cell walls - SharpSchool
... water moves through the phospholipids bilayer and through transport proteins called aquaporins ...
... water moves through the phospholipids bilayer and through transport proteins called aquaporins ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Fredericksburg City Schools
... The goal of most body systems is to ___________________________.These fragile _______________________________ include the following: ________________________---body takes in as food and chemical reactions release energy from it using O2.Carb’s are the main energy source…..Proteins provide nutrients ...
... The goal of most body systems is to ___________________________.These fragile _______________________________ include the following: ________________________---body takes in as food and chemical reactions release energy from it using O2.Carb’s are the main energy source…..Proteins provide nutrients ...
Note
... (hydrophobic) and dissolve into the space between the two layers of the cell membrane, but not in water • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= UgN76naeA1Q ...
... (hydrophobic) and dissolve into the space between the two layers of the cell membrane, but not in water • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= UgN76naeA1Q ...
File
... A specific ‘type of diffusion’, it is the movement of only WATER across a semipermeable membrane. The movement of water from a hypertonic solution(higher in concentration) across a semipermeable membrane to a hypotonic solution(lower in concentration) until both sides become isotonic (equal in conce ...
... A specific ‘type of diffusion’, it is the movement of only WATER across a semipermeable membrane. The movement of water from a hypertonic solution(higher in concentration) across a semipermeable membrane to a hypotonic solution(lower in concentration) until both sides become isotonic (equal in conce ...
Team Publications
... Intracellular distribution of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Gag proteins is independent of interaction with intracellular membranes. Journal of virology : 905-11 ...
... Intracellular distribution of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Gag proteins is independent of interaction with intracellular membranes. Journal of virology : 905-11 ...
CELL BIOLOGY
... intermediate filaments, tubulin filaments and actin filaments. Principal functions of the cytoskeleton. 19. Intermediate filaments. The intermediate filaments. Composition of intermediate filaments. Types, distribution and cellular localization. Functions of the different types of intermediate filam ...
... intermediate filaments, tubulin filaments and actin filaments. Principal functions of the cytoskeleton. 19. Intermediate filaments. The intermediate filaments. Composition of intermediate filaments. Types, distribution and cellular localization. Functions of the different types of intermediate filam ...
Chapter 10 Cell Divison
... - Family of proteins called cyclins - Increase and decrease as cell cycle continues - Without them cycle stops at G1, M or G2 - Allows time for any damage to be repaired ...
... - Family of proteins called cyclins - Increase and decrease as cell cycle continues - Without them cycle stops at G1, M or G2 - Allows time for any damage to be repaired ...
Ch 4 A Tour of the Cell 2016
... The subunits are made in the nucleolus then move through the nuclear pores to the cytoplasm The subunits assemble when mRNA is present (mRNA carries the DNA code) Ribosomes on the ER make protein to be exported Ribosomes in the cytoplasm make proteins to used within the cell ...
... The subunits are made in the nucleolus then move through the nuclear pores to the cytoplasm The subunits assemble when mRNA is present (mRNA carries the DNA code) Ribosomes on the ER make protein to be exported Ribosomes in the cytoplasm make proteins to used within the cell ...
I. Cell Structure and Function (Chapter 4) A. Basic Cell Types 1
... e. Motile through several mechanisms, but flagella and cilia most common (1) structure very different than prokaryotic flagella (2) cilia and flagella similar structure 2. Cytoplasmic matrix and organelles a. endoplasmic reticulum (ER), an extensive system of membranes forming tubes and plates in th ...
... e. Motile through several mechanisms, but flagella and cilia most common (1) structure very different than prokaryotic flagella (2) cilia and flagella similar structure 2. Cytoplasmic matrix and organelles a. endoplasmic reticulum (ER), an extensive system of membranes forming tubes and plates in th ...
Unit 4: Excretion and Waste Management
... The earthworm uses a series of tubules to remove wastes from the blood and body cavity. Cells lined with cilia surround a funnel-like structure (the nephrostome) and draw fluids from the body cavity into tiny tubules. The wastes are stored as urine and are released through small pores (nephridiopor ...
... The earthworm uses a series of tubules to remove wastes from the blood and body cavity. Cells lined with cilia surround a funnel-like structure (the nephrostome) and draw fluids from the body cavity into tiny tubules. The wastes are stored as urine and are released through small pores (nephridiopor ...
Day5 Muscle Tissue Review - Liberty Hill High School
... Muscle Tissue The function of intercalated discs is to transmit the force of __________ from cell to cell. ...
... Muscle Tissue The function of intercalated discs is to transmit the force of __________ from cell to cell. ...
Nervous System - FreeConferenceCall.com
... The respiratory system brings air into the body and removes carbon dioxide. It includes the nose, trachea, and lungs. When you breathe in, air enters your nose or mouth and goes down a long tube called the trachea. The trachea branches into two bronchial tubes, or primary bronchi, which go to the lu ...
... The respiratory system brings air into the body and removes carbon dioxide. It includes the nose, trachea, and lungs. When you breathe in, air enters your nose or mouth and goes down a long tube called the trachea. The trachea branches into two bronchial tubes, or primary bronchi, which go to the lu ...
inside cell - Cloudfront.net
... 2. Endocytosis – large molecules being engulfed by plasma membrane into vesicles 3. Exocytosis – large molecules being expelled out by vesicles out of plasma membrane ...
