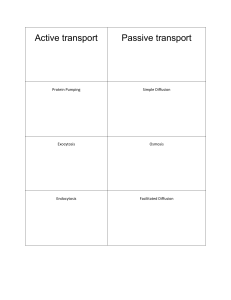
Characteristics of Living Things and Microscopes
... 3. Cells grow, respond the their environment, and reproduce 4. Unicellular= one cell; Multicellular= many cells B. Living things reproduce 1. Sexual reproduction= two cells from different parents unite to produce the first cell of the new organism. 2. Asexual reproduction= the new organism has a sin ...
... 3. Cells grow, respond the their environment, and reproduce 4. Unicellular= one cell; Multicellular= many cells B. Living things reproduce 1. Sexual reproduction= two cells from different parents unite to produce the first cell of the new organism. 2. Asexual reproduction= the new organism has a sin ...
AP Biology Lab 2
... All new cells come from previously existing cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division, which involves both replication of the cell's nucleus (karyokinesis) and division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis). There are two types of nuclear division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis typically r ...
... All new cells come from previously existing cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division, which involves both replication of the cell's nucleus (karyokinesis) and division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis). There are two types of nuclear division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis typically r ...
Cross Section Animal Cell Model
... The animal cell is a typical eukaryotic cell, and while there are some differences between functions of specific cells, they all contain the same basic organelles. The animal cell type is found not just in animals but in humans as well. This animal cell model allows students to investigate the diffe ...
... The animal cell is a typical eukaryotic cell, and while there are some differences between functions of specific cells, they all contain the same basic organelles. The animal cell type is found not just in animals but in humans as well. This animal cell model allows students to investigate the diffe ...
SIA Worksheet
... a. The cell will immediately divide b. Cell processes will continue unchanged. c. The cell will eliminate wastes more efficiently. d. Many chemical reactions in the cell will slow down or even stop. Explain: ...
... a. The cell will immediately divide b. Cell processes will continue unchanged. c. The cell will eliminate wastes more efficiently. d. Many chemical reactions in the cell will slow down or even stop. Explain: ...
Ch 7 - Cell Parts
... cell division, they are not synthesized like other cell parts --function to store energy for cell use. Energy is stored in the ...
... cell division, they are not synthesized like other cell parts --function to store energy for cell use. Energy is stored in the ...
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... cell cycle controlled by STOP & GO chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
... cell cycle controlled by STOP & GO chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... cell cycle controlled by STOP & GO chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
... cell cycle controlled by STOP & GO chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
Cells B - Depoali
... a. Cells can be produced from nonliving matter. b. Only plants are composed of cells. c. Cells are one of several basic units of structure and function in living things. d. All cells are produced from other cells. ...
... a. Cells can be produced from nonliving matter. b. Only plants are composed of cells. c. Cells are one of several basic units of structure and function in living things. d. All cells are produced from other cells. ...
Cell Organelles – Foldable Study Guide Cell Wall Cell membrane
... carbohydrates and lipids to proteins x : Drive/Biology/Woodgrove/JHaugh 2011 Visual Foldable – Google.com images ...
... carbohydrates and lipids to proteins x : Drive/Biology/Woodgrove/JHaugh 2011 Visual Foldable – Google.com images ...
BIO 221
... It is about 1mm long (1000X longer than the cell) It’s localized in the nucleoid Plasmids – small circular pieces of nonchromosomal DNA Functions? Ribosomes (70S) – function? Protein synthesis ...
... It is about 1mm long (1000X longer than the cell) It’s localized in the nucleoid Plasmids – small circular pieces of nonchromosomal DNA Functions? Ribosomes (70S) – function? Protein synthesis ...
Cell Processes Review
... When vesicles are formed at the endoplasmic reticulum of Golgi complex and they carry large particles to the cell membrane to exit the cell, this is called ...
... When vesicles are formed at the endoplasmic reticulum of Golgi complex and they carry large particles to the cell membrane to exit the cell, this is called ...
The Cell - Walton High
... How the light microscope works: • Most microscopes are called light microscopes because they accomplish their task by using lenses to bend light rays. ...
... How the light microscope works: • Most microscopes are called light microscopes because they accomplish their task by using lenses to bend light rays. ...
Directions: For each organelle you need to, draw a picture of the
... processes in the cell. These structures that the cytoplasm contains are called organelles.) ...
... processes in the cell. These structures that the cytoplasm contains are called organelles.) ...
File
... attaches to our normal cells and injects its genetic material into our cell. When the genetic material reaches the nucleus it takes over control of our cell. It directs the hijacked cell to reproduce many more viruses and then bursts our cell, killing it, and sends out the many reproduced viruses to ...
... attaches to our normal cells and injects its genetic material into our cell. When the genetic material reaches the nucleus it takes over control of our cell. It directs the hijacked cell to reproduce many more viruses and then bursts our cell, killing it, and sends out the many reproduced viruses to ...
Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function
... a. Central Vacuole found in plants used for water and food storage Makes plant firm Turgor Pressure ...
... a. Central Vacuole found in plants used for water and food storage Makes plant firm Turgor Pressure ...
Tài liệu PDF
... the site. FtsZ proteins can form filaments, rings, and other three-dimensional structures resembling the way tubulin forms microtubules, centrioles, and various cytoskeleton components. In addition, both FtsZ and tubulin employ the same energy source, GTP (guanosine triphosphate), to rapidly assembl ...
... the site. FtsZ proteins can form filaments, rings, and other three-dimensional structures resembling the way tubulin forms microtubules, centrioles, and various cytoskeleton components. In addition, both FtsZ and tubulin employ the same energy source, GTP (guanosine triphosphate), to rapidly assembl ...
Organelless Are Like Towns - grade6structureoflivingthings
... a town. They both transport materials around the system. The Endoplasmic Reticulum transports materials around the cell, when the cars transport people around the town. Ribosome-Grocery store The Ribosome is like a super market in a town. They both store protein to be used to keep the system healthy ...
... a town. They both transport materials around the system. The Endoplasmic Reticulum transports materials around the cell, when the cars transport people around the town. Ribosome-Grocery store The Ribosome is like a super market in a town. They both store protein to be used to keep the system healthy ...
The Cell
... Cell response to injury is not an all-or-nothing phenomenon: The stronger and the longer the stimulus, the larger the damage Response to a given stimulus depends on the type, status, and genetic make-up of the injured cell: Contrast ischemia in skeletal muscle (tolerates 2 hours) versus cardiac musc ...
... Cell response to injury is not an all-or-nothing phenomenon: The stronger and the longer the stimulus, the larger the damage Response to a given stimulus depends on the type, status, and genetic make-up of the injured cell: Contrast ischemia in skeletal muscle (tolerates 2 hours) versus cardiac musc ...
Plasma Membrane (cell membrane)
... 3. They are self replicating and the most common microbodies in the cell ...
... 3. They are self replicating and the most common microbodies in the cell ...
Cell
... Made up of one or many CELLS Move (or moving parts) Get rid of waste Grow Reproduce ...
... Made up of one or many CELLS Move (or moving parts) Get rid of waste Grow Reproduce ...
cell
... All cells have the following parts in common: The cell membrane and cytoplasm. The cell membrane give the cell shape and protection. The cytoplasm is the fluid part of the cell. Organelles are structures in the cell that carry out specific functions. All cells contain DNA (the genetic material that ...
... All cells have the following parts in common: The cell membrane and cytoplasm. The cell membrane give the cell shape and protection. The cytoplasm is the fluid part of the cell. Organelles are structures in the cell that carry out specific functions. All cells contain DNA (the genetic material that ...