Cells: Its Alive!
... chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions. c. Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems, and systems into organisms. d. Explain that tissues, organs, and organ systems serve the needs cells have for oxygen, food, and waste removal. ...
... chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions. c. Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems, and systems into organisms. d. Explain that tissues, organs, and organ systems serve the needs cells have for oxygen, food, and waste removal. ...
Cells
... 58. Where is the cell wall in plants found, what is its function, and what is it made of? ...
... 58. Where is the cell wall in plants found, what is its function, and what is it made of? ...
Introduction to the Cell 1) Cell Theory a) All living things are
... a) All living things are composed of one or more cells b) Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. c) Cells come only from the reproduction of existing ...
... a) All living things are composed of one or more cells b) Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. c) Cells come only from the reproduction of existing ...
IB104 - Lecture 9 - Membranes Introduction The phospolipid bilayer
... Most famously, salmon smolts leaving their river birthplaces spend weeks adjusting to the ocean, while returning adults must spend several days in the brackish water at river mouths adjusting their physiology. ...
... Most famously, salmon smolts leaving their river birthplaces spend weeks adjusting to the ocean, while returning adults must spend several days in the brackish water at river mouths adjusting their physiology. ...
Chapter 7 section 1,2 and 4- The Cell
... 9. Know the parts of the microscope, how to use it and how to calculate total magnification. (1070-1071). 10. Know these words from section 3 or from the power point.: cell wall, cell membrane, cellulose, flagella, cilia. 11. Know the levels of organization. 12. Know the order for smallest to larges ...
... 9. Know the parts of the microscope, how to use it and how to calculate total magnification. (1070-1071). 10. Know these words from section 3 or from the power point.: cell wall, cell membrane, cellulose, flagella, cilia. 11. Know the levels of organization. 12. Know the order for smallest to larges ...
Cell Notes
... Ribosomes - composed of protein and RNA, sites of protein synthesis Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum - a network of tubes that transport materials, contain ribosomes on their surface ...
... Ribosomes - composed of protein and RNA, sites of protein synthesis Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum - a network of tubes that transport materials, contain ribosomes on their surface ...
Notes
... 1) composed of two subunits a) small subunit – holds mRNA during translation b) large subunit – 2 parts i) A-site – where tRNA brings the amino acids ii) P-site – site of peptide bond formation; also holds the developing protein C) Endoplasmic Reticulum – extensive system of interconnected fluid-fil ...
... 1) composed of two subunits a) small subunit – holds mRNA during translation b) large subunit – 2 parts i) A-site – where tRNA brings the amino acids ii) P-site – site of peptide bond formation; also holds the developing protein C) Endoplasmic Reticulum – extensive system of interconnected fluid-fil ...
Cells - T.R. Robinson High School
... contains salts, minerals and organic molecules Holds organelles which have membranes around them Actual fluid portion of cytoplasm is referred to as cytosol) ...
... contains salts, minerals and organic molecules Holds organelles which have membranes around them Actual fluid portion of cytoplasm is referred to as cytosol) ...
for the cell by
... Ex. In liver cells the smooth ER is capable of releasing enzymes that can detoxify substance such as alcohol. It does this through attached peroxisomes that contain detoxification enzymes). ...
... Ex. In liver cells the smooth ER is capable of releasing enzymes that can detoxify substance such as alcohol. It does this through attached peroxisomes that contain detoxification enzymes). ...
CHAPTER 7
... when molecules move from a high to low concentration it is called moving DOWN the concentration gradient. When molecules move from a low to high concentration it is called moving AGAINST the concentration gradient. When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system, the system is at ...
... when molecules move from a high to low concentration it is called moving DOWN the concentration gradient. When molecules move from a low to high concentration it is called moving AGAINST the concentration gradient. When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system, the system is at ...
Life Science
... movement of dissolved molecules into and out of the cell 2. ____________________________-- a thick gel-like substance that surrounds and supports the organelles inside the cell 3. What are the two types of cells? a. _____________________--cells without a nucleus (ex. bacteria) b. ___________________ ...
... movement of dissolved molecules into and out of the cell 2. ____________________________-- a thick gel-like substance that surrounds and supports the organelles inside the cell 3. What are the two types of cells? a. _____________________--cells without a nucleus (ex. bacteria) b. ___________________ ...
CELLS: The Living Units
... • Continuous with the nuclear membrane • Two varieties – rough ER and smooth ER ...
... • Continuous with the nuclear membrane • Two varieties – rough ER and smooth ER ...
Life Science
... Composed of a network of protein fibers called microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Cytoskeleton Function 1. gives cells support and helps the cell keep its shape 2. anchors organelles into a certain position or allows them to move around in the cell 3. allows cells to move by ...
