NOT animal cells.
... Chloroplasts are where PHOTOSYNTHESIS occurs. • Contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps the energy from light. • Found in plant cells and some protists, NOT found in animal cells. ...
... Chloroplasts are where PHOTOSYNTHESIS occurs. • Contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps the energy from light. • Found in plant cells and some protists, NOT found in animal cells. ...
Ribosome - Hartland High School
... Structure Can take up as much as 90% of the volume of cell. Function Large water vacuoles are found in plant cells; stores enzymes and waste products. ...
... Structure Can take up as much as 90% of the volume of cell. Function Large water vacuoles are found in plant cells; stores enzymes and waste products. ...
CELLS
... Composed of a phospholipid bilayer that has proteins embedded in it Cholesterol is also an important component of cell membranes since it keeps the membrane intact yet fluid The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and leave the cell ...
... Composed of a phospholipid bilayer that has proteins embedded in it Cholesterol is also an important component of cell membranes since it keeps the membrane intact yet fluid The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and leave the cell ...
CELL TRANSPORT
... 7. A solution is composed of a solute (sugar) dissolved in a solvent (water). The direction water will move across a membrane depends on the concentration of the 2 substances. A solution may be: a) hypotonic - concentration of solute molecules outside cell is lower than in cell - water will diffuse ...
... 7. A solution is composed of a solute (sugar) dissolved in a solvent (water). The direction water will move across a membrane depends on the concentration of the 2 substances. A solution may be: a) hypotonic - concentration of solute molecules outside cell is lower than in cell - water will diffuse ...
Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic Cells Quiz Review • Draw, label, and
... o DNA is not enclosed within a membrane and forms one circular chromosome o Their DNA is not attached to proteins (free DNA). o They lack membrane-bound organelles o Their cell wall is made of peptidoglycan o Usually divide by binary fission o Small in size (1-10 µm) o Ribosomes – 70S State that pro ...
... o DNA is not enclosed within a membrane and forms one circular chromosome o Their DNA is not attached to proteins (free DNA). o They lack membrane-bound organelles o Their cell wall is made of peptidoglycan o Usually divide by binary fission o Small in size (1-10 µm) o Ribosomes – 70S State that pro ...
Ch 3 Check Your Progress Answers BC Biology 12 3.1 p 67 1
... c) cell recognition protein: glycoproteins that help the body recognize self vs others and can help recognize invaders like bacteria d) receptor proteins: have a shape that allows a specific molecule to bind to it. The binding causes the shape of the protein to change and to have a cellular response ...
... c) cell recognition protein: glycoproteins that help the body recognize self vs others and can help recognize invaders like bacteria d) receptor proteins: have a shape that allows a specific molecule to bind to it. The binding causes the shape of the protein to change and to have a cellular response ...
cells final - educ399portfolioedwinawilson
... Most hormones circulate in blood, coming into contact with essentially all cells. ...
... Most hormones circulate in blood, coming into contact with essentially all cells. ...
Oncofertility 2b. Student Lab A Study of the Relationship between
... Oncofertility 2b. Student Lab ...
... Oncofertility 2b. Student Lab ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Student Exploration: Cell Structure Vocabulary: cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plasma membrane, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle ...
... Student Exploration: Cell Structure Vocabulary: cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plasma membrane, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle ...
chromosome aberrations induced by the Auger Emitter I
... h post-stimulation. All slides were stained with 10 % Giemsa, and 100 metaphases were analyzed microscopically for each dose point. Results: After 18 h labeling with I-125-UdR the cell cycle distribution is severely disturbed. Furthermore, 40% of PBL are fully labelled and 20% show a moderate uptake ...
... h post-stimulation. All slides were stained with 10 % Giemsa, and 100 metaphases were analyzed microscopically for each dose point. Results: After 18 h labeling with I-125-UdR the cell cycle distribution is severely disturbed. Furthermore, 40% of PBL are fully labelled and 20% show a moderate uptake ...
Science - B3 Revision
... ◦ organism can be larger ◦ Allows for cell differentiation ◦ organism can be more complex Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems: ◦ communication between cells (nervous system) ◦ supplying the cells with nutrients (digestive system) ◦ controlling exchanges with ...
... ◦ organism can be larger ◦ Allows for cell differentiation ◦ organism can be more complex Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems: ◦ communication between cells (nervous system) ◦ supplying the cells with nutrients (digestive system) ◦ controlling exchanges with ...
BIO 311 C Introductory Biology I K. Sathasivan
... 3. Predict the logical process by which simple monomers were formed and led to polymers, protobionts and the early forms of cells. 4. Explain how the first possible macromolecule could be RNA to store genetic information and be able to catalyze reactions. CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Cell and Molecul ...
... 3. Predict the logical process by which simple monomers were formed and led to polymers, protobionts and the early forms of cells. 4. Explain how the first possible macromolecule could be RNA to store genetic information and be able to catalyze reactions. CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Cell and Molecul ...
