Cell parts flipbook
... 3. New cells are produced from EXISTING cells _____________________________________________________________________ ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY Proposed by LYNN MARGULIS Ancient prokaryotes were taken in by eukaryotic cells and stayed to live inside them in symbiotic relationship; eventually lead to mitoch ...
... 3. New cells are produced from EXISTING cells _____________________________________________________________________ ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY Proposed by LYNN MARGULIS Ancient prokaryotes were taken in by eukaryotic cells and stayed to live inside them in symbiotic relationship; eventually lead to mitoch ...
Lecture 22: Cancer II and Cell Junctions
... Size of gap junction channel can be determined with fluorescent molecules of different sizes ...
... Size of gap junction channel can be determined with fluorescent molecules of different sizes ...
The Cell The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of
... • The nucleus is a large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. • Cell typing is categorized by their nucleus: – Eukaryotes (Greek for “true nucleus/center”) – Prokaryotes (Greek for “before nucleus/center”) ...
... • The nucleus is a large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. • Cell typing is categorized by their nucleus: – Eukaryotes (Greek for “true nucleus/center”) – Prokaryotes (Greek for “before nucleus/center”) ...
cells
... • Polar phosphate group allows membrane to interact with its environment. • Fatty acid tails create a water-insoluble layer in the middle which is non-polar. ...
... • Polar phosphate group allows membrane to interact with its environment. • Fatty acid tails create a water-insoluble layer in the middle which is non-polar. ...
Final Review Questions
... • Diffusion: the natural tendency of molecules to move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration • Osmosis: the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. 6. Cell Theory • What are the ma ...
... • Diffusion: the natural tendency of molecules to move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration • Osmosis: the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. 6. Cell Theory • What are the ma ...
FLECs - Biology 11 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... cells are capable of rapid contraction; nerve cells transmit special ...
... cells are capable of rapid contraction; nerve cells transmit special ...
The Cell - Harris7Science
... Ribosomes – manufacture of proteins Cytoplasm – substance that holds all other parts in suspension Mitochondria – Release energy for food Lyosomes – gobble up waste materials (very rare in plant cells) ...
... Ribosomes – manufacture of proteins Cytoplasm – substance that holds all other parts in suspension Mitochondria – Release energy for food Lyosomes – gobble up waste materials (very rare in plant cells) ...
Study Guide/Cheat sheet for Cell Unit
... (specialized proteins) help control the rate of chemical reactions (usually speeds it up without being used up). They are effected by Temperature (hotter is faster) and pH (acid/base amounts) -they are effected by concentration (higher concentration the faster it will happen) ...
... (specialized proteins) help control the rate of chemical reactions (usually speeds it up without being used up). They are effected by Temperature (hotter is faster) and pH (acid/base amounts) -they are effected by concentration (higher concentration the faster it will happen) ...
Study Guide/Cheat sheet for Cell Unit
... (specialized proteins) help control the rate of chemical reactions (usually speeds it up without being used up). They are effected by Temperature (hotter is faster) and pH (acid/base amounts) -they are effected by concentration (higher concentration the faster it will happen) ...
... (specialized proteins) help control the rate of chemical reactions (usually speeds it up without being used up). They are effected by Temperature (hotter is faster) and pH (acid/base amounts) -they are effected by concentration (higher concentration the faster it will happen) ...
Levels of Organization
... 1. Which is true of cell differentiation? A. Tissues produce various stem cells. B. Stem cells become different types of cells. C. Unicellular organisms become multicellular. 2. Which is true of unicellular organisms? A. They lack cells. B. They all are eukaryotes. C. They lack cell differentiation. ...
... 1. Which is true of cell differentiation? A. Tissues produce various stem cells. B. Stem cells become different types of cells. C. Unicellular organisms become multicellular. 2. Which is true of unicellular organisms? A. They lack cells. B. They all are eukaryotes. C. They lack cell differentiation. ...
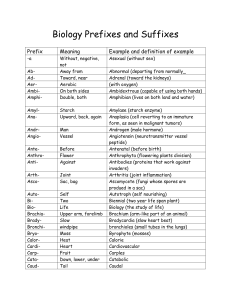
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... internally to maintain a constant body temperature) Epiphyte (A plant that grows on the surface of another plant for support) Erythrocyte (red blood cell) Eukaryote (Organism whose cells contains a “true” membrane bound nucleus) Exoskeleton (hard outer surface that provides support or protection for ...
... internally to maintain a constant body temperature) Epiphyte (A plant that grows on the surface of another plant for support) Erythrocyte (red blood cell) Eukaryote (Organism whose cells contains a “true” membrane bound nucleus) Exoskeleton (hard outer surface that provides support or protection for ...
