Practice!
... position of one body part relative to another, usually along one of the three major body ...
... position of one body part relative to another, usually along one of the three major body ...
You Can`t Sneeze On This Tissue
... in the New Learning Standards to call attention to the depth of knowledge required to build to one of biology’s important foundational theories: Modern Cell Theory. It is recommended that the content statements be combined and taught as a whole. As a result, the sixth-grade life science New Learning ...
... in the New Learning Standards to call attention to the depth of knowledge required to build to one of biology’s important foundational theories: Modern Cell Theory. It is recommended that the content statements be combined and taught as a whole. As a result, the sixth-grade life science New Learning ...
The Cell - liflhsLivingEnv
... produced by the rough E.R. they pass into the sacklike cisternae囊泡 that are the main part of the golgi ...
... produced by the rough E.R. they pass into the sacklike cisternae囊泡 that are the main part of the golgi ...
Lesson Plan - Colorado FFA
... Show Slide #14 – Where do we find ribosomes? Let’s review where we would find ribosomes in the cells! Who can tell me? Show Slide #15 - Functions of the Nucleus The nucleus of the cell performs three important functions. The nucleus contains and processes genetic information (located in the DNA), co ...
... Show Slide #14 – Where do we find ribosomes? Let’s review where we would find ribosomes in the cells! Who can tell me? Show Slide #15 - Functions of the Nucleus The nucleus of the cell performs three important functions. The nucleus contains and processes genetic information (located in the DNA), co ...
Journal Club Pack
... therapeutic potential in a mouse model of acute myocardial infarction. Not only is the inherent paracrine activity greater as evidenced by improved capillary density, cell survival, and proliferation within the border zone of the infarct but also the modified cells acquire cardiomyogenic potential. ...
... therapeutic potential in a mouse model of acute myocardial infarction. Not only is the inherent paracrine activity greater as evidenced by improved capillary density, cell survival, and proliferation within the border zone of the infarct but also the modified cells acquire cardiomyogenic potential. ...
Nervous Tissue 113
... The units of nervous tissue. They receive and transmit nerve impulses to & from the CNS. A neuron = nerve cell body + all its processes: ...
... The units of nervous tissue. They receive and transmit nerve impulses to & from the CNS. A neuron = nerve cell body + all its processes: ...
Immune system dysregulation in chronic lung disease EDITORIAL B.J. Marsland* , M. Ko
... damaging the lung tissue, and more related to the need for NE for neutrophil migration into tissues and recruitment of alternate cell types, such as monocytes. The balance between neutrophil and macrophage recruitment, clearance and effector function, remains at the core of COPD pathogenesis. Lung f ...
... damaging the lung tissue, and more related to the need for NE for neutrophil migration into tissues and recruitment of alternate cell types, such as monocytes. The balance between neutrophil and macrophage recruitment, clearance and effector function, remains at the core of COPD pathogenesis. Lung f ...
AUS Biological Sciences 8: Science Unde
... Students know that cells are the tiny living units that make up an organism. Students compare and contrast the structure of a typical animal cell with the structure of a typical plant cell. x Students are aware that cells contain a cell nucleus (except red blood cells) and structures called organell ...
... Students know that cells are the tiny living units that make up an organism. Students compare and contrast the structure of a typical animal cell with the structure of a typical plant cell. x Students are aware that cells contain a cell nucleus (except red blood cells) and structures called organell ...
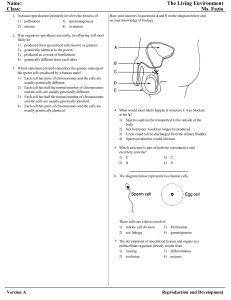
Reproduction and Development
... • both produce new organisms • both transfer genetic material Differences between asexual and sexual reproduction: • no fusion of nuclei in asexual reproduction; fusion of gamete nuclei in sexual reproduction • asexual reproduction involves no sex cells; sexual reproduction involves sex cells, the s ...
