* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Connective Tissue
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
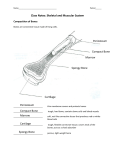
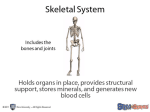
Chapter 40 Tissues of the Body The Human Animal • Coelom: Is the Body Cavity – Divided into 2 parts – Thoracic & Abdominal • Body is organized – Cells…tissues…organs…systems… 11 Principal Systems 1. Circulatory: Transport cells & materials 2. Digestive: Captures nutrients from ingested food 3. Endocrine: Hormones…coordinates activity of body 4. Excretory: Removes wastes from body 5. Immune: Removes foreign bodies from bloodstream. 6. Integumentary: Skin…covers the body. 11 Principal Systems Cont. 7. Muscular: Produces body movement 8. Nervous: Information & relays it to the body. 9. Reproductive: Reproduction 10. Respiratory: Captures O2 & exchanges gases. 11. Skeletal: Protects body & provides support for movement. Tissues • 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 Main Types Epithelium Tissue: Protective Tissue (Skin) Connective Tissue: Support the Body Muscle Tissues: Provides movement Nervous Tissue: Conducts signals rapidly Epithelium • Functions – Protects from dehydration & mechanical damage – Provide selectively permeable barrier – Secrete materials • 3 Classes 1. Simple Epithelium 2. Stratified Epithelium 3. Glands 1. Simple Epithelium • Single cell layer thick a) Simple Squamous: flattened, irregular shape (Line Lungs & major Cavities) b) Simple Cuboidal: full shape, equal height & width (line respiratory tract & ducts of testes.) c) Columnar: full shape, height greater than width (line respiratory tract & ducts of testes.) 2. Stratified Epithelium • Several Layers Thick – Ex SKIN • 3. Glands – Produces different substances – 2 types: 1) Exocrine glands: connected to epithelium by a DUCT 2) Endocrine glands: connected to epithelium ductless. Connective Tissue • • • Derived from mesoderm Composed of living cells imbedded in a nonliving matrix Divided into 3 categories 1. Defensive: matrix of blood plasma 2. Structural: matrix of fibrous proteins 3. Sequestering: acts as storage sites Connective Tissue Cont. • Defensive Connective Tissue 1. Macrophages: in blood & fibrous mesh of tissues a) Engulfs cellular debris & bacteria (foreign material) 2. Lymphocytes: circulate in blood a) Fighting infections (B cells & T cells) 3. Mast Cells (Blood vessels) a) Enlarges the blood vessels to speed healing process. Structural Connective Tissue 1. Fibroblasts a) Most common connective tissue b) Secretes collagen: makes cartilage, tendons, & bones 2. Cartilage a) Possess great strength & flexibility b) Tendons: connects muscle to bone c) Ligaments: connects bone to bone 3. Bone: (206 Bones) a) Cartilage fibers coated with calcium phosphate salt Muscle Tissue • • • Derived from the mesoderm Provides movement 3 types 1. Smooth: earliest to evolve (lines internal cavities) Involuntary muscle 2. Skeletal: Striated muscle (Has Sarcoplasm) a) Acts like a raft being towed by many small canoes (Attaches to bone) Voluntary muscle 3. Cardiac: Heart muscle Nervous Tissue • Composed of : – Neurons: conducts an electrical impulse • Dendrites: Receives impulses from other cells • Axon: Transmits nerve impulse away from the cell body – GIAL Cells: Bunch around axons – Nerves are cluster of axons & Dendrites Homeostasis (p. 895-899) • Maintaining a stable internal conditions – pH, Glucose, Body Temp., etc… • Know difference between negative & positive feedback • What is the HYPOTHALAMUS Skeletal System Function Skeletal System 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Locomotion Support Protection Makes Blood Storages of minerals (Ca, P, etc.) 206 Bones • Axial Skeletal (80 bones) – Ex. Spine, ribs, skull, sacrum, sternum • Appendicular Skeleton (126 bones) – Ex. Arms, legs, pelvic, & shoulders • Ossification: making of bone • Smallest bones found in the ear – Stirrup (Stapes), Anvil (incus), Hammer (Malleus) Joints 1. Hinge: moves in 1 plane…Knee & Elbow 2. Ball & Socket: moves in many directions… Shoulder & Hips 3. Gliding: Between vertebrae of spine 4. Pivot: Neck 5. Angular: wrist Vocabulary • • • • Tendons: Muscle to bone Ligaments: Bone to bone Synorial Fluid: Lubricates the joints Cartilage: Soft bone Muscle Attachment to bones • By tendons • Point of Insertion: attachment of muscle to movable bone • Point of Origin: attachment of muscle to stationary bone • Flexor: Bends joints • Extensors: Straighten joints • Antagonism: muscles working together CLASSIFICATION • APPEARED DURING PALEOCENE EPOCH • MONOTREMATA: EGG-LAYERS DUCK-BILLED PLATYPUS & SPINY ANTEATER (ECHIDNA) – – MARSUPIAL: POUCHED MAMMALS PLACENTAL MAMMALS: 17 ORDERS 95% OF ALL ANIMALS ORDERS • MONOTREMATA: OVIPAROUS – EGG LAYERS – NOT COMPLETELY ENDOTHERMIC – NIPPLELESS MAMMARY GLANDS – DUCK-BILL PLATYPUS – SPINY ANTEATER (ECHIDNA) ORDERS CONTINUED • MARSUPIALIA – POUCHED MAMMALS – SHORTEST GESTATION PERIOD • (10-12 DAYS) – OPOSSUM FOUND IN NORTH AMERICA 2 Essays • How muscles work (page 1066-1071) • WS question #7 (Homeostasis)