Cell Analogy Project - Warren Hills Regional School District
... Mitochondrion DNA Cell wall cell membrane nuclear membrane Chloroplast ribosomes cytoplasm ...
... Mitochondrion DNA Cell wall cell membrane nuclear membrane Chloroplast ribosomes cytoplasm ...
Cell Structure
... Golgi Apparatus • resembles flattened stack of hollow tubes, i.e. similar to smooth endoplasmic reticulum, but closer to cell membrane • function: sorting, modification (assembly), & packaging of substances for storage or secretion e.g. produces glycolipids by joining carbohydrates to lipids • rece ...
... Golgi Apparatus • resembles flattened stack of hollow tubes, i.e. similar to smooth endoplasmic reticulum, but closer to cell membrane • function: sorting, modification (assembly), & packaging of substances for storage or secretion e.g. produces glycolipids by joining carbohydrates to lipids • rece ...
Cell Study Guide
... 43. Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? 44. Two organelles that are common to plant cells but not to animal cells are 45. Which parts do prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and viruses all share? 46. A wet mount of unstained elodea (a green aquatic plant) is ob ...
... 43. Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? 44. Two organelles that are common to plant cells but not to animal cells are 45. Which parts do prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and viruses all share? 46. A wet mount of unstained elodea (a green aquatic plant) is ob ...
Cell Organelles
... -found on surface of E.R. (for producing proteins to be exported out of cell) -also found free floating in cytoplasm in small groups called polysomes -polysomes produce proteins to be used inside the cell. Rough E.R. (Endoplasmic Reticulum) -series of tubular canals connected in places with nuclear ...
... -found on surface of E.R. (for producing proteins to be exported out of cell) -also found free floating in cytoplasm in small groups called polysomes -polysomes produce proteins to be used inside the cell. Rough E.R. (Endoplasmic Reticulum) -series of tubular canals connected in places with nuclear ...
Cell Biology Unit Study Guide
... 43. Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? 44. Two organelles that are common to plant cells but not to animal cells are 45. Which parts do prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and viruses all share? 46. A wet mount of unstained elodea (a green aquatic plant) is ob ...
... 43. Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? 44. Two organelles that are common to plant cells but not to animal cells are 45. Which parts do prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and viruses all share? 46. A wet mount of unstained elodea (a green aquatic plant) is ob ...
CELL TRANSPORT
... 7. A solution is composed of a solute (sugar) dissolved in a solvent (water). The direction water will move across a membrane depends on the concentration of the 2 substances. A solution may be: a) hypotonic - concentration of solute molecules outside cell is lower than in cell - water will diffuse ...
... 7. A solution is composed of a solute (sugar) dissolved in a solvent (water). The direction water will move across a membrane depends on the concentration of the 2 substances. A solution may be: a) hypotonic - concentration of solute molecules outside cell is lower than in cell - water will diffuse ...
ch4 cells guided notes
... 1. Found only in _________________________, type of _____________________ 2. Contains its own ___________________ 3. Enclosed in a ___________________________________________ - inside is made up of flattened sacs called _____________________________ Function: a. Makes ____________ & _____________ th ...
... 1. Found only in _________________________, type of _____________________ 2. Contains its own ___________________ 3. Enclosed in a ___________________________________________ - inside is made up of flattened sacs called _____________________________ Function: a. Makes ____________ & _____________ th ...
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport
... Consists of three different threadlike structures: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules ◦ Microfilaments and microtubules both components of intracellular transport Microfilaments composed of protein called actin; act like tracks within cells for myosin molecules Microtubules t ...
... Consists of three different threadlike structures: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules ◦ Microfilaments and microtubules both components of intracellular transport Microfilaments composed of protein called actin; act like tracks within cells for myosin molecules Microtubules t ...
Cell Structure & Function
... • All living things are composed of cells • Cells are the basic units of structure & function in living things • New cells are produced from existing cells ...
... • All living things are composed of cells • Cells are the basic units of structure & function in living things • New cells are produced from existing cells ...
Cell Organelles
... An organelle is a membranebound structure that carries out specific activities for the cell. ...
... An organelle is a membranebound structure that carries out specific activities for the cell. ...
Chapt03 Lecture 13ed Pt 2
... • A ____________: the semi-fluid substance inside the cell that contains organelles • DNA ...