... • both produce new organisms • both transfer genetic material Differences between asexual and sexual reproduction: • no fusion of nuclei in asexual reproduction; fusion of gamete nuclei in sexual reproduction • asexual reproduction involves no sex cells; sexual reproduction involves sex cells, the s ...
Name - Southington Public Schools
... Iodine stain (use only in designated area) Methylene blue stain (use only in designated area) Procedure *NOTE: The two specimens may be observed in any order, so if there is no onion available, do the cheek cell (Step 6) first. Trade your onion slide with a cheek slide to save time. 1. Crack you ...
... Iodine stain (use only in designated area) Methylene blue stain (use only in designated area) Procedure *NOTE: The two specimens may be observed in any order, so if there is no onion available, do the cheek cell (Step 6) first. Trade your onion slide with a cheek slide to save time. 1. Crack you ...
Back to the question I
... A vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane protein ...
... A vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane protein ...
Cell Transport Notes
... Osmosis and Diffusion Passive transport does not require energy input from cell. Molecules can move across cell membrane through passive transport. There are two types of passive transport: ...
... Osmosis and Diffusion Passive transport does not require energy input from cell. Molecules can move across cell membrane through passive transport. There are two types of passive transport: ...
scientific method
... ______ uses a carrier protein to move particles from low to high concentration ______ uses a carrier protein to move particles from high to low concentration ______ moves small particles across a membrane ______ examples are endocytosis and exocytosis PHOTOSYNTHESIS and CELL RESPIRATION 38. Where do ...
... ______ uses a carrier protein to move particles from low to high concentration ______ uses a carrier protein to move particles from high to low concentration ______ moves small particles across a membrane ______ examples are endocytosis and exocytosis PHOTOSYNTHESIS and CELL RESPIRATION 38. Where do ...
breakdown of living things
... jobs (there are more) Make up structure of cells (our bodies) Enzymes control the chemical reactions in our bodies ...
... jobs (there are more) Make up structure of cells (our bodies) Enzymes control the chemical reactions in our bodies ...
Your Heart…
... • The heart is the most vital organ in the circulatory system. • About the size of your fist. • It is made up of four main parts called chambers. • Left and right ventricle • Left and right atrium ...
... • The heart is the most vital organ in the circulatory system. • About the size of your fist. • It is made up of four main parts called chambers. • Left and right ventricle • Left and right atrium ...
Slide ()
... PTH effects on bone. PTH binds to osteoblast parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1), stimulating the cell surface expression of RANKL, which binds to RANK, a cell surface protein on osteoclast precursors. Binding of RANKL to RANK activates osteoclast gene transcription and the differentiation into a ...
... PTH effects on bone. PTH binds to osteoblast parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1), stimulating the cell surface expression of RANKL, which binds to RANK, a cell surface protein on osteoclast precursors. Binding of RANKL to RANK activates osteoclast gene transcription and the differentiation into a ...
Chromosomal basis of inheritance cell division – mitosis and meiosis
... 2N = number of chromosomes in somatic cells of diploid species • number and size of chromosomes is unrelated to complexity of organism (e.g., nematode N varies from 1 to 48) ...
... 2N = number of chromosomes in somatic cells of diploid species • number and size of chromosomes is unrelated to complexity of organism (e.g., nematode N varies from 1 to 48) ...
Biology 1st Semester Study Guide
... ______ uses a carrier protein to move particles from low to high concentration ______ uses a carrier protein to move particles from high to low concentration ______ moves small particles across a membrane ______ examples are endocytosis and exocytosis PHOTOSYNTHESIS and CELL RESPIRATION 38. Where do ...
... ______ uses a carrier protein to move particles from low to high concentration ______ uses a carrier protein to move particles from high to low concentration ______ moves small particles across a membrane ______ examples are endocytosis and exocytosis PHOTOSYNTHESIS and CELL RESPIRATION 38. Where do ...