FISH BODY SYSTEMS
... PYLORIC CAECA (pouches where stomach joins DUODENUM)- help with digestion & absorption of nutrients INTESTINE-completes digestion; absorbs nutrients; collect digestive waste; 1st part called DUODENUM VILLI (fingerlike extensions inside intestine) increase surface area to absorb more nutrients ANUS- ...
... PYLORIC CAECA (pouches where stomach joins DUODENUM)- help with digestion & absorption of nutrients INTESTINE-completes digestion; absorbs nutrients; collect digestive waste; 1st part called DUODENUM VILLI (fingerlike extensions inside intestine) increase surface area to absorb more nutrients ANUS- ...
A. Interphase B. Prophase C. Metaphase D
... B. The sun heats the Earth’s atmosphere D. Either photosynthetic organisms or organisms that have eaten them provide energy for all other organisms on Earth _____6. The process of cellular respiration A. Is performed only by organisms that are incapable of photosynthesis B. Occurs only in animals C. ...
... B. The sun heats the Earth’s atmosphere D. Either photosynthetic organisms or organisms that have eaten them provide energy for all other organisms on Earth _____6. The process of cellular respiration A. Is performed only by organisms that are incapable of photosynthesis B. Occurs only in animals C. ...
Bacterial Growth and Laboratory Cultivation
... agar is chemical from seaweed that melts at 100C and freezes at 45C ...
... agar is chemical from seaweed that melts at 100C and freezes at 45C ...
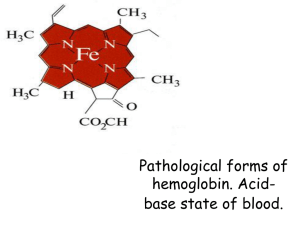
Pathological forms of hemoglobin. Acid
... above reaction to the right such that less hydrogen ions are free; thus the pH will rise back to normal. For alkalemia, the opposite occurs. The kidneys are slower to compensate, but renal physiology has several powerful mechanisms to control pH by the excretion of excess acid or base. In responses ...
... above reaction to the right such that less hydrogen ions are free; thus the pH will rise back to normal. For alkalemia, the opposite occurs. The kidneys are slower to compensate, but renal physiology has several powerful mechanisms to control pH by the excretion of excess acid or base. In responses ...
The Big Picture: A Review of Biology
... Liver secretes bile (emulsify fats) into the small intestine (duodenum). Pancreas secretes pancreatic juices (lots of enzymes) into the duodenum. Reabsorption of water happens in the large intestine. Feces are expelled through the rectum out the anus. ...
... Liver secretes bile (emulsify fats) into the small intestine (duodenum). Pancreas secretes pancreatic juices (lots of enzymes) into the duodenum. Reabsorption of water happens in the large intestine. Feces are expelled through the rectum out the anus. ...
Teacher Guide - Cleveland Museum of Natural History
... some images of its internal anatomy. Ask them to prepare a report on what organs are similar or different in location or function compared to mammals. Check out images of bird air sacs (we have attached one image to this guide ) and be ready to discuss why these organs are important to a bird’s ...
... some images of its internal anatomy. Ask them to prepare a report on what organs are similar or different in location or function compared to mammals. Check out images of bird air sacs (we have attached one image to this guide ) and be ready to discuss why these organs are important to a bird’s ...
A change in ocean current causes the climate on an island to
... such as Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, and Nitrogen. In nature, the materials needed by all organisms in an ecosystem are re-used or recycled. Nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon move through ecosystems in a predictable pattern or cycle. These nutrient cycles in nature are called BIOCHEMICAL CYCLES. ...
... such as Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, and Nitrogen. In nature, the materials needed by all organisms in an ecosystem are re-used or recycled. Nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon move through ecosystems in a predictable pattern or cycle. These nutrient cycles in nature are called BIOCHEMICAL CYCLES. ...
Characteristics of normal cell division Primary culture of normal cells
... Primary culture of transformed cells • Cancer cells exhibit neither density-dependent inhibition nor anchorage dependence • And have only limited dependence on growth factors Cancer cells usually continue to divide well beyond a single layer, forming a clump of overlapping cells. Many transformed ...
