asdfs
... Kind of endocytosis used to take in large particles or whole cells. phagocytosis Putting a plant cell in a HYPOTONIC solution will cause an ____________ increase increase ...
... Kind of endocytosis used to take in large particles or whole cells. phagocytosis Putting a plant cell in a HYPOTONIC solution will cause an ____________ increase increase ...
Welcome to Anatomy and Physiology Honors
... The process by which specific kinds of particles are moved through the cell membrane even when a substance is present only in very small concentrations is called _____________ ___________ _____________. ...
... The process by which specific kinds of particles are moved through the cell membrane even when a substance is present only in very small concentrations is called _____________ ___________ _____________. ...
DNA: So, Just What Is This Stuff?
... Cell nucleus: a spherical body within the cell that contains many organelles and contains DNA (in chromosomes). Nuclear membrane: the membrane that surrounds the nucleus Cell membrane: the thin layer that surrounds the cell and is inside of the cell wall. It is made up of lipids (fats) and proteins ...
... Cell nucleus: a spherical body within the cell that contains many organelles and contains DNA (in chromosomes). Nuclear membrane: the membrane that surrounds the nucleus Cell membrane: the thin layer that surrounds the cell and is inside of the cell wall. It is made up of lipids (fats) and proteins ...
introduction to the cell
... 4.12 Vacuoles function in the general maintenance of the cell Vacuoles are membranous sacs that are found in a variety of cells and possess an assortment of functions – Examples are the central vacuole in plants with hydrolytic functions, pigment vacuoles in plants to provide color to flowers, an ...
... 4.12 Vacuoles function in the general maintenance of the cell Vacuoles are membranous sacs that are found in a variety of cells and possess an assortment of functions – Examples are the central vacuole in plants with hydrolytic functions, pigment vacuoles in plants to provide color to flowers, an ...
lysosomes - cfonjungosite.com
... lysosomes are cellular organelles. organelles are a cell that have a specific function. They are usually in a lipid bilayer and a lipid bilayer is fat that has two layers. ...
... lysosomes are cellular organelles. organelles are a cell that have a specific function. They are usually in a lipid bilayer and a lipid bilayer is fat that has two layers. ...
Name - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... opposite side, draw the solution across the slide. 6. Observe on low-power, medium-power and then high-power. c. Complete a scientific drawing of a few onion cells at high-power. Identify any organelles that are visible (cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, Golgi apparatus, etc.). For organelles that can ...
... opposite side, draw the solution across the slide. 6. Observe on low-power, medium-power and then high-power. c. Complete a scientific drawing of a few onion cells at high-power. Identify any organelles that are visible (cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, Golgi apparatus, etc.). For organelles that can ...
Cell Wall
... altered or is partly missing, resulting in a spherical shape. – L forms are wall-less cells that swell into irregular shapes. – Protoplasts and spheroplasts are susceptible to osmotic lysis. • Penicillin (beta-lactam antibiotics) inhibits peptide bridges in ...
... altered or is partly missing, resulting in a spherical shape. – L forms are wall-less cells that swell into irregular shapes. – Protoplasts and spheroplasts are susceptible to osmotic lysis. • Penicillin (beta-lactam antibiotics) inhibits peptide bridges in ...
Chapter 5 - ltcconline.net
... – Serves as selectively permeable barrier in transport – Eukaryotic cells also contain membrane-bound organelles that account for 60-80% of their volume ...
... – Serves as selectively permeable barrier in transport – Eukaryotic cells also contain membrane-bound organelles that account for 60-80% of their volume ...
Lecture four
... • also known as the intracellular fluid or ICF • made up of multiple levels of organization: – concentration gradients of ions and small molecules – larger complexes of enzymes for metabolic pathways – large complexes of proteins • e.g. proteasomes in eukaryotes – protein degradation • e.g. carboxys ...
... • also known as the intracellular fluid or ICF • made up of multiple levels of organization: – concentration gradients of ions and small molecules – larger complexes of enzymes for metabolic pathways – large complexes of proteins • e.g. proteasomes in eukaryotes – protein degradation • e.g. carboxys ...
Cell Membrane
... – The Cytoskeleton is made of 3 types of fibers: • Actin Fibers- long slender strands of protein • Microtubules- hollow tubes made of tubulin, that transmit information from the nucleus to different parts of the cell • Intermediate Filaments- thick ropes of protein that provide structural support in ...
... – The Cytoskeleton is made of 3 types of fibers: • Actin Fibers- long slender strands of protein • Microtubules- hollow tubes made of tubulin, that transmit information from the nucleus to different parts of the cell • Intermediate Filaments- thick ropes of protein that provide structural support in ...
Document
... • also known as the intracellular fluid or ICF • made up of multiple levels of organization: – concentration gradients of ions and small molecules – larger complexes of enzymes for metabolic pathways – large complexes of proteins • e.g. proteasomes in eukaryotes – protein degradation • e.g. carboxys ...
... • also known as the intracellular fluid or ICF • made up of multiple levels of organization: – concentration gradients of ions and small molecules – larger complexes of enzymes for metabolic pathways – large complexes of proteins • e.g. proteasomes in eukaryotes – protein degradation • e.g. carboxys ...
Cell structure and functions - formatted
... The structurally simple prokaryote cells are found among unicellular organisms particularly bacteria. All multicellular organisms consist of structurally complex eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are classified into plant and animal cells as these two differ slightly in their structure. ...
