Cell Organelles
... • A cell is like a factory. It has many machines inside to make it work correctly. • The “machines” in a cell are called organelles ...
... • A cell is like a factory. It has many machines inside to make it work correctly. • The “machines” in a cell are called organelles ...
Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles
... Some organelles do jobs other than making proteins. Mitochondria Mitochondria are bean-shaped organelles that produce chemical energy that is usable by a cell. They have two membranes. The inner membrane has lots of folds that form compartments. Mitochondria also have their own ribosomes and DNA. At ...
... Some organelles do jobs other than making proteins. Mitochondria Mitochondria are bean-shaped organelles that produce chemical energy that is usable by a cell. They have two membranes. The inner membrane has lots of folds that form compartments. Mitochondria also have their own ribosomes and DNA. At ...
congratulations!!! you have found the vacuole!
... forms that are usable by the mitochondria during ATP synthesis. Vacuoles bring their stored material to any organelle inside the cell that needs it or to other cells if they need the stored material. Vacuoles in plant and animal cells are different in size and numbers but they ultimately have the sa ...
... forms that are usable by the mitochondria during ATP synthesis. Vacuoles bring their stored material to any organelle inside the cell that needs it or to other cells if they need the stored material. Vacuoles in plant and animal cells are different in size and numbers but they ultimately have the sa ...
The Cell Theory and Membrane Transport
... • [ ] of dissolved substances is lower outside cell than inside cell • HYPO means “below strength” • Water will move INTO cell causing it to SWELL • Cells could rupture if the cell takes in too much water • This increases pressure inside of cell (TURGOR ...
... • [ ] of dissolved substances is lower outside cell than inside cell • HYPO means “below strength” • Water will move INTO cell causing it to SWELL • Cells could rupture if the cell takes in too much water • This increases pressure inside of cell (TURGOR ...
ch1 Pro &Euo
... Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the three basic shapes of bacteria. Describe structure and function of the glycocalyx, flagella, axial filaments, fimbriae, and pili. Compare and contrast the cell walls of gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative b ...
... Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the three basic shapes of bacteria. Describe structure and function of the glycocalyx, flagella, axial filaments, fimbriae, and pili. Compare and contrast the cell walls of gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative b ...
Cell Structure and Genetic Control
... B. As each successive tRNA molecule bonds to its complementary codon, the amino acid it carries is added to the end of a growing polypeptide chain. III. Proteins destined for secretion are produced in ribosomes located on the rough endoplasmic reticulum and enter the cisternae of this organelle. IV. ...
... B. As each successive tRNA molecule bonds to its complementary codon, the amino acid it carries is added to the end of a growing polypeptide chain. III. Proteins destined for secretion are produced in ribosomes located on the rough endoplasmic reticulum and enter the cisternae of this organelle. IV. ...
Pollard: Cell Biology, 2nd Edition
... ANS: D Many of the signal transduction systems are very ancient, although some of them have arisen later in evolution. Their main role is to relay an extracellular signal to a specific effector molecule to allow the cell to adjust its behavior to environmental signal. 11. The nucleus a. contains her ...
... ANS: D Many of the signal transduction systems are very ancient, although some of them have arisen later in evolution. Their main role is to relay an extracellular signal to a specific effector molecule to allow the cell to adjust its behavior to environmental signal. 11. The nucleus a. contains her ...
chapter 7 – cell structure and function
... Which kind of transport do white blood cells use when they engulf and destroy bacteria? What kind of transport do Golgi bodies use to transport substances out of cells? Be able to explain what HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC, and ISOTONIC means? Be able to identify these 3 kinds of solutions using a diagram. ...
... Which kind of transport do white blood cells use when they engulf and destroy bacteria? What kind of transport do Golgi bodies use to transport substances out of cells? Be able to explain what HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC, and ISOTONIC means? Be able to identify these 3 kinds of solutions using a diagram. ...
Description
... Description: small and round Function: to break down food and destroy old cells “Clean-up Crew” – garbage disposal Found in animal cells and rare in plant cells ...
