Ribosomes
... The Nucleus contains the cell's DNA, which is the blueprint or instructions for all of the cell's activities. Everything a cell does is directed by the DNA. ...
... The Nucleus contains the cell's DNA, which is the blueprint or instructions for all of the cell's activities. Everything a cell does is directed by the DNA. ...
Prokaryote Eukaryote Worksheet
... Here's a simple visual comparison between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell: ...
... Here's a simple visual comparison between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell: ...
Cell Organelles - Shelton School District
... The “assembly line” of the cell Made up of proteins and nucleic acids Ribosomes are found on the outside of the Endoplasmic Reticulum and others are found floating in the cell. ...
... The “assembly line” of the cell Made up of proteins and nucleic acids Ribosomes are found on the outside of the Endoplasmic Reticulum and others are found floating in the cell. ...
Cell-testRvwPPT_Answers to Questions
... • Golgi Apparatus – “fedEx of Cell”, packages proteins for delivery in/out of cell • Endoplasmic Reticulum – “highway of the cell”, transports proteins throughout cell. – Rough E.R. = has Ribosomes – Smooth E.R. = no ribosomes ...
... • Golgi Apparatus – “fedEx of Cell”, packages proteins for delivery in/out of cell • Endoplasmic Reticulum – “highway of the cell”, transports proteins throughout cell. – Rough E.R. = has Ribosomes – Smooth E.R. = no ribosomes ...
The Cell Study Guide
... 1. able to describe the internal structure of eukaryotic cells. 2. Summarize the functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. 3. Know how organelles can work together as a system. For example, ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, they exit through the pores in the nucleus and are found in the ...
... 1. able to describe the internal structure of eukaryotic cells. 2. Summarize the functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. 3. Know how organelles can work together as a system. For example, ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, they exit through the pores in the nucleus and are found in the ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... Here's a simple visual comparison between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell: ...
... Here's a simple visual comparison between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell: ...
Cell Unit Notes
... Made possible by the discovery of the microscope in 17th century 1665 – Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. Observed pores and compartments and developed the term “Cell.” Did Hooke see living cells? 1673 – Antoine van Leeuwenhoek a Dutch microscope maker was the f ...
... Made possible by the discovery of the microscope in 17th century 1665 – Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. Observed pores and compartments and developed the term “Cell.” Did Hooke see living cells? 1673 – Antoine van Leeuwenhoek a Dutch microscope maker was the f ...
worksheet - Humble ISD
... _______ Division of the cytoplasm _______ DNA uncoils; returns to chromatin form _______ Spindle fibers begin to form as centrioles move apart _______ Sister chromatids are pulled apart _______ Nucleolus, nuclear membrane re-form _______ Cell is doing its cell job _______ Sister chromatids align in ...
... _______ Division of the cytoplasm _______ DNA uncoils; returns to chromatin form _______ Spindle fibers begin to form as centrioles move apart _______ Sister chromatids are pulled apart _______ Nucleolus, nuclear membrane re-form _______ Cell is doing its cell job _______ Sister chromatids align in ...
Organelles of the Plant Cell - University of Central Oklahoma
... Consists of an inner membrane and an outer membrane Cristae - foldings in the inner membrane Matrix – central space Intermembrane space – space between the membranes Contain their own DNA ...
... Consists of an inner membrane and an outer membrane Cristae - foldings in the inner membrane Matrix – central space Intermembrane space – space between the membranes Contain their own DNA ...
Cells: The Living Units: Part D
... • mRNA–ribosome complex is directed to rough ER by a signalrecognition particle (SRP) • Forming protein enters the ER • Sugar groups may be added to the protein, and its shape may be altered • Protein is enclosed in a vesicle for transport to Golgi apparatus Other Roles of DNA • Intron (―junk‖) regi ...
... • mRNA–ribosome complex is directed to rough ER by a signalrecognition particle (SRP) • Forming protein enters the ER • Sugar groups may be added to the protein, and its shape may be altered • Protein is enclosed in a vesicle for transport to Golgi apparatus Other Roles of DNA • Intron (―junk‖) regi ...
Blank flipbook
... 2. have ____________________like bacteria 3. have _____________________ in their inner membranes like bacteria 4. divide using ________________________ like bacteria 5. have a __________________________ loop of DNA like bacteria ...
... 2. have ____________________like bacteria 3. have _____________________ in their inner membranes like bacteria 4. divide using ________________________ like bacteria 5. have a __________________________ loop of DNA like bacteria ...
Note 2.1 Cell Structures
... c. the cell is the smallest entity that expresses the characteristics of life. ...
... c. the cell is the smallest entity that expresses the characteristics of life. ...
7.2 Cell structureGS
... Describe the role of vacuoles, lysosomes, and the cytoskeleton. Identify the role of ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus in making proteins. Describe the function of the chloroplasts and mitochondria in the cell. Describe the function of the cell membrane. ...
... Describe the role of vacuoles, lysosomes, and the cytoskeleton. Identify the role of ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus in making proteins. Describe the function of the chloroplasts and mitochondria in the cell. Describe the function of the cell membrane. ...
Cellular Sundae
... variety of sweet treats. The activity will be performed in pairs, but each student will create their own model. Some pairs will create whole animal cells using ziploc bags as the cell membrane that they will fill with cytoplasm (ice cream) and organelles (a variety of candies). The other pairs will ...
... variety of sweet treats. The activity will be performed in pairs, but each student will create their own model. Some pairs will create whole animal cells using ziploc bags as the cell membrane that they will fill with cytoplasm (ice cream) and organelles (a variety of candies). The other pairs will ...
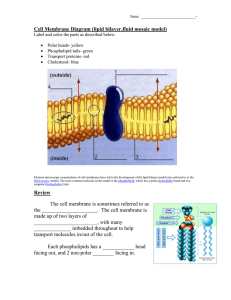
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.