Weather Assessment Review
... The cells of plants and animals were the same. B. All plant parts were made of cells. C. The cells of plants were different from those of animals. D. All animal tissues were made of cells A. ...
... The cells of plants and animals were the same. B. All plant parts were made of cells. C. The cells of plants were different from those of animals. D. All animal tissues were made of cells A. ...
Viruses and Bacteria worksheet
... 1. How are bacterial cells different from the cells of eukaryotes? ...
... 1. How are bacterial cells different from the cells of eukaryotes? ...
Recitation 13 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... regulatory molecules (determinants) that include transcription factors, miRNA and translation factors. Development of multi-cellular organisms proceeds in steps, with increasing complexity over time. In animal development, a key step is the initial generation of asymmetry, which can occur before, at ...
... regulatory molecules (determinants) that include transcription factors, miRNA and translation factors. Development of multi-cellular organisms proceeds in steps, with increasing complexity over time. In animal development, a key step is the initial generation of asymmetry, which can occur before, at ...
Cells
... The cells of plants and animals were the same. B. All plant parts were made of cells. C. The cells of plants were different from those of animals. D. All animal tissues were made of cells A. ...
... The cells of plants and animals were the same. B. All plant parts were made of cells. C. The cells of plants were different from those of animals. D. All animal tissues were made of cells A. ...
Anim al and P lant C ells
... Define each cell organelle and color it the color indicated below it. Cell Membrane – The semipermeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. ...
... Define each cell organelle and color it the color indicated below it. Cell Membrane – The semipermeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. ...
File - Mr. Downing Science 10
... the same structure as the cell membrane – transport substances throughout the cell ...
... the same structure as the cell membrane – transport substances throughout the cell ...
Name
... 1. The tendency of an organism to maintain a stable internal environment is called (a) homeostasis (b) cell theory (c) reproduction (d) synthesis 2. The energy available for use by the cell is obtained from the life function of (a) reproduction (b) respiration (c) transport (d) synthesis 3. The chem ...
... 1. The tendency of an organism to maintain a stable internal environment is called (a) homeostasis (b) cell theory (c) reproduction (d) synthesis 2. The energy available for use by the cell is obtained from the life function of (a) reproduction (b) respiration (c) transport (d) synthesis 3. The chem ...
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
... 35. Microfilaments are solid, and they are built from a double chain of actin. What are four functions of microfilaments? What are the motor proteins that move the microfilaments? ...
... 35. Microfilaments are solid, and they are built from a double chain of actin. What are four functions of microfilaments? What are the motor proteins that move the microfilaments? ...
Influenza_H5N1
... RNA polymerase transcribes negative- sense vRNA into positivesense (translatable into proteins) vRNA. The vRNA then either remains in the nucleus or is transported into the cytoplasm, where it is translated into viral proteins. These are then either secreted by the Golgi body to the cell surface, or ...
... RNA polymerase transcribes negative- sense vRNA into positivesense (translatable into proteins) vRNA. The vRNA then either remains in the nucleus or is transported into the cytoplasm, where it is translated into viral proteins. These are then either secreted by the Golgi body to the cell surface, or ...
topic-4.doc
... o primarily proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and organic ions o major structures DNA ribosomes inclusions ...
... o primarily proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and organic ions o major structures DNA ribosomes inclusions ...
chapter 1 - cloudfront.net
... Cell division Centriole Asexual reproduction Chromatid Sexual reproduction Metaphase Chromosome Anaphase Chromatin Telophase Centromere Cytokinesis Interphase Cyclin Cell cycle Growth factor Mitosis Apoptosis Prophase Cancer ...
... Cell division Centriole Asexual reproduction Chromatid Sexual reproduction Metaphase Chromosome Anaphase Chromatin Telophase Centromere Cytokinesis Interphase Cyclin Cell cycle Growth factor Mitosis Apoptosis Prophase Cancer ...
Characteristics of Living Things and Microscopes
... 3. Cells grow, respond the their environment, and reproduce 4. Unicellular= one cell; Multicellular= many cells B. Living things reproduce 1. Sexual reproduction= two cells from different parents unite to produce the first cell of the new organism. 2. Asexual reproduction= the new organism has a sin ...
... 3. Cells grow, respond the their environment, and reproduce 4. Unicellular= one cell; Multicellular= many cells B. Living things reproduce 1. Sexual reproduction= two cells from different parents unite to produce the first cell of the new organism. 2. Asexual reproduction= the new organism has a sin ...