... Description: small and round Function: to break down food and destroy old cells “Clean-up Crew” – garbage disposal Found in animal cells and rare in plant cells ...
Cell Wall
... Stiff, rigid, protective barrier outside of the membrane. The cell wall is made of cellulose (sugars) and helps the cell keep its shape. ...
... Stiff, rigid, protective barrier outside of the membrane. The cell wall is made of cellulose (sugars) and helps the cell keep its shape. ...
Plant and Animal cells
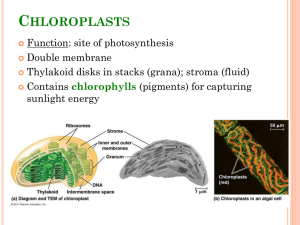
... make food (photosynthesis). The stroma is an area inside of the chloroplast where sugars are created. Chlorophyll uses radiant energy to create glucose. ...
... make food (photosynthesis). The stroma is an area inside of the chloroplast where sugars are created. Chlorophyll uses radiant energy to create glucose. ...
Cells PP - jl041.k12.sd.us
... D. Cytoplasm – Liquid between cell membrane and nucleus (if the cell were a water balloon, this would be the water). ...
... D. Cytoplasm – Liquid between cell membrane and nucleus (if the cell were a water balloon, this would be the water). ...
Class6 1-10 Win16 Transport and Organelles Notes
... Lysosomes are singlemembrane-bound centers for storage and/or waste processing. ...
... Lysosomes are singlemembrane-bound centers for storage and/or waste processing. ...
FREE Sample Here
... ANS: D Many of the signal transduction systems are very ancient, although some of them have arisen later in evolution. Their main role is to relay an extracellular signal to a specific effector molecule to allow the cell to adjust its behavior to environmental signal. 11. The nucleus a. contains her ...
... ANS: D Many of the signal transduction systems are very ancient, although some of them have arisen later in evolution. Their main role is to relay an extracellular signal to a specific effector molecule to allow the cell to adjust its behavior to environmental signal. 11. The nucleus a. contains her ...
Test Date:______ Essential Concepts and Skills READINGS 1
... mitochondria, ribosome, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, cell membrane, cell wall, nucleolus, cilia/flagella, vacuoles, microtubules, centrioles and nuclear membrane. a) Nucleus controls cell’s activities and contains DNA. Only found in eukaryotic cells. b) Nucleolus locate ...
... mitochondria, ribosome, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, cell membrane, cell wall, nucleolus, cilia/flagella, vacuoles, microtubules, centrioles and nuclear membrane. a) Nucleus controls cell’s activities and contains DNA. Only found in eukaryotic cells. b) Nucleolus locate ...
Study Guide for Science Test
... Cell respiration: Process of using oxygen to break down sugar molecules. Photosynthesis: Process by which light energy is used to make food. ...
... Cell respiration: Process of using oxygen to break down sugar molecules. Photosynthesis: Process by which light energy is used to make food. ...
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW
... • THE CELLS WOULD SWELL DUE TO THE HYPOTONIC SOLUTION SURROUNDING THEM- WATER WOULD MOVE INTO THE CELL. ...
... • THE CELLS WOULD SWELL DUE TO THE HYPOTONIC SOLUTION SURROUNDING THEM- WATER WOULD MOVE INTO THE CELL. ...
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
... 3. The cell membrane is made of a ___________________ ______________________. 4. The cell membrane is _________________permeable. This means that ____________ ______________________________________________________________________. 5. Diffusion always causes particles to move from a region of _______ ...
... 3. The cell membrane is made of a ___________________ ______________________. 4. The cell membrane is _________________permeable. This means that ____________ ______________________________________________________________________. 5. Diffusion always causes particles to move from a region of _______ ...
File
... ancestors of eukaryotic cells Evidence: Double-membrane structure Have own ribosomes & DNA Reproduce independently within cell ...
... ancestors of eukaryotic cells Evidence: Double-membrane structure Have own ribosomes & DNA Reproduce independently within cell ...