... • A ____________: the semi-fluid substance inside the cell that contains organelles • DNA ...
Section 3 Summary – page 179-187 Energy Transformers Cells
... • To investigate and explain cellular processes, such as homeostasis, converting energy, the production of new materials, and transporting materials. ...
... • To investigate and explain cellular processes, such as homeostasis, converting energy, the production of new materials, and transporting materials. ...
CELL ANALOGY PICTURE BOOK
... Apparatus, Cell Wall, Mitochondria, Large Central Vacuole, Chloroplast, Chlorophyll, Cell Membrane, Cytoskeleton Cover with Title & Illustration of Cell Type ...
... Apparatus, Cell Wall, Mitochondria, Large Central Vacuole, Chloroplast, Chlorophyll, Cell Membrane, Cytoskeleton Cover with Title & Illustration of Cell Type ...
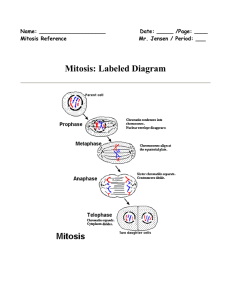
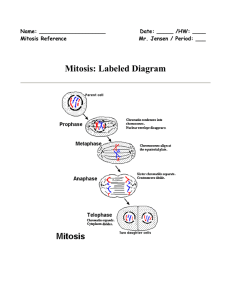
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
The Cell
... The Cell Cells vary in size, shape, content, and function. Composite Cell 3 main parts 1.nucleus 2.cell membrane 3.cytoplasm includes protein rods and tubules that form a framework called cytoskeleton Organelles within the cytoplasm Endoplasmic reticulum – transportation system for lipids and ...
... The Cell Cells vary in size, shape, content, and function. Composite Cell 3 main parts 1.nucleus 2.cell membrane 3.cytoplasm includes protein rods and tubules that form a framework called cytoskeleton Organelles within the cytoplasm Endoplasmic reticulum – transportation system for lipids and ...
A tour of the cell
... – Thousands are located suspended in the cytoplasm – Major process: • Protein synthesis (translation) ...
... – Thousands are located suspended in the cytoplasm – Major process: • Protein synthesis (translation) ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide - Conackamack Middle School
... C. Looking Inside Cells (pages 60-67) a. Eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes i. Definitions of each ii. Differences between the two b. Organelles of the plant and animal cells i. Structure of each ii. Function of each c. Similarities/Differences of plant and animal cells d. Vocabulary to include – organelle, ...
... C. Looking Inside Cells (pages 60-67) a. Eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes i. Definitions of each ii. Differences between the two b. Organelles of the plant and animal cells i. Structure of each ii. Function of each c. Similarities/Differences of plant and animal cells d. Vocabulary to include – organelle, ...
5.1-5.9 Study Guide
... ● 5.1 - Membranes are a fluid mosaic of phospholipids and proteins ○ Membrane are composed of phospholipids and proteins and it is sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic. ...
... ● 5.1 - Membranes are a fluid mosaic of phospholipids and proteins ○ Membrane are composed of phospholipids and proteins and it is sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic. ...
Cell Organelles - Cloudfront.net
... An organelle is a membranebound structure that carries out specific activities for the cell. ...
... An organelle is a membranebound structure that carries out specific activities for the cell. ...
0495116572_102919
... – mRNA codes for amino acid sequence to form protein – mRNA is synthesized in nucleus, then moves to RER in cytoplasmic matrix – Codons - 3-base sequences that code for amino acids – tRNA bring AAs to mRNA on ribosomes 2009 Cengage-Wadsworth ...
... – mRNA codes for amino acid sequence to form protein – mRNA is synthesized in nucleus, then moves to RER in cytoplasmic matrix – Codons - 3-base sequences that code for amino acids – tRNA bring AAs to mRNA on ribosomes 2009 Cengage-Wadsworth ...
Normal Protein Trafficking and the Unfolded Protein Response
... Normal trafficking of proteins through the cell involves: 1) Production of proteins along the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) ...
... Normal trafficking of proteins through the cell involves: 1) Production of proteins along the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) ...
Study Guide
... Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organization Each cell in your body has a specific function. Most ...
... Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organization Each cell in your body has a specific function. Most ...