Cell Transport, Osmosis and Diffusion PowerPoint
... - Made of a lipid bi-layer: a double layered sheet of lipids (=fatty acids) ...
... - Made of a lipid bi-layer: a double layered sheet of lipids (=fatty acids) ...
Cells
... • Eukaryotic cells– cells with membrane – bound structures like protists, fungi, plant, and animal cells. ...
... • Eukaryotic cells– cells with membrane – bound structures like protists, fungi, plant, and animal cells. ...
Bacterial Structure and Function-1
... How phospholipids work Polar head groups associate with water but hydrophobic tails associate with each other to avoid water. When placed in water, phospholipids associate spontaneously side by side and tail to tail to form membranes. ...
... How phospholipids work Polar head groups associate with water but hydrophobic tails associate with each other to avoid water. When placed in water, phospholipids associate spontaneously side by side and tail to tail to form membranes. ...
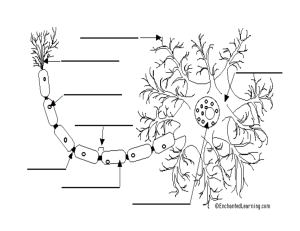
axon diagram
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
Media Release
... process are still a mystery, but in a study published August 22 in Developmental Cell, a research team reports one protein responsible for giving a cell's nucleus its durable, deformable nature. These results, the authors say, may explain the invasiveness of certain cancer cells. "The nucleus is the ...
... process are still a mystery, but in a study published August 22 in Developmental Cell, a research team reports one protein responsible for giving a cell's nucleus its durable, deformable nature. These results, the authors say, may explain the invasiveness of certain cancer cells. "The nucleus is the ...
Final Review
... 36. How much energy gets passed on in each level in an energy pyramid? 37. What happens to a food web if we remove the producers? 38. What happens to a food web if a toxin is introduced to an ecosystem? 39 – 42. Label the organisms below as producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, or decompos ...
... 36. How much energy gets passed on in each level in an energy pyramid? 37. What happens to a food web if we remove the producers? 38. What happens to a food web if a toxin is introduced to an ecosystem? 39 – 42. Label the organisms below as producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, or decompos ...
BIO 221
... It is about 1mm long (1000X longer than the cell) It’s localized in the nucleoid Plasmids – small circular pieces of nonchromosomal DNA Functions? Ribosomes (70S) – function? Protein synthesis ...
... It is about 1mm long (1000X longer than the cell) It’s localized in the nucleoid Plasmids – small circular pieces of nonchromosomal DNA Functions? Ribosomes (70S) – function? Protein synthesis ...
1900 Animal Cell Model GUD
... H. Mitochondria – The main energy source for a cell. The mitochondria converts oxygen and nutrients into energy for the cell to use. I. Vacuole – Helps with digestion by storing food and waste material. J. Lysosomes – Digestion is the main function of lysosomes. K. Ribosome – Some ribosomes are atta ...
... H. Mitochondria – The main energy source for a cell. The mitochondria converts oxygen and nutrients into energy for the cell to use. I. Vacuole – Helps with digestion by storing food and waste material. J. Lysosomes – Digestion is the main function of lysosomes. K. Ribosome – Some ribosomes are atta ...
Unit 2: THE CELL - science-b
... -Because of the lipid bilayer, water needs a way in…so Aquporins are specific protein channels to allow for H2O to pass quickly through the cell membrane. In the presence of a hypertonic (++) and hypotonic(--) solution, equilibrium is needed= a isotonic solution Hypertonic: “above strength” ...
... -Because of the lipid bilayer, water needs a way in…so Aquporins are specific protein channels to allow for H2O to pass quickly through the cell membrane. In the presence of a hypertonic (++) and hypotonic(--) solution, equilibrium is needed= a isotonic solution Hypertonic: “above strength” ...
Cell_analogies_collageAC 09
... "It takes 3 million cells to cover the head of a pin, but only one cell collage to cover a large part of your Science grade!" Name ______________________________ Date Due: Monday, Dec. 7, 2009 (AC) Objective: To make functional analogies between cell organelles and everyday objects. Definition: Anal ...
... "It takes 3 million cells to cover the head of a pin, but only one cell collage to cover a large part of your Science grade!" Name ______________________________ Date Due: Monday, Dec. 7, 2009 (AC) Objective: To make functional analogies between cell organelles and everyday objects. Definition: Anal ...
Review Sheet Answers
... Nervous tissue – carries messages back and forth between your brain and other parts of your body. Epithelial tissue – covers the surfaces of your body ...
... Nervous tissue – carries messages back and forth between your brain and other parts of your body. Epithelial tissue – covers the surfaces of your body ...
Cell Project - WordPress.com
... Surrounding the nucleus are two membranes that form a structure called the nuclear envelope. A ribosome is not surrounded by a membrane. Ribosomes are in a cells cytoplasm. The ER spreads from the nucleus throughout most of the cytoplasm’s. Most eukaryotic cells contain hundreds of organelles called ...
