Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
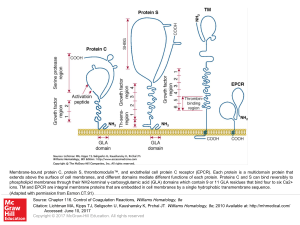
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
Ch 6 Practice Questions
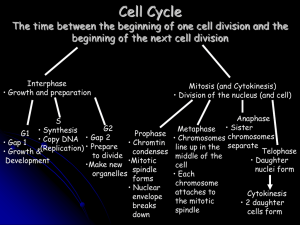
... the nucleus, which is typically about 5 micrometers in diameter chromosomes in the nucleus during cell division nuclear pore complexes (100 nanometers in diameter) on the nuclear membrane a typical bacterial cell, which is between 0.5 and 2.0 micrometers in diameter a typical eukaryotic cell, which ...
... the nucleus, which is typically about 5 micrometers in diameter chromosomes in the nucleus during cell division nuclear pore complexes (100 nanometers in diameter) on the nuclear membrane a typical bacterial cell, which is between 0.5 and 2.0 micrometers in diameter a typical eukaryotic cell, which ...
Cell Structure Review
... Coils of DNA and protein that form chromosomes. Can be thought of as chromosomes without shape. Granular-like material found in the nucleus containing genetic information ...
... Coils of DNA and protein that form chromosomes. Can be thought of as chromosomes without shape. Granular-like material found in the nucleus containing genetic information ...
Year 8 Cell VOCAB
... Single-celled microorganisms, some of which are pathogenic in humans, animals and plants. Singular is bacterium. A selectively permeable membrane surrounding the cell and controlling the entry and exit of materials. Outer structure which provides support and prevents the cell from bursting by the up ...
... Single-celled microorganisms, some of which are pathogenic in humans, animals and plants. Singular is bacterium. A selectively permeable membrane surrounding the cell and controlling the entry and exit of materials. Outer structure which provides support and prevents the cell from bursting by the up ...
Prokaryotic Cells, Eukaryotic cells and HIV: Structures, Transcription
... The cis-Golgi is near the ER and the trans Golgi is across the rest of the Golgi from the ER. As proteins in the Golgi move from the cis to the trans Golgi this is when processing occurs since there are different proteins in the different compartments. The contents of the compartments are overlappin ...
... The cis-Golgi is near the ER and the trans Golgi is across the rest of the Golgi from the ER. As proteins in the Golgi move from the cis to the trans Golgi this is when processing occurs since there are different proteins in the different compartments. The contents of the compartments are overlappin ...
Cell Tour Writing - Model High School
... 1) Pick a typical ANIMAL CELL or a typical PLANT CELL to talk about. 2) Pretend you are a Jurassic Park tour guide taking visitors on a tour through the cell. DESCRIBE what you would see as you toured the cell. Choose 5 of the 10 organelles and briefly describe their STRUCTURE and FUNCTION: •Animal ...
... 1) Pick a typical ANIMAL CELL or a typical PLANT CELL to talk about. 2) Pretend you are a Jurassic Park tour guide taking visitors on a tour through the cell. DESCRIBE what you would see as you toured the cell. Choose 5 of the 10 organelles and briefly describe their STRUCTURE and FUNCTION: •Animal ...
AP Cell Organelles
... Bound Ribosomes: are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or the nuclear envelope; makes proteins that are used in the endomembrane system or for export Cells can adjust the number and type of ribosomes depending on metabolism changes ...
... Bound Ribosomes: are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or the nuclear envelope; makes proteins that are used in the endomembrane system or for export Cells can adjust the number and type of ribosomes depending on metabolism changes ...
Date - Pearland ISD
... 8. Nucleus is called the ______________________ of the cell. It is a large __________ spot in eukaryotic cells. It _________________ all cell activity. The nuclear membrane has many ____________________. The thick ropy strands are the _____________________________. The large solid spot is the _____ ...
... 8. Nucleus is called the ______________________ of the cell. It is a large __________ spot in eukaryotic cells. It _________________ all cell activity. The nuclear membrane has many ____________________. The thick ropy strands are the _____________________________. The large solid spot is the _____ ...
Macromolecules & the Cell Membrane
... concentrated; water leaves cell – Hypotonic: solution outside of the cell is LESS concentrated; water enters the cell ...
... concentrated; water leaves cell – Hypotonic: solution outside of the cell is LESS concentrated; water enters the cell ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... 8. Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum 9. Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists 10. Produces a usable form of energy for the cell 11. Packages proteins for transport out of the cell 12. Site where ribosomes ...
... 8. Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum 9. Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists 10. Produces a usable form of energy for the cell 11. Packages proteins for transport out of the cell 12. Site where ribosomes ...
Cell Membranes The boundary of the cell, sometimes called the
... * Protein pumps are catalyses in the splitting of ATP to ADP + phosphate, so they are called ATPase enzyme. * The sodium-potassium pump actively moves sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell. and are essential in transmission of nerve impulses and in muscular contractions. *Vesicular Tran ...
... * Protein pumps are catalyses in the splitting of ATP to ADP + phosphate, so they are called ATPase enzyme. * The sodium-potassium pump actively moves sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell. and are essential in transmission of nerve impulses and in muscular contractions. *Vesicular Tran ...
Guided Notes The Cell
... Made up of water, ions, and macromolecules of the cell Organelles float within cytosol ...
... Made up of water, ions, and macromolecules of the cell Organelles float within cytosol ...
I can: State that the cell membrane is made of lipids and proteins
... Name glucose, carbon dioxide, oxygen and amino acids as examples of substances that diffuse across cell membranes. Explain the importance of diffusion to organisms as being the means by which substances enter and leave cells by movement down the concentration gradient. Identify osmosis as a ‘special ...
... Name glucose, carbon dioxide, oxygen and amino acids as examples of substances that diffuse across cell membranes. Explain the importance of diffusion to organisms as being the means by which substances enter and leave cells by movement down the concentration gradient. Identify osmosis as a ‘special ...
Structure and function of the cell
... Gives plant cells the ability to stand up and grow into trees, flowers etc. Cell wall is thicker than cell membrane ...
... Gives plant cells the ability to stand up and grow into trees, flowers etc. Cell wall is thicker than cell membrane ...
Ch. 7 Review
... Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the structures found in an animal cell that correspond with the numbers in the diagram. Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus ...
... Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the structures found in an animal cell that correspond with the numbers in the diagram. Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus ...
Transport
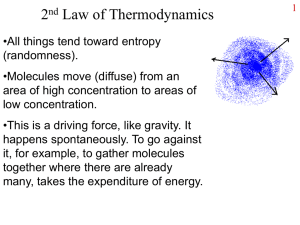
... •Molecules move (diffuse) from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration. •This is a driving force, like gravity. It happens spontaneously. To go against it, for example, to gather molecules together where there are already many, takes the expenditure of energy. ...
... •Molecules move (diffuse) from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration. •This is a driving force, like gravity. It happens spontaneously. To go against it, for example, to gather molecules together where there are already many, takes the expenditure of energy. ...
Peripheral proteins are on the outside layer… just draw one…
... chloroplasts have their own DNA… (in fact it is one of the pieces of endosymbiotic theory… they originated on their own first) ...
... chloroplasts have their own DNA… (in fact it is one of the pieces of endosymbiotic theory… they originated on their own first) ...