Chapter 5
... DNA stays in the nucleus but RNA can move from out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm. Some RNA acts like a messenger for DNA. It delivers instructions for making proteins at the ribosomes. Before a cell reproduces, it’s chromosomes are copied so that the new cell has the same genes. ...
... DNA stays in the nucleus but RNA can move from out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm. Some RNA acts like a messenger for DNA. It delivers instructions for making proteins at the ribosomes. Before a cell reproduces, it’s chromosomes are copied so that the new cell has the same genes. ...
DNA Extraction Lab
... enzyme to cut proteins just like a pair of scissors. The DNA in the nucleus of the cell is molded, folded, and protected by proteins. The meat tenderizer cuts the proteins away from the DNA. ...
... enzyme to cut proteins just like a pair of scissors. The DNA in the nucleus of the cell is molded, folded, and protected by proteins. The meat tenderizer cuts the proteins away from the DNA. ...
extreme conditions
... • Almost never capable of movement • Build cell walls that don’t contain cellulose • They have many nucleii but do not always have complete cell walls between them. ...
... • Almost never capable of movement • Build cell walls that don’t contain cellulose • They have many nucleii but do not always have complete cell walls between them. ...
Science Review Midterm 10
... For hundreds of years, it was believed that living things could sometimes come from non-living things: Ex: mice were created by a pile of straw ...
... For hundreds of years, it was believed that living things could sometimes come from non-living things: Ex: mice were created by a pile of straw ...
Functions of Organelles - Belle Vernon Area School District
... The Cell Theory • The cell is the basic unit of life • All organisms are made up of cells • All cells come from other cells ...
... The Cell Theory • The cell is the basic unit of life • All organisms are made up of cells • All cells come from other cells ...
word - marric
... Scientists found that, over a period of 200 years, a mountain pond was transformed into a meadow. During that time, several communities of organisms were replaced by different communities. Explain why new communities were able to replace older communities. ...
... Scientists found that, over a period of 200 years, a mountain pond was transformed into a meadow. During that time, several communities of organisms were replaced by different communities. Explain why new communities were able to replace older communities. ...
Cytology R
... All living things are composed of cells Cells are basic units of life New cells come from pre-existing cells ...
... All living things are composed of cells Cells are basic units of life New cells come from pre-existing cells ...
Ch 4 Modern Bio Cell Biology Student copy The History of Cell
... 3. What are peripheral proteins 4. What is often attached to integral proteins? 5. What function do some integral proteins have? iv. Fluid Mosaic Model 1. What is meand by the fluid mosaic model of the bilayer? b. Nucleus i. What is nucleoplasm and what is it’s function: ii. What does the nucleus ho ...
... 3. What are peripheral proteins 4. What is often attached to integral proteins? 5. What function do some integral proteins have? iv. Fluid Mosaic Model 1. What is meand by the fluid mosaic model of the bilayer? b. Nucleus i. What is nucleoplasm and what is it’s function: ii. What does the nucleus ho ...
Cells - SchoolRack
... organelles which are special structures that perform important cellular functions – Ex: All ...
... organelles which are special structures that perform important cellular functions – Ex: All ...
Cell Organelle Collage Project
... Remember, it takes 3 million cells to cover the head of a pin, but only one cell collage to cover a large part of your Biology grade. Assignment: You must write an original and appropriate analogy between cell organelles/structures and everyday objects. “An analogy is a comparison between two things ...
... Remember, it takes 3 million cells to cover the head of a pin, but only one cell collage to cover a large part of your Biology grade. Assignment: You must write an original and appropriate analogy between cell organelles/structures and everyday objects. “An analogy is a comparison between two things ...
Monday, February 16, 2009
... Name the different cell types (do not need to label the letters yet! But you will have to in Section 2.3) ...
... Name the different cell types (do not need to label the letters yet! But you will have to in Section 2.3) ...
The Living Cell
... • All living things are composed of cells • The cell is the fundamental unit of life • All cells arise from previous cells ...
... • All living things are composed of cells • The cell is the fundamental unit of life • All cells arise from previous cells ...
Eukaryotic Cellular Organelles
... Cells manufacture proteins which serve many different functions within the cell or beyond the cell. Imagine you are a protein—write journal entries describing your adventures as you are created and travel through the cell to your final destination. ...
... Cells manufacture proteins which serve many different functions within the cell or beyond the cell. Imagine you are a protein—write journal entries describing your adventures as you are created and travel through the cell to your final destination. ...
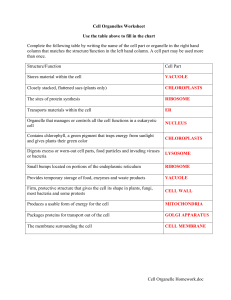
cell organelle WS 2014
... C. Put a check in the appropriate column(s) to indicate whether the following organelles are found in plant cells, animal cells or both plant & animal cells. ...
... C. Put a check in the appropriate column(s) to indicate whether the following organelles are found in plant cells, animal cells or both plant & animal cells. ...
DNA Half-Life
... 1. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including most bacteria) or multicellular (including animals, plants and most fungi). 2. Organisms can be classified as prokaryotic (made of cells that do not have a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (made of cells that have t ...
... 1. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including most bacteria) or multicellular (including animals, plants and most fungi). 2. Organisms can be classified as prokaryotic (made of cells that do not have a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (made of cells that have t ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.