOMES in each: ...
... 79. Name, in order, the phases of mitosis AND briefly tell what happens to the CHROMOSOMES in each: ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Review Questions
... d. An internal membrane system in which components _____ Mitochondria of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed e. Saclike structure that stores materials f. Small particle of RNA and protein that produces protein following instructions from nucleus g. Filled with enzymes used to break down ...
... d. An internal membrane system in which components _____ Mitochondria of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed e. Saclike structure that stores materials f. Small particle of RNA and protein that produces protein following instructions from nucleus g. Filled with enzymes used to break down ...
Parts of the Cell: Cellular Organelles 1. Nucleus • The central core of
... • Small bag-like structures that allow for the storage and transportation of waste in a cell. In plant cells these are VERY large. They are full of water in plant cells and that keeps plant cells rigid. Vacuoles fuse with the cell membrane to release waste out of the cell. 10. Endoplasmic Reticulum ...
... • Small bag-like structures that allow for the storage and transportation of waste in a cell. In plant cells these are VERY large. They are full of water in plant cells and that keeps plant cells rigid. Vacuoles fuse with the cell membrane to release waste out of the cell. 10. Endoplasmic Reticulum ...
Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... 2. Any unicellular or multicellular organism that has a nucleus and other organelles within its cell or cells is called a ______________________. 3. __________________ is an organism that eats producers or other organisms for energy. 4. A phospholipids bilayer that covers a cell’s surface and regula ...
... 2. Any unicellular or multicellular organism that has a nucleus and other organelles within its cell or cells is called a ______________________. 3. __________________ is an organism that eats producers or other organisms for energy. 4. A phospholipids bilayer that covers a cell’s surface and regula ...
SOLVING REAL WORLD PROBLEMS- - Uplift Summit International
... Nucleus houses DNA, Organelles carry specific activities in the cell Cytoplasm outside nucleus, inside cell membrane ...
... Nucleus houses DNA, Organelles carry specific activities in the cell Cytoplasm outside nucleus, inside cell membrane ...
Macromolecules and Cells – Study Guide
... a wide variety of functions in cells ____________________________ made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio ____________________________ made from nucleotide subunits which store and carry information ____________________________ hydrophobic fats, oils, waxes, & steroids made mai ...
... a wide variety of functions in cells ____________________________ made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio ____________________________ made from nucleotide subunits which store and carry information ____________________________ hydrophobic fats, oils, waxes, & steroids made mai ...
Name - Net Start Class
... Remember this worksheet is meant only to be a guide to help you prepare for the up coming test. You should also access the online textbook, study your journal, and cell diagrams. ...
... Remember this worksheet is meant only to be a guide to help you prepare for the up coming test. You should also access the online textbook, study your journal, and cell diagrams. ...
The Cell - Biology Mad
... One set from the mother in the haploid egg cell, the other from the father’s haploid sperm cell. Sex Chromosomes: the 23rd pair. Female: XX Male XY Each chromosome has a unique set of genes. Each gene has a specific locus – it is on a particular chromosome at a specific site. Different (mutant) form ...
... One set from the mother in the haploid egg cell, the other from the father’s haploid sperm cell. Sex Chromosomes: the 23rd pair. Female: XX Male XY Each chromosome has a unique set of genes. Each gene has a specific locus – it is on a particular chromosome at a specific site. Different (mutant) form ...
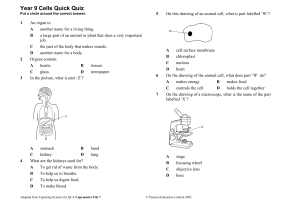
Year 9 Cells Quick Quiz
... a collection of organs helping each other. B another name for an organ. C a group of cells which are all different, all doing different jobs. D a group of cells which are the same, all doing the same job. A nerve cell has to carry messages around the body quickly. To help it do this it is: A short a ...
... a collection of organs helping each other. B another name for an organ. C a group of cells which are all different, all doing different jobs. D a group of cells which are the same, all doing the same job. A nerve cell has to carry messages around the body quickly. To help it do this it is: A short a ...
REVIEW of CELL PARTS AND FUNCTION:
... CELL MEMBRANE…..boundary setting structure that retains the contents of the cell; serves as a selectively permeable barrier to the environment and regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. NUCLEAR MEMBRANE: the double membrane that encloses the nucleus of the cell. Regulates move ...
... CELL MEMBRANE…..boundary setting structure that retains the contents of the cell; serves as a selectively permeable barrier to the environment and regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. NUCLEAR MEMBRANE: the double membrane that encloses the nucleus of the cell. Regulates move ...
CHROMOSOMAL INSTABILITY AND CANCER CELL STEMNESS
... very frequent, while structural rearrangements affect almost every single chromosome. This challenging context provides excellent grounds to study telomere dysfunction driven CIN in a single cell basis. Many cancers are considered to be driven by cancer stem cells (CSCs) that may differentiate into ...
... very frequent, while structural rearrangements affect almost every single chromosome. This challenging context provides excellent grounds to study telomere dysfunction driven CIN in a single cell basis. Many cancers are considered to be driven by cancer stem cells (CSCs) that may differentiate into ...
Cell Structure and theory
... A network of protein filaments (microtubules and microfilaments) that help the cell move and maintain its shape ...
... A network of protein filaments (microtubules and microfilaments) that help the cell move and maintain its shape ...
Cell Structure Common Cell Traits Living cells are dynamic and
... Inside a Cell Activity 2(50 pts.) Cell Structure and Function Each organelle of a cell has its own specific job or duty. It is like a miniature city working to keep the cell alive and functioning. Researches the following websites listed below and create a test that will enable you and classmate to ...
... Inside a Cell Activity 2(50 pts.) Cell Structure and Function Each organelle of a cell has its own specific job or duty. It is like a miniature city working to keep the cell alive and functioning. Researches the following websites listed below and create a test that will enable you and classmate to ...
Swine Jeopardy
... Plant cells have a large membrane-bound space in which water, waste products, and nutrients can be stored. This space is called the vacuole. ...
... Plant cells have a large membrane-bound space in which water, waste products, and nutrients can be stored. This space is called the vacuole. ...
Life Science vocabulary quiz
... A. in plant cells, green organelles that capture the energy from sunlight and use it to make food. B. A false foot or temporary bulge of cytoplasm used for feeding and movement in some protozoans. C. A small round cell structure containing chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ...
... A. in plant cells, green organelles that capture the energy from sunlight and use it to make food. B. A false foot or temporary bulge of cytoplasm used for feeding and movement in some protozoans. C. A small round cell structure containing chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ...
Answer Key: checkpoint cell organelles, prokaryotic and eukaryotic
... Instructions: write a short answer using FULL, COMPLETE SENTENCES. 1) What are three features found in plant cells, but not in animal cells? (3 marks) large vacuole, chloroplasts, cell walls 2) What organelles do all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell have in common? ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell membrane ...
... Instructions: write a short answer using FULL, COMPLETE SENTENCES. 1) What are three features found in plant cells, but not in animal cells? (3 marks) large vacuole, chloroplasts, cell walls 2) What organelles do all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell have in common? ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell membrane ...
Biology: Cell Test
... Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell A cell without a nucleus is a: Plant Cell Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell The following are correct about the nucleus except for: It is the control center of the cell It is the site where lipid components are assembled It contains the cell’s genetic material It cont ...
... Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell A cell without a nucleus is a: Plant Cell Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell The following are correct about the nucleus except for: It is the control center of the cell It is the site where lipid components are assembled It contains the cell’s genetic material It cont ...