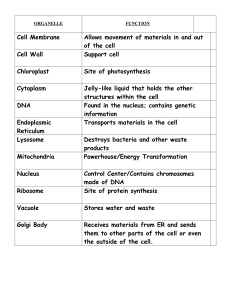
CELL PARTS MATCHING - SD43 Teacher Sites
... PACKAGES PROTEIN AND MAKES IT AVAILABLE TO THE CELL ...
... PACKAGES PROTEIN AND MAKES IT AVAILABLE TO THE CELL ...
AP Biology Cell Lab
... b. Prokaryotes tend to be large and multicellular while eukaryotes tend to be much smaller and usually unicellular. c. Unlike prokaryotes, eukaryotes have various membrane-bound organelles. d. Eukaryotic DNA is linear and stored typically in a nucleus while prokaryotic DNA occurs in small loops. ___ ...
... b. Prokaryotes tend to be large and multicellular while eukaryotes tend to be much smaller and usually unicellular. c. Unlike prokaryotes, eukaryotes have various membrane-bound organelles. d. Eukaryotic DNA is linear and stored typically in a nucleus while prokaryotic DNA occurs in small loops. ___ ...
Cell wall: A protective layer external to the plasma membrane in
... and flexible, whereas the secondary cell wall is stronger and more rigid and is the primary constituent of wood. Central vacuole: A membranous sac in a mature plant cell with diverse roles in reproduction, growth, and development. Chloroplasts: An organelle found only in plants and photosynthetic pr ...
... and flexible, whereas the secondary cell wall is stronger and more rigid and is the primary constituent of wood. Central vacuole: A membranous sac in a mature plant cell with diverse roles in reproduction, growth, and development. Chloroplasts: An organelle found only in plants and photosynthetic pr ...
Cell Theory`s 3 Main Ideas
... • Both types of cells contain a plasma membrane which creates a boundary between the cell and its environment • The membrane allows only certain materials to enter or leave (Selective Permeability). This helps the cells maintain homeostasis – Kind of like the screen in a window; It lets air in but k ...
... • Both types of cells contain a plasma membrane which creates a boundary between the cell and its environment • The membrane allows only certain materials to enter or leave (Selective Permeability). This helps the cells maintain homeostasis – Kind of like the screen in a window; It lets air in but k ...
Cell Test Review
... Cells work together to form a __________________. Tissue What organelles are used to store water, food, or waste materials? Vacuoles What threadlike structures contain information about the organism? Chromosomes What is the jelly-like substance between the cell membrane and the nucleus? Cytoplasm Wh ...
... Cells work together to form a __________________. Tissue What organelles are used to store water, food, or waste materials? Vacuoles What threadlike structures contain information about the organism? Chromosomes What is the jelly-like substance between the cell membrane and the nucleus? Cytoplasm Wh ...
Diffusion - Union High School
... membranes by proteins in the membrane that act like pumps. • Many cells use protein pumps to move calcium, potassium, and sodium ions across cell membranes. ...
... membranes by proteins in the membrane that act like pumps. • Many cells use protein pumps to move calcium, potassium, and sodium ions across cell membranes. ...
A Tour of the Cell
... Used for lipid synthesis, carbohydrate storage, detoxification of poisons. Rough ER: with ribosomes. Makes secretory proteins. ...
... Used for lipid synthesis, carbohydrate storage, detoxification of poisons. Rough ER: with ribosomes. Makes secretory proteins. ...
Cell Architecture
... • Single Membrane Structures – Plasma Membrane – Endoplasmic Reticulum – Golgi Apparatus – Lysosome – Peroxisome – Endosome ...
... • Single Membrane Structures – Plasma Membrane – Endoplasmic Reticulum – Golgi Apparatus – Lysosome – Peroxisome – Endosome ...
Organelle Notes
... Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
... Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
Bio Ch 4-2 Notes
... A system of membranous tubules and sacs Functions as a pathway for molecules to move from one part of a cell to another ...
... A system of membranous tubules and sacs Functions as a pathway for molecules to move from one part of a cell to another ...
The Plasma Membrane aka the cell membrane http://sun
... • 3. Separates the contents of the cell from the external environment. • 4. It is extremely thin (you could stack 10,000 plasma membranes to equal the thickness of a piece of paper). ...
... • 3. Separates the contents of the cell from the external environment. • 4. It is extremely thin (you could stack 10,000 plasma membranes to equal the thickness of a piece of paper). ...
