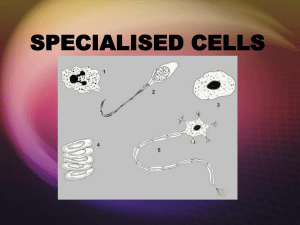
Cells Section 1 – Cell Structure
... A. Composes of cellulose, a cell wall grows, gives shape to, and protects the cells of plants, algae, fungi, and most bacteria. B. Cell membrane – protective layer around the cells A. For cells with cell walls, the cell membrane is inside the cell wall. B. A cell membrane allows food and oxygen into ...
... A. Composes of cellulose, a cell wall grows, gives shape to, and protects the cells of plants, algae, fungi, and most bacteria. B. Cell membrane – protective layer around the cells A. For cells with cell walls, the cell membrane is inside the cell wall. B. A cell membrane allows food and oxygen into ...
Cell Organelles - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... • Contains DNA – the coded instructions for making proteins & other molecules for the cell • The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores, where things can enter or leave See? ...
... • Contains DNA – the coded instructions for making proteins & other molecules for the cell • The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores, where things can enter or leave See? ...
Concept 6.4: The cell builds a diversity of products
... 1. Rough ER-The rough ER has ribosomes which insert proteins right into or through the ER membrane or packaged in vesicles and transported outside the cell 2. Smooth ER-The smooth ER lacks ribosomes but enzymes in the smooth ER allow it to make lipid molecules IV. The Golgi Apparatus A. The golgi ap ...
... 1. Rough ER-The rough ER has ribosomes which insert proteins right into or through the ER membrane or packaged in vesicles and transported outside the cell 2. Smooth ER-The smooth ER lacks ribosomes but enzymes in the smooth ER allow it to make lipid molecules IV. The Golgi Apparatus A. The golgi ap ...
SECTION3.3QUIZWITHANSWERS
... 4. Which phrase best describes the property of selective permeability? a. some molecules pass b. all ions pass c. large molecules pass d. all molecules pass ANSWER: A 5. A ligand produces a response in a cell if it finds the right kind of a. carbohydrate. ...
... 4. Which phrase best describes the property of selective permeability? a. some molecules pass b. all ions pass c. large molecules pass d. all molecules pass ANSWER: A 5. A ligand produces a response in a cell if it finds the right kind of a. carbohydrate. ...
Concept 6.4 - Plain Local Schools
... 1. Rough ER-The rough ER has ribosomes which insert proteins right into or through the ER membrane or packaged in vesicles and transported outside the cell 2. Smooth ER-The smooth ER lacks ribosomes but enzymes in the smooth ER allow it to make lipid molecules IV. The Golgi Apparatus A. The golgi ap ...
... 1. Rough ER-The rough ER has ribosomes which insert proteins right into or through the ER membrane or packaged in vesicles and transported outside the cell 2. Smooth ER-The smooth ER lacks ribosomes but enzymes in the smooth ER allow it to make lipid molecules IV. The Golgi Apparatus A. The golgi ap ...
6-cell-theory-15-16
... 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. Living cells come only from other living cells. ...
... 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. Living cells come only from other living cells. ...
Slide 1
... – Ribosomes: composed of proteins and RNA; bacterial ribosomes have a different size and structure than those in eukaryotes – DNA, RNA, and the Genetic Code: bacterial chromosome a simple ring of DNA; in eukaryotes, DNA is packaged with proteins – Other molecules / structures: membrane proteins (ex. ...
... – Ribosomes: composed of proteins and RNA; bacterial ribosomes have a different size and structure than those in eukaryotes – DNA, RNA, and the Genetic Code: bacterial chromosome a simple ring of DNA; in eukaryotes, DNA is packaged with proteins – Other molecules / structures: membrane proteins (ex. ...
Chapter 6 Notes and Outline - Bremen High School District 228
... - break fatty acids down & transport to mitochondria=fuel for cellular respiration. - detoxify alcohol and other harmful compounds in liver - Specialized peroxisomes in seeds (GLYOXYSOMES) convert fatty acids → sugars used as energy source until able to start photosynthesizing • Contain enzymes that ...
... - break fatty acids down & transport to mitochondria=fuel for cellular respiration. - detoxify alcohol and other harmful compounds in liver - Specialized peroxisomes in seeds (GLYOXYSOMES) convert fatty acids → sugars used as energy source until able to start photosynthesizing • Contain enzymes that ...
Exercises - Tiwari Academy
... its homeostasis, i.e., constant internal composition of the cell. If it ruptures or breaks down the constant internal chemical composition of the cell will be lost and it will not be able to perform its basic functions. Such a cell with ruptured plasma membrane is killed. www.tiwariacademy.com Quest ...
... its homeostasis, i.e., constant internal composition of the cell. If it ruptures or breaks down the constant internal chemical composition of the cell will be lost and it will not be able to perform its basic functions. Such a cell with ruptured plasma membrane is killed. www.tiwariacademy.com Quest ...
1a. What are the two major parts of the cell?