... Surrounding the nucleus are two membranes that form a structure called the nuclear envelope. A ribosome is not surrounded by a membrane. Ribosomes are in a cells cytoplasm. The ER spreads from the nucleus throughout most of the cytoplasm’s. Most eukaryotic cells contain hundreds of organelles called ...
Organelles of cells
... • Storage : in striated muscle cells, there are a highly specialized sER called sarcoplasmic reticulum which stores calcium ions and is involved in the muscle contraction • Detoxification : in the liver cells both rough and smooth ER are involved in detoxification of various drugs 3. Golgi apparatus ...
... • Storage : in striated muscle cells, there are a highly specialized sER called sarcoplasmic reticulum which stores calcium ions and is involved in the muscle contraction • Detoxification : in the liver cells both rough and smooth ER are involved in detoxification of various drugs 3. Golgi apparatus ...
Cell Structure Questions
... 10. State two ways in which red blood cells differ from typical body cells e.g. from the cheek lining. 11. Name two features of a plant cell which are not normally associated with an animal cell. 12. The liquid in which chemical reactions take place in the cell is … 13. True or false. Plant cells ha ...
... 10. State two ways in which red blood cells differ from typical body cells e.g. from the cheek lining. 11. Name two features of a plant cell which are not normally associated with an animal cell. 12. The liquid in which chemical reactions take place in the cell is … 13. True or false. Plant cells ha ...
Cell – a basic unit of structure and function in all organisms
... Cell theory – states that: all organisms are made up of one or more cells the cell is the basic unit of life all cells come from other cells Eukaryote – an organism whose cells have a nucleus and organelles Multicellular – composed of more than one cell Organelle – structure in the cytoplasm o ...
... Cell theory – states that: all organisms are made up of one or more cells the cell is the basic unit of life all cells come from other cells Eukaryote – an organism whose cells have a nucleus and organelles Multicellular – composed of more than one cell Organelle – structure in the cytoplasm o ...
Cell City - CAC
... F. Construction Company – builds structures for the city G. Delivery Van – delivers products made at the construction company to other locations in the city H. Food Processing Plant – processes large quantities of food entering the city into smaller packages that can be used more easily I. Warehouse ...
... F. Construction Company – builds structures for the city G. Delivery Van – delivers products made at the construction company to other locations in the city H. Food Processing Plant – processes large quantities of food entering the city into smaller packages that can be used more easily I. Warehouse ...
Gram positive cell wall
... The peptidoglycan layer is substantially thicker in Grampositive bacteria (20 to 80 nanometers) than in Gramnegative bacteria (7 to 8 nanometers), Peptidoglycan forms around 90% of the dry weight of Gram-positive bacteria but only 10% of Gram-negative strains. Thus, presence of high levels of pepti ...
... The peptidoglycan layer is substantially thicker in Grampositive bacteria (20 to 80 nanometers) than in Gramnegative bacteria (7 to 8 nanometers), Peptidoglycan forms around 90% of the dry weight of Gram-positive bacteria but only 10% of Gram-negative strains. Thus, presence of high levels of pepti ...
Modification of Cell Surface/ Cell Communication
... • Second messengers, such as cyclic GMP, cyclic AMP calcium ions (Ca2+), and inositol triphosphate (IP3) 3. Many signal transduction pathways include: i. Protein modifications (an illustrative example could be how methylation changes the signaling process) ii. Phosphorylation cascades in which a ser ...
... • Second messengers, such as cyclic GMP, cyclic AMP calcium ions (Ca2+), and inositol triphosphate (IP3) 3. Many signal transduction pathways include: i. Protein modifications (an illustrative example could be how methylation changes the signaling process) ii. Phosphorylation cascades in which a ser ...
Viruses and Bacteria worksheet
... d. a tiny, nonliving particle that enters and then reproduces inside a living cell ...
... d. a tiny, nonliving particle that enters and then reproduces inside a living cell ...
Eukaryotic cells
... dissolved nutrients like amino acids and sugars. The water allows for reactions to occur within the cell ...
... dissolved nutrients like amino acids and sugars. The water allows for reactions to occur within the cell ...
Cell Structure and Function Notes
... uses food to make high energy compounds for the cell (power plant) only found in plant cells; supports and protects the cell; made of cellulose (non-living) only found in plant cells; uses energy from sunlight to make food molecules through photosynthesis ...
... uses food to make high energy compounds for the cell (power plant) only found in plant cells; supports and protects the cell; made of cellulose (non-living) only found in plant cells; uses energy from sunlight to make food molecules through photosynthesis ...
Cell Theory
... multiple, linear chromosomes -surrounded by a nuclear envelope composed of 2 phospholipid bilayers -in chromosomes – DNA is organized with proteins to form chromatin ...
... multiple, linear chromosomes -surrounded by a nuclear envelope composed of 2 phospholipid bilayers -in chromosomes – DNA is organized with proteins to form chromatin ...