... Primary culture of transformed cells • Cancer cells exhibit neither density-dependent inhibition nor anchorage dependence • And have only limited dependence on growth factors Cancer cells usually continue to divide well beyond a single layer, forming a clump of overlapping cells. Many transformed ...
Body Systems - Lauer Science
... from the roots to all the cells in the rest of the plant. Phloem carries sugar (sap) from the leaves to the roots in the summer and from the roots to the stem, branches and leaves in the spring. In animals, especially vertebrates, special vessels carry water, nutrients and oxygen to the cells. These ...
... from the roots to all the cells in the rest of the plant. Phloem carries sugar (sap) from the leaves to the roots in the summer and from the roots to the stem, branches and leaves in the spring. In animals, especially vertebrates, special vessels carry water, nutrients and oxygen to the cells. These ...
public exam_movement of substances across cell membrane
... 2. A student carried out a study on the effect of two different sodium chloride solutions on red blood cells. He added a drop of citrated mammalian blood to 2 cm3 of each solution in separate test tubes, A and B. After five minutes, the mixtures in both tubes appeared light red in colour. He then ex ...
... 2. A student carried out a study on the effect of two different sodium chloride solutions on red blood cells. He added a drop of citrated mammalian blood to 2 cm3 of each solution in separate test tubes, A and B. After five minutes, the mixtures in both tubes appeared light red in colour. He then ex ...
Anatomy and Physiology Part 1-Midterm-12-2011
... c. blood vessels b. melanocytes d. lymphatic vessels The epidermis and dermis are normally firmly connected together. However a burn or friction may cause these layers to separate which results in a: a. abscess c. sty b. pimple d. blister There are two types of sweat glands (also called sudoriferous ...
... c. blood vessels b. melanocytes d. lymphatic vessels The epidermis and dermis are normally firmly connected together. However a burn or friction may cause these layers to separate which results in a: a. abscess c. sty b. pimple d. blister There are two types of sweat glands (also called sudoriferous ...
Respiratory System As you learned, the circulatory system was
... sweat, your skin excretes excess water, salts, and some nitrogen wastes. CO2 and water are excreted as you exhale. The liver is responsible for filtering toxins and dead red blood cells from the blood. The blood also carries other cellular wastes to the kidneys, the primary organs of excretion. Your ...
... sweat, your skin excretes excess water, salts, and some nitrogen wastes. CO2 and water are excreted as you exhale. The liver is responsible for filtering toxins and dead red blood cells from the blood. The blood also carries other cellular wastes to the kidneys, the primary organs of excretion. Your ...
Plant Tissues and Growth
... _____ 8. Plant cells walls can contain both cellulose and lignin. _____ 9. Some types of parenchymal cells are photosynthetic cells. _____ 10. Cell walls of sclerenchyma are very thick. _____ 11. Xylem and phloem are types of dermal tissue. _____ 12. The plant cuticle protects and waterproofs the ab ...
... _____ 8. Plant cells walls can contain both cellulose and lignin. _____ 9. Some types of parenchymal cells are photosynthetic cells. _____ 10. Cell walls of sclerenchyma are very thick. _____ 11. Xylem and phloem are types of dermal tissue. _____ 12. The plant cuticle protects and waterproofs the ab ...
File - Anatomy & Physiology
... Called involuntary muscle because it is not under direct conscious control…slow and sustained contractions ...
... Called involuntary muscle because it is not under direct conscious control…slow and sustained contractions ...
Ppt
... the cell and Na+ not able to enter the cell. Increase in negative charge since + ions are leaving axon with no + ions being able to enter the neuron. ...
... the cell and Na+ not able to enter the cell. Increase in negative charge since + ions are leaving axon with no + ions being able to enter the neuron. ...
Chapter 9 PowerPoint
... Lymph node: an organ that filters lymph and that is found along the lymphatic vessels. Small and bean shaped. Contain lymphocytes (also called killer t cells) surround and destroy pathogens. Other lymphocytes are called B cells (produce antibodies that attaches to pathogens—serve as markers. Swollen ...