BIO STUDY GUIDE - Biochemistry and Cells
... 28. Review the chemistry quiz … you may see these types of questions again! (know how to use the periodic table). 29. balance equations (simple … matter can not be created or destroyed but it may be rearranged). 30. How many different amino acids are there? 31. What tests are used to identify the fo ...
... 28. Review the chemistry quiz … you may see these types of questions again! (know how to use the periodic table). 29. balance equations (simple … matter can not be created or destroyed but it may be rearranged). 30. How many different amino acids are there? 31. What tests are used to identify the fo ...
The Cell: Organelles and Functions
... Nuclear envelope surrounds chromatin, 2 layers Function: Cellular “Command Center” Difference between chromatin and chromosomes? ...
... Nuclear envelope surrounds chromatin, 2 layers Function: Cellular “Command Center” Difference between chromatin and chromosomes? ...
CELLULAR ORGANELLES Chapter 2 Lesson 2 Part 2
... mitochondria many be large and numerous with many cristae (as in muscle cells) or they may be small and relatively few with only a few cristae. ...
... mitochondria many be large and numerous with many cristae (as in muscle cells) or they may be small and relatively few with only a few cristae. ...
Cell Organelles
... Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope Usually one per cell ...
... Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope Usually one per cell ...
Cell Organelle Web Quest
... 2. What do vacuoles store? (3 things) 3. The golgi apparatus groups __________________ and _________________, packages them in ___________________________, then ____________________ them outside or within the cell. 4. Chloroplasts help plant cells use ______________ through a process called ________ ...
... 2. What do vacuoles store? (3 things) 3. The golgi apparatus groups __________________ and _________________, packages them in ___________________________, then ____________________ them outside or within the cell. 4. Chloroplasts help plant cells use ______________ through a process called ________ ...
File
... 14. A system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materialsare made is the ______________________. 15. Two forms of endoplasmic reticulum are and ______________________. ...
... 14. A system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materialsare made is the ______________________. 15. Two forms of endoplasmic reticulum are and ______________________. ...
Cell Transport Notes Learning Targets 8. Explain the significance of
... 10 Explain the terms: hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic in relationship to the internal environments of cells. ...
... 10 Explain the terms: hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic in relationship to the internal environments of cells. ...
Cell Organelles - Mayfield City Schools
... • The Golgi will release these proteins in vesicles: sort of like a sac, which will protect the protein(s). An example are lysosomes, which are produced by Rough ER /Golgi activity. These sacs (lysosomes), are often considered a type of cell organelle, and they contain enzymes, which digest and brea ...
... • The Golgi will release these proteins in vesicles: sort of like a sac, which will protect the protein(s). An example are lysosomes, which are produced by Rough ER /Golgi activity. These sacs (lysosomes), are often considered a type of cell organelle, and they contain enzymes, which digest and brea ...
organellesNed2013 35.5 KB
... protein synthesis from RNA template. Ribosomes can be loose or ER-bound. See board for diagram. E: Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): membranous tubules and sacs are involved in circulation and transport (maze-like). comes off of nucleus. Ribosomes can be attached (Rough ER or RER); otherwise, ER is smooth ...
... protein synthesis from RNA template. Ribosomes can be loose or ER-bound. See board for diagram. E: Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): membranous tubules and sacs are involved in circulation and transport (maze-like). comes off of nucleus. Ribosomes can be attached (Rough ER or RER); otherwise, ER is smooth ...
name date ______ period - West Ashley High School
... A. endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus B. mitochondria and Golgi apparatus C. nucleus and lysosomes D. vacuoles and mitochondria 4. Cells like muscle cells which require lots of energy would probably have many _____________. A. nuclei B. Flagella C. Mitochondria D. lysosomes 5. Viruses, bacter ...
... A. endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus B. mitochondria and Golgi apparatus C. nucleus and lysosomes D. vacuoles and mitochondria 4. Cells like muscle cells which require lots of energy would probably have many _____________. A. nuclei B. Flagella C. Mitochondria D. lysosomes 5. Viruses, bacter ...
The Cell
... Two types: Smooth and Rough The smooth is ribosome free and functions in poison detoxification. The rough contains ribosomes and releases newly made protein from the cell. ...
... Two types: Smooth and Rough The smooth is ribosome free and functions in poison detoxification. The rough contains ribosomes and releases newly made protein from the cell. ...
Science - B1 Cell Structure and Transport in and out of Cells
... real thing looks like • Just ‘google’ the name of the organelle followed by the word photomicrograph ...
... real thing looks like • Just ‘google’ the name of the organelle followed by the word photomicrograph ...