... 2. Endocytosis – large molecules being engulfed by plasma membrane into vesicles 3. Exocytosis – large molecules being expelled out by vesicles out of plasma membrane ...
the circulatory system
... The body takes the oxygen out of the blood and uses it in your body's cells. When the cells use the oxygen, they make carbon dioxide and other stuff that gets carried away by the blood. It's like the blood delivers lunch to the cells and then has to pick up the trash! The white blood cells have a ra ...
... The body takes the oxygen out of the blood and uses it in your body's cells. When the cells use the oxygen, they make carbon dioxide and other stuff that gets carried away by the blood. It's like the blood delivers lunch to the cells and then has to pick up the trash! The white blood cells have a ra ...
Why do cancer cells have too many centrosomes?
... Why do cancer cells have too many centrosomes? Suzy Prosser and Andrew Fry Department of Biochemistry, University of Leicester Introduction Cell division is the biological basis of life, allowing a single fertilised egg cell to become a multicellular organism containing trillions of cells. This pr ...
... Why do cancer cells have too many centrosomes? Suzy Prosser and Andrew Fry Department of Biochemistry, University of Leicester Introduction Cell division is the biological basis of life, allowing a single fertilised egg cell to become a multicellular organism containing trillions of cells. This pr ...
ROYAL PUBLIC SCHOOL
... 14. Why are chloroplasts found in plant cells only? 15. How do chromatin fibres form chromosome? 16. What are unicellular and multicellular organisms? Give two examples of each. 17. What are eukaryotic cells? Name any two eukaryotes. 18. Different organs work together to perform a specific life func ...
... 14. Why are chloroplasts found in plant cells only? 15. How do chromatin fibres form chromosome? 16. What are unicellular and multicellular organisms? Give two examples of each. 17. What are eukaryotic cells? Name any two eukaryotes. 18. Different organs work together to perform a specific life func ...
Chapter 16—The Urinary System. I. Eliminating waste. a. This is
... v. Neural, endocrine, and local controls (vasodilation and vasoconstriction of afferent & efferent arterioles) insure that the volume of blood flow to glomeruli remains relatively constant, even when blood pressure changes. vi. These factors result in the production of about 45 gallons (180 liters) ...
... v. Neural, endocrine, and local controls (vasodilation and vasoconstriction of afferent & efferent arterioles) insure that the volume of blood flow to glomeruli remains relatively constant, even when blood pressure changes. vi. These factors result in the production of about 45 gallons (180 liters) ...
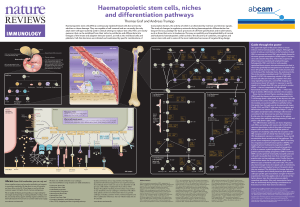
Haematopoietic stem cells, niches and differentiation
... T-cell lineage (lower right panel). In the thymus, the cells travel from the cortex through the subcapsular zone to the medulla, encountering different epithelial niches that guide them through several developmental stages. Finally, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells enter the circulation and differentiate into ...
... T-cell lineage (lower right panel). In the thymus, the cells travel from the cortex through the subcapsular zone to the medulla, encountering different epithelial niches that guide them through several developmental stages. Finally, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells enter the circulation and differentiate into ...
Cell City Project of
... Floating around in the cytoplasm of a cell are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive. In order to survive, the cell must be able to interact with its surroundings, use energy, produce material ...
... Floating around in the cytoplasm of a cell are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive. In order to survive, the cell must be able to interact with its surroundings, use energy, produce material ...
Types of Reproduction notesheet
... Pollen is taken from the male parts of one plant and delivered to the female parts of another plant, usually by an insect. The pollen then travels inside the flower and fertilizes an egg. The egg will grow into a seed, which can become a new plant. Pollination allows for genetic variation because th ...
... Pollen is taken from the male parts of one plant and delivered to the female parts of another plant, usually by an insect. The pollen then travels inside the flower and fertilizes an egg. The egg will grow into a seed, which can become a new plant. Pollination allows for genetic variation because th ...
NEURONAL DIFFERENTIATION OF HUMAN INDUCED
... (iPSCs) were first derived from human fibroblasts by the Nobel Prize winner Yamanaka and his colleagues [1]. Human iPSCs have two prominent properties: pluripotency and the ability to self-renew. Human iPSCs are an alternative to human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) since reprogramming adult cells can ...
... (iPSCs) were first derived from human fibroblasts by the Nobel Prize winner Yamanaka and his colleagues [1]. Human iPSCs have two prominent properties: pluripotency and the ability to self-renew. Human iPSCs are an alternative to human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) since reprogramming adult cells can ...
CELL PARTS Chapter 4 - Laurens County School District
... (Between nucleus and cell membrane) Image from: http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/cytoplasm.html ...
... (Between nucleus and cell membrane) Image from: http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/cytoplasm.html ...
TOPIC: Cells AIM: What are the parts of a cell?
... Do Now: Explain what all living cells are made up of. ...
... Do Now: Explain what all living cells are made up of. ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... Factors that affect the rate of diffusion: size of molecules, size of pores in membrane, temperature, pressure, and concentration. ...
... Factors that affect the rate of diffusion: size of molecules, size of pores in membrane, temperature, pressure, and concentration. ...