... Lymph node: an organ that filters lymph and that is found along the lymphatic vessels. Small and bean shaped. Contain lymphocytes (also called killer t cells) surround and destroy pathogens. Other lymphocytes are called B cells (produce antibodies that attaches to pathogens—serve as markers. Swollen ...
File
... 1. Heart - The muscle that pumps blood to and from cells. 2. Blood Vessels: The tubes that transport blood from the heart throughout the body and back again. a) Arteries - Carry oxygen-rich blood cells from the heart throughout the body. ...
... 1. Heart - The muscle that pumps blood to and from cells. 2. Blood Vessels: The tubes that transport blood from the heart throughout the body and back again. a) Arteries - Carry oxygen-rich blood cells from the heart throughout the body. ...
Phytoplankton Cell Model Building: Expanded Teaching Notes The
... The day before this activity, build a cell model of a cyanobacterium (see the How to Build a Cyanobacterium Cell Model worksheet) On the day of the activity, begin with a brief lecture (see Phytoplankton Cell Model Building Powerpoint) about the distinct types of phytoplankton in the ocean o Emphasi ...
... The day before this activity, build a cell model of a cyanobacterium (see the How to Build a Cyanobacterium Cell Model worksheet) On the day of the activity, begin with a brief lecture (see Phytoplankton Cell Model Building Powerpoint) about the distinct types of phytoplankton in the ocean o Emphasi ...
Name: Date: Period:______ Sheppard Software Cell Games: Plant
... -Which one of the organelles above gives the plant its rectangular shape? Cell wall - Which one of the organelles do you think gives the plant cell its green color? Chloroplast 2. Click on the word “cell wall.” -What does the website compare the cell wall to? Security guard -How does the cell wall m ...
... -Which one of the organelles above gives the plant its rectangular shape? Cell wall - Which one of the organelles do you think gives the plant cell its green color? Chloroplast 2. Click on the word “cell wall.” -What does the website compare the cell wall to? Security guard -How does the cell wall m ...
1 mark
... Any 2 of: Same number of plants in each group, same species of plant in each group, same amount of sunlight, same volume of water, same watering regime 1 mark each I have given ½ mark for each point if they haven’t clearly indicated the idea of these2variables marks being the SAME (is this OK with y ...
... Any 2 of: Same number of plants in each group, same species of plant in each group, same amount of sunlight, same volume of water, same watering regime 1 mark each I have given ½ mark for each point if they haven’t clearly indicated the idea of these2variables marks being the SAME (is this OK with y ...
Glial Cells
... Glial Cells Most neurons are surrounded by glial cells (neuroglia), the other cell type found in the nervous tissue. Glial cells are the supportive cells of the nervous system and are 10 times more numerous than neurons. The most well defined role for neuroglia is to provide structure to the delicat ...
... Glial Cells Most neurons are surrounded by glial cells (neuroglia), the other cell type found in the nervous tissue. Glial cells are the supportive cells of the nervous system and are 10 times more numerous than neurons. The most well defined role for neuroglia is to provide structure to the delicat ...
... (c) smooth muscle and cardiac muscle are two involuntary muscles Q.3. How is striated squamous epithelial tissue different from squamous epithelial tissue ? Ans: A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one laye ...
10A Interactions in Animals
... mobility. No single life process can be achieved without the integration of multiple body systems. 2. The digestive system converts food into simpler substances for the body to absorb as nutrients. Nutrient absorption is possible through ingestion and digestion in organisms. Digestion breaks down bo ...
... mobility. No single life process can be achieved without the integration of multiple body systems. 2. The digestive system converts food into simpler substances for the body to absorb as nutrients. Nutrient absorption is possible through ingestion and digestion in organisms. Digestion breaks down bo ...
Role of intestinal permeability and endotoxemia in alcoholic
... • AMPK : same effect as PPARα and inhibits SREBP1 • Ethanol reduces AMPK activity ...
... • AMPK : same effect as PPARα and inhibits SREBP1 • Ethanol reduces AMPK activity ...
Connective Tissue
... 1. Macrophages: in blood & fibrous mesh of tissues a) Engulfs cellular debris & bacteria (foreign ...
... 1. Macrophages: in blood & fibrous mesh of tissues a) Engulfs cellular debris & bacteria (foreign ...