Chapter 5 Homeostasis and Cell Transport
... 1. The process by which water molecules diffuse across a membrane from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. 2. Hypotonic solution = when concentration of water is higher outside the cell = cell grows 3. Hypertonic solution = when concentration of water is lower than inside the cel ...
... 1. The process by which water molecules diffuse across a membrane from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. 2. Hypotonic solution = when concentration of water is higher outside the cell = cell grows 3. Hypertonic solution = when concentration of water is lower than inside the cel ...
Slide
... Electron micrographs of tangential sections through the cribriform TM region. (A) The cribriform cell (CR) was attached to BM-like material (BM) at places where the cribriform elastic fibers (EL) were connected to the cell by cross-banded connecting fibrils (CFs; arrows). The cell membrane was undul ...
... Electron micrographs of tangential sections through the cribriform TM region. (A) The cribriform cell (CR) was attached to BM-like material (BM) at places where the cribriform elastic fibers (EL) were connected to the cell by cross-banded connecting fibrils (CFs; arrows). The cell membrane was undul ...
File
... other side according to concentration this process is known as diffusion b- Carrier proteins: Carrier proteins change their shape to transport certain molecules from one side of the membrane to the other side against concentration this process is known as active transport. ...
... other side according to concentration this process is known as diffusion b- Carrier proteins: Carrier proteins change their shape to transport certain molecules from one side of the membrane to the other side against concentration this process is known as active transport. ...
Final Tech Project
... The nucleus controls the cell. its gives the orders -- kind of like a brain. And it's protected by a nuclear membrane. Around the cell, you'll find another "skin," The cellular membrane holds the whole cell in But its job isn't simple there's no doubt, It lets some particles go in and out. Now pleas ...
... The nucleus controls the cell. its gives the orders -- kind of like a brain. And it's protected by a nuclear membrane. Around the cell, you'll find another "skin," The cellular membrane holds the whole cell in But its job isn't simple there's no doubt, It lets some particles go in and out. Now pleas ...
CH 3 PPT
... It is believed that the motion of cilia may play a part in determining the placement of organs within the thoracic and abdominal cavities. In the absence of ciliary motion, organ placement becomes a random event, giving each affected embryo a 50/50 chance of having typical or atypical ...
... It is believed that the motion of cilia may play a part in determining the placement of organs within the thoracic and abdominal cavities. In the absence of ciliary motion, organ placement becomes a random event, giving each affected embryo a 50/50 chance of having typical or atypical ...
Your Pre AP biology final exam
... Give 3 examples of digestive enzymes and the reactions they catalyze: What’s an easy way to tell if a chemical named is an enzyme? Name 4 things that can affect an enzyme functioning Label the structure of ATP using the following terms: phosphate, bonds with high stored energy, sugar, and adenine ...
... Give 3 examples of digestive enzymes and the reactions they catalyze: What’s an easy way to tell if a chemical named is an enzyme? Name 4 things that can affect an enzyme functioning Label the structure of ATP using the following terms: phosphate, bonds with high stored energy, sugar, and adenine ...
Factors Affecting the Rate of Diffusion Across the Cell Membrane
... ◦ As cell size increases, the surface area-tovolume ratio becomes smaller and many parts of the cell are farther from the external environment making the rate of exchange between internal and external environments more difficult (diffusion rate is slower). ◦ As a cell increases in size its volume i ...
... ◦ As cell size increases, the surface area-tovolume ratio becomes smaller and many parts of the cell are farther from the external environment making the rate of exchange between internal and external environments more difficult (diffusion rate is slower). ◦ As a cell increases in size its volume i ...
Powerpoint notes
... ratio of a small object is larger than that of a large object of similar shape. This ratio limits how large cells can be. ...
... ratio of a small object is larger than that of a large object of similar shape. This ratio limits how large cells can be. ...
Cells Summary - Elgin Academy
... The energy released from the breakdown of glucose is used to generate ATP from ADP and phosphate. The chemical energy stored in ATP can be released by breaking it down to ADP and phosphate. This energy can be used for cellular activities including muscle cell contraction, cell division, protein synt ...
... The energy released from the breakdown of glucose is used to generate ATP from ADP and phosphate. The chemical energy stored in ATP can be released by breaking it down to ADP and phosphate. This energy can be used for cellular activities including muscle cell contraction, cell division, protein synt ...
CP Bio Study Guide
... Controls what goes in and out of the nucleus Stores water for the cell. Plant cells have one large central. Animal cells small and numerous. Transports membrane and secretory proteins inside of a cell from the nucleus to the Golgi Body via transport vesicles. Nucleolus 1. List the 4 structures that ...
... Controls what goes in and out of the nucleus Stores water for the cell. Plant cells have one large central. Animal cells small and numerous. Transports membrane and secretory proteins inside of a cell from the nucleus to the Golgi Body via transport vesicles. Nucleolus 1. List the 4 structures that ...
