Major Parts of Eukaryotic Cells A cell wall is a tough, usually flexible
... cytoplasm in cells, separating the interior of the cell from the outside environment. It is semipermeable and controls what enters and exits the cell. Small molecules such as water and oxygen can flow freely between the membrane but larger molecules are actively pumped in our out by the proteins emb ...
... cytoplasm in cells, separating the interior of the cell from the outside environment. It is semipermeable and controls what enters and exits the cell. Small molecules such as water and oxygen can flow freely between the membrane but larger molecules are actively pumped in our out by the proteins emb ...
Cole Research RCST 4029B Offic
... Many years of biochemical research have concluded that organisms are extraordinarily uniform at the molecular level ...
... Many years of biochemical research have concluded that organisms are extraordinarily uniform at the molecular level ...
1.2 * Cells: The Basic Units of Life
... cells are ‘semi-permeable’ (meaning they selectively allow certain substances through) Cell wall – firm, porous structures found outside of the cell membrane which give plants rigidity while allowing water and dissolved materials to pass through; found ONLY in PLANTS ...
... cells are ‘semi-permeable’ (meaning they selectively allow certain substances through) Cell wall – firm, porous structures found outside of the cell membrane which give plants rigidity while allowing water and dissolved materials to pass through; found ONLY in PLANTS ...
Cell surface dynamics, and the role of endocytic machineries All
... very dynamic and accounts for a major part of the endocytosed material in fibroblasts. Uptake is orchestrated by the small G-protein cdc42, which cooperates with GRAF1, Arf1 and ARHGAP10 to control carrier formation (For review see (Mayor S et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014). Caveolae Cave ...
... very dynamic and accounts for a major part of the endocytosed material in fibroblasts. Uptake is orchestrated by the small G-protein cdc42, which cooperates with GRAF1, Arf1 and ARHGAP10 to control carrier formation (For review see (Mayor S et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014). Caveolae Cave ...
Study Sheet: Endomembrane System and Endosymbiosis
... of a protein from its site of manufacture in the RER to the outside of the cell with a red arrow. Finally, trace the path of an enzyme incorporated into a lysosome in blue. ...
... of a protein from its site of manufacture in the RER to the outside of the cell with a red arrow. Finally, trace the path of an enzyme incorporated into a lysosome in blue. ...
Document
... 2. Which part of the cell is selectively permeable, allowing only certain things in and out, in order to maintain this balance? 3. Give a creative example of diffusion. ...
... 2. Which part of the cell is selectively permeable, allowing only certain things in and out, in order to maintain this balance? 3. Give a creative example of diffusion. ...
Cell Division and Mitosis
... When cells grow, they increase faster in volume than in surface area Different microscopes modify light rays or accelerated beams of electrons that allow small images to be observed ...
... When cells grow, they increase faster in volume than in surface area Different microscopes modify light rays or accelerated beams of electrons that allow small images to be observed ...
Part B: Cell Organelles Structure and Function
... Using information that can be found using the Modern Biology book (chapter 5) OR your text (chapter 7), give the function of the following organelles as well as the type of cell they are found in. Structure 1. Cytoplasm ...
... Using information that can be found using the Modern Biology book (chapter 5) OR your text (chapter 7), give the function of the following organelles as well as the type of cell they are found in. Structure 1. Cytoplasm ...
Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, and Lysosomes
... cytoplasm.. This environment actiivates the hy hydrolases and confiness their destruuctive work k to the ...
... cytoplasm.. This environment actiivates the hy hydrolases and confiness their destruuctive work k to the ...
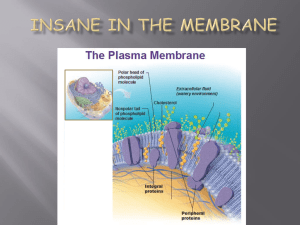
Cell Membrane aka Plasma Membrane
... (attract water) Tails are made of fatty acids and are hydrophobic (repel water) Make up a bilayer where tails point inward toward each other Can move laterally to allow small molecules (O2, CO2, & H2O to enter) copyright cmassengale ...
... (attract water) Tails are made of fatty acids and are hydrophobic (repel water) Make up a bilayer where tails point inward toward each other Can move laterally to allow small molecules (O2, CO2, & H2O to enter) copyright cmassengale ...