... The structurally simple prokaryote cells are found among unicellular organisms particularly bacteria. All multicellular organisms consist of structurally complex eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are classified into plant and animal cells as these two differ slightly in their structure. ...
Bacterial Morphology
... • fimbriae and Pili: many bacteria cells have numerous hairlike structure (fimbriae) that are shorted than flagella. • Fimbriae help the cell to adhere to surfaces such as mucous membranes. • They are often a factor in pathogenicity. • Pili: are les in number than fimbriae (one or two) and called se ...
... • fimbriae and Pili: many bacteria cells have numerous hairlike structure (fimbriae) that are shorted than flagella. • Fimbriae help the cell to adhere to surfaces such as mucous membranes. • They are often a factor in pathogenicity. • Pili: are les in number than fimbriae (one or two) and called se ...
Cells have - Staff UNY
... • The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells • The ER membrane is continuous with the nuclear envelope • There are two distinct regions of ER: – Smooth ER, which lacks ribosomes – Rough ER, with ribosomes studding its surface ...
... • The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells • The ER membrane is continuous with the nuclear envelope • There are two distinct regions of ER: – Smooth ER, which lacks ribosomes – Rough ER, with ribosomes studding its surface ...
Cells - American Academy
... 1.Draw and color a picture of one cell type from the list, fill up the bottom half of this page, focus on the structure. (use the search in DE Techbook) 2 Describe the function. (complete sentences) 3.How does the unique structure help with its function (cell specialization)? (complete sentences) ...
... 1.Draw and color a picture of one cell type from the list, fill up the bottom half of this page, focus on the structure. (use the search in DE Techbook) 2 Describe the function. (complete sentences) 3.How does the unique structure help with its function (cell specialization)? (complete sentences) ...
THE CELL model: Activity 4.1 – Science / Biology Objective: On a
... Enzymes assisting synthesis of some lipids and final processing of proteins found here. Similar to smooth ER, but with ribosomes embedded in membrane. Proteins to be exported from cell produced here. Stacks of saucer shaped membranes where export proteins are modified and stored prior to entering ve ...
... Enzymes assisting synthesis of some lipids and final processing of proteins found here. Similar to smooth ER, but with ribosomes embedded in membrane. Proteins to be exported from cell produced here. Stacks of saucer shaped membranes where export proteins are modified and stored prior to entering ve ...
Transport in Bacterial Cells
... • Facilitated diffusion is a type of diffusion which uses a transport molecule . • Permease are proteins which are embedded in the cell membrane • They assist in the movement of other molecules across the membrane • This is a speedier process than regular diffusion, but again is highly specific • No ...
... • Facilitated diffusion is a type of diffusion which uses a transport molecule . • Permease are proteins which are embedded in the cell membrane • They assist in the movement of other molecules across the membrane • This is a speedier process than regular diffusion, but again is highly specific • No ...
Name___________________ Date Section 1 2 3 4 (circle one
... Follow my lead and copy the picture of a typical eukaryotic cell that I am going to draw on the white board. The labels will match the terms on the vocabulary list for “Looking Inside Cells” on page 5 of this packet. ...
... Follow my lead and copy the picture of a typical eukaryotic cell that I am going to draw on the white board. The labels will match the terms on the vocabulary list for “Looking Inside Cells” on page 5 of this packet. ...
Chemistry for Biotech
... • Chemicallly very different from carbohydrates • Hydrophobic • 3 groups: – Triglycerides—animal fats & plant oils • Energy storage ...
... • Chemicallly very different from carbohydrates • Hydrophobic • 3 groups: – Triglycerides—animal fats & plant oils • Energy storage ...
cellcookie
... with the cookies and the organelles with the candy. With each depiction they must make note of which candy represents the organelle and why on their Organelle Checklist. Explore – Time Estimate __20____ Create a model of a cell using supplies provided at the table (Cookie, candy, frosting). As stude ...
... with the cookies and the organelles with the candy. With each depiction they must make note of which candy represents the organelle and why on their Organelle Checklist. Explore – Time Estimate __20____ Create a model of a cell using supplies provided at the table (Cookie, candy, frosting). As stude ...
Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation • Cells need to control
... • Secondary messenger attached to phospholipid of the cell membrane • Sent to Ca channels on the ER • Allows a flood of Ca2+ into the cytoplasm from the ER, activating a cell response ...
... • Secondary messenger attached to phospholipid of the cell membrane • Sent to Ca channels on the ER • Allows a flood of Ca2+ into the cytoplasm from the ER, activating a cell response ...
Bacterial Structure and Function-1
... How phospholipids work Polar head groups associate with water but hydrophobic tails associate with each other to avoid water. When placed in water, phospholipids associate spontaneously side by side and tail to tail to form membranes. ...
... How phospholipids work Polar head groups associate with water but hydrophobic tails associate with each other to avoid water. When placed in water, phospholipids associate spontaneously side by side and tail to tail to form membranes. ...
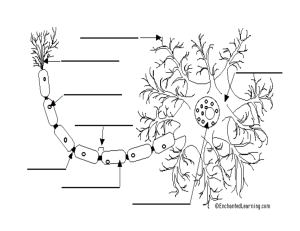
axon diagram
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...