... 5a. Why is the cell membrane sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic? What part of the cell membrane acts like a fluid? And what makes it like a mosaic? 5a. The cell membrane is sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic because it is made of many parts that can float around in the membrane. 5c. Why do ...
... 5a. Why is the cell membrane sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic? What part of the cell membrane acts like a fluid? And what makes it like a mosaic? 5a. The cell membrane is sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic because it is made of many parts that can float around in the membrane. 5c. Why do ...
File - HSHP Biology
... -Living things are made of cells -All cells come from pre-existing cells. -Cells contain genetic information. -All cells are similar in composition. -Energy flow of life occurs in cells. ...
... -Living things are made of cells -All cells come from pre-existing cells. -Cells contain genetic information. -All cells are similar in composition. -Energy flow of life occurs in cells. ...
Instructor`s Copy
... into action to start digesting the pizza with digestive enzymes. A stomach cell first needs to get the instructions from the nucleus on how to make the digestive enzyme. The cell then constructs many of the digestive enzymes (a protein). The digestive enzymes are quickly transported through the cell ...
... into action to start digesting the pizza with digestive enzymes. A stomach cell first needs to get the instructions from the nucleus on how to make the digestive enzyme. The cell then constructs many of the digestive enzymes (a protein). The digestive enzymes are quickly transported through the cell ...
Document
... 1. Place a check mark in the correct boxes to indicate whether the cell part listed is found in plant cells, animal cells, or both: ...
... 1. Place a check mark in the correct boxes to indicate whether the cell part listed is found in plant cells, animal cells, or both: ...
File
... Complete each statement. Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. cell membrane nucleus lysosome ribosome organelle Golgi complex mitochondria organs prokaryotic 1. Various tissues that work together to perform a specific job constitute ORGANS. 2. The role of the cell’s ...
... Complete each statement. Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. cell membrane nucleus lysosome ribosome organelle Golgi complex mitochondria organs prokaryotic 1. Various tissues that work together to perform a specific job constitute ORGANS. 2. The role of the cell’s ...
Cells test study guide
... ____7. Part of the plant cell that contains chlorophyll ____8. Thin layer that encloses and gives shape to any cell ...
... ____7. Part of the plant cell that contains chlorophyll ____8. Thin layer that encloses and gives shape to any cell ...
Cell Design and Function
... Produces cellular energy for the cell in the form of ATP. (=Adenosine-P-P-P). image Contains highly folded internal membranes called cristae. image Contains it’s own DNA (theorized to have once been a ...
... Produces cellular energy for the cell in the form of ATP. (=Adenosine-P-P-P). image Contains highly folded internal membranes called cristae. image Contains it’s own DNA (theorized to have once been a ...
Section 3 Summary – page 179-187
... • allows a steady supply of glucose, amino acids, and lipids to come into the cell no matter what the external conditions are. • removes excess amounts of these nutrients when levels get so high that they are harmful. • allows waste and other products to leave the cell. ...
... • allows a steady supply of glucose, amino acids, and lipids to come into the cell no matter what the external conditions are. • removes excess amounts of these nutrients when levels get so high that they are harmful. • allows waste and other products to leave the cell. ...
The Cell
... Membranes that envelop organelles in eukaryotic cells are partial barriers ensuring that the chemical composition of the organelle’s interior differs from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. ...
... Membranes that envelop organelles in eukaryotic cells are partial barriers ensuring that the chemical composition of the organelle’s interior differs from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. ...
RG Transport Review 0910
... 8. Critical Thinking – The cell membrane regulate what enters and exits the cell. Most materials can pass through by diffusion, without a problem. The graph below shows the size of some molecules that need to move across the lipid bilayer. Size of Molecules water ...
... 8. Critical Thinking – The cell membrane regulate what enters and exits the cell. Most materials can pass through by diffusion, without a problem. The graph below shows the size of some molecules that need to move across the lipid bilayer. Size of Molecules water ...
Cell Study Guide - Biology Junction
... What are cell membranes made of? PHOSPHOLIPIDS & PROTEINS How are membranes arranged? PHOSPHOLIPIDS make a BILAYER with POLAR HEADS FACING OUT and HYDROPHOBIC TAILS FACING IN Which molecule in cell membranes helps cells recognize “self”? ...
... What are cell membranes made of? PHOSPHOLIPIDS & PROTEINS How are membranes arranged? PHOSPHOLIPIDS make a BILAYER with POLAR HEADS FACING OUT and HYDROPHOBIC TAILS FACING IN Which molecule in cell membranes helps cells recognize “self”? ...
The eucaryotic cell
... Present-day living cells are classified as procaryotic (bacteria and their close relatives) or eucaryotic. Although they have a relatively simple structure, procaryotic cells are biochemically versatile and diverse - for example, all of the major metabolic pathways can be found in bacteria, includin ...
... Present-day living cells are classified as procaryotic (bacteria and their close relatives) or eucaryotic. Although they have a relatively simple structure, procaryotic cells are biochemically versatile and diverse - for example, all of the major metabolic pathways can be found in bacteria, includin ...