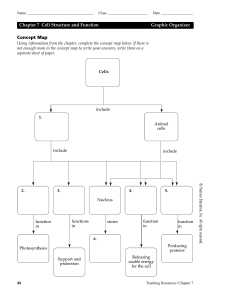
Concept Map Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Graphic
... Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the structures found in an animal cell that correspond with the numbers in the diagram. Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus ...
... Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the structures found in an animal cell that correspond with the numbers in the diagram. Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus ...
Biology Today is Monday Aug 31, 2015
... • There are 20 different types of amino acids • Change based on the “R” Group ...
... • There are 20 different types of amino acids • Change based on the “R” Group ...
Two Basic Cell Types: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... • carry out metabolism • provide energy • transport chemicals throughout the cell ...
... • carry out metabolism • provide energy • transport chemicals throughout the cell ...
Chitin is a component of ______ cell walls
... 2. Which of the following organisms do not have cell walls? a. plants b. fungi c. monerans d. animals. 3. Which of the following is NOT true of membranes? a. Folded membranes increase surface area for efficiency. b. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. c. Endoplasmic reticulum is m ...
... 2. Which of the following organisms do not have cell walls? a. plants b. fungi c. monerans d. animals. 3. Which of the following is NOT true of membranes? a. Folded membranes increase surface area for efficiency. b. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. c. Endoplasmic reticulum is m ...
ANIMAL CELL CULTURE
... Cell to cell interaction Forms adherens junctions for attachment Polypeptides that undergo many post-translational modifications to become the proteins which mediate cell-cell adhesion and recognition 720–750 amino acids long over 80 types of cadherins in humans have been identified and sequenced Be ...
... Cell to cell interaction Forms adherens junctions for attachment Polypeptides that undergo many post-translational modifications to become the proteins which mediate cell-cell adhesion and recognition 720–750 amino acids long over 80 types of cadherins in humans have been identified and sequenced Be ...
Organelles in a Eukaryotic cell
... Membranes throughout cytoplasm. Rough ER- ribosomes on surface. Smooth ER- no ribosomes Functions Transport material thru cytoplasm Rough ER- site of protein synthesis Smooth ER- site of lipid synthesis ...
... Membranes throughout cytoplasm. Rough ER- ribosomes on surface. Smooth ER- no ribosomes Functions Transport material thru cytoplasm Rough ER- site of protein synthesis Smooth ER- site of lipid synthesis ...
The Cell
... composed of tightly coiled strands of DNA C) Segments of DNA that are responsible for the production of a protein are called genes, which produce m-RNA D) While the cell is not dividing, loose strands of DNA appear grainy and are called chromatin E) Nucleolus- dark spherical structure in the nucleus ...
... composed of tightly coiled strands of DNA C) Segments of DNA that are responsible for the production of a protein are called genes, which produce m-RNA D) While the cell is not dividing, loose strands of DNA appear grainy and are called chromatin E) Nucleolus- dark spherical structure in the nucleus ...
Topic 1 Introduction to the Study of Life
... Most Bacteria cell walls contain peptidoglycan – a modified sugar polymer cross-linked by short polypeptides Archaea cell walls contain a variety of polysaccharides and proteins A technique called Gram stain is often used to classify Bacterial species on the basis of differences in cell wall composi ...
... Most Bacteria cell walls contain peptidoglycan – a modified sugar polymer cross-linked by short polypeptides Archaea cell walls contain a variety of polysaccharides and proteins A technique called Gram stain is often used to classify Bacterial species on the basis of differences in cell wall composi ...
Bio07_TR_U03_CH07.QXD
... c. digestive system 15. A group of similar cells that perform a particular function is called a(an) a. organ. b. organ system. c. tissue. ...
... c. digestive system 15. A group of similar cells that perform a particular function is called a(an) a. organ. b. organ system. c. tissue. ...
1
... reticulum or nuclear envelope. Free and bound ribosomes are structurally identical, and ribosomes can alternate between the two locations. Ribosomes are composed of a large and small subunit. Most of the proteins made on free ribosomes function within the cytoplasm. Bound ribosomes make proteins tha ...
... reticulum or nuclear envelope. Free and bound ribosomes are structurally identical, and ribosomes can alternate between the two locations. Ribosomes are composed of a large and small subunit. Most of the proteins made on free ribosomes function within the cytoplasm. Bound ribosomes make proteins tha ...
coloring packet cells and organelles
... their own food. Color and label the chloroplasts dark green. Cells also contain fluid-filled sacs called vacuoles. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. In plant cells, a large central vacuole takes up most of the space in the cell in a pla ...
... their own food. Color and label the chloroplasts dark green. Cells also contain fluid-filled sacs called vacuoles. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. In plant cells, a large central vacuole takes up most of the space in the cell in a pla ...