Bacteria
... • Endospore is a dormant bacterial cell • Under extreme conditions that do not allow reproduction a bacterial cell protects the esstials with a thick coat, becoming very small and dry • Upon favorable conditins the endospore absorbs moisture, grows to full size and begins its life cycle ...
... • Endospore is a dormant bacterial cell • Under extreme conditions that do not allow reproduction a bacterial cell protects the esstials with a thick coat, becoming very small and dry • Upon favorable conditins the endospore absorbs moisture, grows to full size and begins its life cycle ...
Chapter 3 Cells
... • contents released outside the cell • release of neurotransmitters from nerve cells ...
... • contents released outside the cell • release of neurotransmitters from nerve cells ...
Slide 1
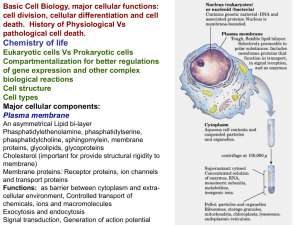
... of gene expression and other complex biological reactions Cell structure Cell types Major cellular components: Plasma membrane An asymmetrical Lipid bi-layer Phasphatidylethenolamine, phasphatidylserine, phasphatidylcholine, sphingomylein, membrane proteins, glycolipids, glycoproteins Cholesterol (i ...
... of gene expression and other complex biological reactions Cell structure Cell types Major cellular components: Plasma membrane An asymmetrical Lipid bi-layer Phasphatidylethenolamine, phasphatidylserine, phasphatidylcholine, sphingomylein, membrane proteins, glycolipids, glycoproteins Cholesterol (i ...
Cell Growth and Division
... all of its DNA, so each new daughter cell gets one complete copy of genetic information and there is no shortage. Material Exchange: Each new daughter cell has an increased ratio of surface area to volume, so enough materials may be exchanged based on the demands of the cell. Why else must things re ...
... all of its DNA, so each new daughter cell gets one complete copy of genetic information and there is no shortage. Material Exchange: Each new daughter cell has an increased ratio of surface area to volume, so enough materials may be exchanged based on the demands of the cell. Why else must things re ...
• dendrite - Dental Decks
... central nervous system as clusters called nuclei, some found in the peripheral nervous system as groups called ganglia (two types: sensory and autonomic). - Sensory ganglia contain cell bodies of either pseudounipolar or bipolar sensory neurons. There are no synapses in sensory ganglia. - Autonomic ...
... central nervous system as clusters called nuclei, some found in the peripheral nervous system as groups called ganglia (two types: sensory and autonomic). - Sensory ganglia contain cell bodies of either pseudounipolar or bipolar sensory neurons. There are no synapses in sensory ganglia. - Autonomic ...
The importance of cells: basic unit of living things, form follows
... LYSOSOMES: produced by golgi--contain digestive enzymes --can fuse w/ damaged/old organelles break down recycled by cell ...
... LYSOSOMES: produced by golgi--contain digestive enzymes --can fuse w/ damaged/old organelles break down recycled by cell ...
File - Science with Snyder
... • The major difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is the presence of a nucleus. • 1. prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus, the DNA in pro cell is circular and called plasmid. • 2. Eukaryotic cells, the DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes and the chromosome ...
... • The major difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is the presence of a nucleus. • 1. prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus, the DNA in pro cell is circular and called plasmid. • 2. Eukaryotic cells, the DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes and the chromosome ...
Grade 10 Academic Science – Biology
... 9. From your results, which configuration (eight small cells or one large cell) has more cell membrane for nutrients and waste to pass through? What do your findings suggest about the size of a cell? Questions 1. Muscle cells are highly active. They tend to be small. From your findings, suggest one ...
... 9. From your results, which configuration (eight small cells or one large cell) has more cell membrane for nutrients and waste to pass through? What do your findings suggest about the size of a cell? Questions 1. Muscle cells are highly active. They tend to be small. From your findings, suggest one ...
Cell Processes Notes
... sugar for energy, oxygen (animals), carbon dioxide (plants), and amino acids for proteins. Materials may pass through the cell membrane when in water solution. Transport processes control the amount of each entering and leaving the cell. Certain materials, like food molecules, oxygen, carbon dioxide ...
... sugar for energy, oxygen (animals), carbon dioxide (plants), and amino acids for proteins. Materials may pass through the cell membrane when in water solution. Transport processes control the amount of each entering and leaving the cell. Certain materials, like food molecules, oxygen, carbon dioxide ...
Notes 2-4
... 2. “Brain” of the cell. 3. Nuclear Membrane (envelope) -- like cell membrane. 4. Chromosomes (Chromatin): a. Rod-like objects. b. Direct all the activities of the cell (growth & reproduction). c. Pass on traits to new cells. d. Made of nucleic acids -- store information that helps a cell make the pr ...
... 2. “Brain” of the cell. 3. Nuclear Membrane (envelope) -- like cell membrane. 4. Chromosomes (Chromatin): a. Rod-like objects. b. Direct all the activities of the cell (growth & reproduction). c. Pass on traits to new cells. d. Made of nucleic acids -- store information that helps a cell make the pr ...