... Composed of a network of protein fibers called microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Cytoskeleton Function 1. gives cells support and helps the cell keep its shape 2. anchors organelles into a certain position or allows them to move around in the cell 3. allows cells to move by ...
HW 2.1 Organelles Homework Name: Date: ___ In the Venn
... b) Endoplasmic Reticulum c) Golgi Body d) Mitochondria ...
... b) Endoplasmic Reticulum c) Golgi Body d) Mitochondria ...
What is the Chapter 4 Test Like
... o How do you calculate surface area to volume ratios? o What is the significance of surface area to volume ratios? o Is a small cell or a large cell more efficient? 2. Activity: The Cell Theory o What were the contributions of each of the timeline people? o Can you list the three parts of the cell t ...
... o How do you calculate surface area to volume ratios? o What is the significance of surface area to volume ratios? o Is a small cell or a large cell more efficient? 2. Activity: The Cell Theory o What were the contributions of each of the timeline people? o Can you list the three parts of the cell t ...
Cell Analogies Poster Project – BIO II
... Cell Analogies Poster Project – BIO II Purpose: For this project you will be challenged to make 15 original and appropriate functional analogies between cell structures and everyday objects. What is an analogy? “A comparison between two things which are similar in some respects, but otherwise are di ...
... Cell Analogies Poster Project – BIO II Purpose: For this project you will be challenged to make 15 original and appropriate functional analogies between cell structures and everyday objects. What is an analogy? “A comparison between two things which are similar in some respects, but otherwise are di ...
Cells! - Personal
... • The Golgi apparatus is the site of accumulation, concentration, packaging, and chemical modification of the secretory products synthesized on the rough ER. – The transport vesicles pinch off from the ER and carry the secretions to the Golgi apparatus, where the secretions fuse with its cisternae. ...
... • The Golgi apparatus is the site of accumulation, concentration, packaging, and chemical modification of the secretory products synthesized on the rough ER. – The transport vesicles pinch off from the ER and carry the secretions to the Golgi apparatus, where the secretions fuse with its cisternae. ...
PCDU Seminar Myriam Murillo 11 November 2015
... http://web.stanford.edu/group/virus/1999/jchow/endoem.jpg ...
... http://web.stanford.edu/group/virus/1999/jchow/endoem.jpg ...
membrane notes - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Slide6: Membranes have an inside and an outside surface. The cell membrane is built by the golgi complex and the endoplasmic reticulum. Proteins made by ribosomes associated with the rough ER are packed in vesicles that drift to the golgi where they are modified and then released to fuse with the me ...
... Slide6: Membranes have an inside and an outside surface. The cell membrane is built by the golgi complex and the endoplasmic reticulum. Proteins made by ribosomes associated with the rough ER are packed in vesicles that drift to the golgi where they are modified and then released to fuse with the me ...
I1-3 Cell organelle notes
... A. Prokaryotes – very simple (bacteria) B. Eukaryotes 1. Cytoplasm – gel-like material that fills cells 2. Cytoskeleton – protein fibers that support structures in the cell 3. Organelles – carry out essential cell processes C. Organelles (see pg 199 and fill out notes on structure and function) 1. N ...
... A. Prokaryotes – very simple (bacteria) B. Eukaryotes 1. Cytoplasm – gel-like material that fills cells 2. Cytoskeleton – protein fibers that support structures in the cell 3. Organelles – carry out essential cell processes C. Organelles (see pg 199 and fill out notes on structure and function) 1. N ...
Bacterial Cell Walls Contain Peptidoglycans
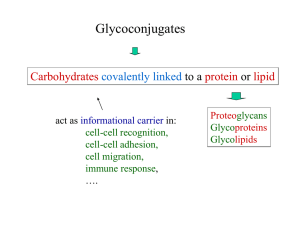
... • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination l ...
... • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination l ...
Animal Cell Label # Organelle Function Nuclear membrane
... Supports and protects the cell A thin wall or skin that protects the cell and allows things to enter and leave the cell. (think of your skin) Is the storage or closet area of the cell to hold food, waste (think vacuum cleaner holding dust) Largest organelle, “The boss” that controls cell’s activitie ...
... Supports and protects the cell A thin wall or skin that protects the cell and allows things to enter and leave the cell. (think of your skin) Is the storage or closet area of the cell to hold food, waste (think vacuum cleaner holding dust) Largest organelle, “The boss” that controls cell’s activitie ...
General Biology lab
... • Some bacteria cause disease, but most are actually helpful. • Because of their small size, it is impossible to see details inside bacterial cell with the ...
... • Some bacteria cause disease, but most are actually helpful. • Because of their small size, it is impossible to see details inside bacterial cell with the ...