Monkemeier - Madison Public Schools
... a. This is the outer boundary of a bacteria (prokaryote). It provides structure and support. b. This is the area in the cytoplasm that contains the chromosome (DNA) c. This is the only membrane that the bacteria (prokaryote) is allowed to have. It lies just inside the cell wall. d. This is the fluid ...
... a. This is the outer boundary of a bacteria (prokaryote). It provides structure and support. b. This is the area in the cytoplasm that contains the chromosome (DNA) c. This is the only membrane that the bacteria (prokaryote) is allowed to have. It lies just inside the cell wall. d. This is the fluid ...
Cell Study Guide - Miss Gleason`s Science
... _________________ are found in the cell membrane, including some which are transmembrane and some that are peripheral membrane. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm consists of a clear liquid called ______________________, a supportive ____________________________, and networks of membranes and organelles. ribo ...
... _________________ are found in the cell membrane, including some which are transmembrane and some that are peripheral membrane. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm consists of a clear liquid called ______________________, a supportive ____________________________, and networks of membranes and organelles. ribo ...
KEY WORDS/
... F: cholesterol: prevents membrane from solidifying G: sugars: helps as an ID tag for the cell H: skip I: skip J: cytoskeleton fibers: cell structure Fluid: all the stuff moves around with in the cell membrane Mosaic: membrane made up of lots of different parts ...
... F: cholesterol: prevents membrane from solidifying G: sugars: helps as an ID tag for the cell H: skip I: skip J: cytoskeleton fibers: cell structure Fluid: all the stuff moves around with in the cell membrane Mosaic: membrane made up of lots of different parts ...
Chapt 7 review worksheet answers
... The beaker in the diagram has a selectively permeable membrane separating two solutions. Assume that the water molecules can pass freely through the membrane but salt and starch molecules cannot. When equilibrium is reached, which side will contain the ...
... The beaker in the diagram has a selectively permeable membrane separating two solutions. Assume that the water molecules can pass freely through the membrane but salt and starch molecules cannot. When equilibrium is reached, which side will contain the ...
Bio1A Unit 1-3 The Cell Notes File
... Some types of cell can engulf another cell by phagocytosis; this forms a food vacuole ...
... Some types of cell can engulf another cell by phagocytosis; this forms a food vacuole ...
Cellular Architecture
... eukaryotic • B. Typical cell – 1. animal – 2. plant – 3. discuss the similarities first ...
... eukaryotic • B. Typical cell – 1. animal – 2. plant – 3. discuss the similarities first ...
Cells - Weebly
... Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. ...
... Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. ...
Cell Structure and Membrane Transport Study Guide
... Tissue types- epithelial, muscle, connective and nervous. Animal organ systems include respiratory, digestive, nervous and other systems. Plant organs include leaves, root, stem and flower Eukaryotic Cell Organelles: Nucleus – large, central, surrounded by double membrane “envelope,” holds the DNA. ...
... Tissue types- epithelial, muscle, connective and nervous. Animal organ systems include respiratory, digestive, nervous and other systems. Plant organs include leaves, root, stem and flower Eukaryotic Cell Organelles: Nucleus – large, central, surrounded by double membrane “envelope,” holds the DNA. ...
Cellular Architecture
... eukaryotic • B. Typical cell – 1. animal – 2. plant – 3. discuss the similarities first ...
... eukaryotic • B. Typical cell – 1. animal – 2. plant – 3. discuss the similarities first ...
Cell Transport Review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... What process is shown in Figure A? _____________________________ What process is shown in Figure B? _____________________________ ...
... What process is shown in Figure A? _____________________________ What process is shown in Figure B? _____________________________ ...
Cell Test Study Guide Answers
... 3) What do chloroplasts and mitochondria have in common? They both make energy for the cells (mitochondria in animal cells chloroplasts in plant cells) 4) What limits how large a cell can grow? Surface area 5) What is the difference between a eukaryote and a prokaryote? Eukaryotes have a nucleus and ...
... 3) What do chloroplasts and mitochondria have in common? They both make energy for the cells (mitochondria in animal cells chloroplasts in plant cells) 4) What limits how large a cell can grow? Surface area 5) What is the difference between a eukaryote and a prokaryote? Eukaryotes have a nucleus and ...
Note taking guide
... depending upon activity of cell. Cells with high metabolic activity have many lysosomes. Different types of lysosomes depend on content and density. Lysosomes work with a nucleus to make proteins. ...
... depending upon activity of cell. Cells with high metabolic activity have many lysosomes. Different types of lysosomes depend on content and density. Lysosomes work with a nucleus to make proteins. ...